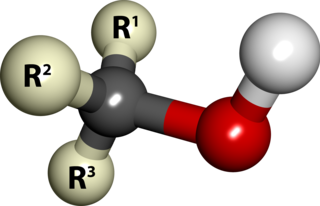
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sucrose and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, confering hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur.

In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.

Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst. Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst.

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei, and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur.

Redox is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state.
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (EC number 4.1.1).
Phenylalanine hydroxylase. (PAH) (EC 1.14.16.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of the aromatic side-chain of phenylalanine to generate tyrosine. PAH is one of three members of the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases, a class of monooxygenase that uses tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, a pteridine cofactor) and a non-heme iron for catalysis. During the reaction, molecular oxygen is heterolytically cleaved with sequential incorporation of one oxygen atom into BH4 and phenylalanine substrate. In humans, mutations in its encoding gene, PAH, can lead to the metabolic disorder phenylketonuria.
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
Fenton's reagent is a solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with ferrous iron (typically iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4) as a catalyst that is used to oxidize contaminants or waste waters as part of an advanced oxidation process. Fenton's reagent can be used to destroy organic compounds such as trichloroethylene (TCE) and tetrachloroethylene (perchloroethylene, PCE). It was developed in the 1890s by Henry John Horstman Fenton as an analytical reagent.

Methane monooxygenase (MMO) is an enzyme capable of oxidizing the C-H bond in methane as well as other alkanes. Methane monooxygenase belongs to the class of oxidoreductase enzymes.
Asymmetric catalytic oxidation is a technique of oxidizing various substrates to give an enantio-enriched product using a catalyst. Typically, but not necessarily, asymmetry is induced by the chirality of the catalyst. Typically, but again not necessarily, the methodology applies to organic substrates. Functional groups that can be prochiral and readily susceptible to oxidation include certain alkenes and thioethers. Challenging but pervasive prochiral substrates are C-H bonds of alkanes. Instead of introducing oxygen, some catalysts, biological and otherwise, enantioselectively introduce halogens, another form of oxidation.
In enzymology, an alkane 1-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.15.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions

Procollagen-proline dioxygenase, commonly known as prolyl hydroxylase, is a member of the class of enzymes known as alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases. These enzymes catalyze the incorporation of oxygen into organic substrates through a mechanism that requires alpha-Ketoglutaric acid, Fe2+, and ascorbate. This particular enzyme catalyzes the formation of (2S, 4R)-4-hydroxyproline, a compound that represents the most prevalent post-translational modification in the human proteome.
In enzymology, an ethylbenzene hydroxylase (EC 1.17.99.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Dioxygenases are oxidoreductase enzymes. Aerobic life, from simple single-celled bacteria species to complex eukaryotic organisms, has evolved to depend on the oxidizing power of dioxygen in various metabolic pathways. From energetic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation to xenobiotic degradation, the use of dioxygen as a biological oxidant is widespread and varied in the exact mechanism of its use. Enzymes employ many different schemes to use dioxygen, and this largely depends on the substrate and reaction at hand.
A transition metal oxo complex is a coordination complex containing an oxo ligand. Formally O2-, an oxo ligand can be bound to one or more metal centers, i.e. it can exist as a terminal or (most commonly) as bridging ligands (Fig. 1). Oxo ligands stabilize high oxidation states of a metal. They are also found in several metalloproteins, for example in molybdenum cofactors and in many iron-containing enzymes. One of the earliest synthetic compounds to incorporate an oxo ligand is potassium ferrate (K2FeO4), which was likely prepared by Georg E. Stahl in 1702.
John T. Groves is an American chemist, and Hugh Stott Taylor Chair of Chemistry, at Princeton University.

The White–Chen catalyst is an Iron-based coordination complex named after Professor M. Christina White and her graduate student Mark S. Chen. The catalyst is used along with hydrogen peroxide and acetic acid additive to oxidize aliphatic sp3 C-H bonds in organic synthesis. The catalyst is the first to allow for preparative and predictable aliphatic C–H oxidations over a broad range of organic substrates. Oxidations with the catalyst have proven to be remarkably predictable based on sterics, electronics, and stereoelectronics allowing for aliphatic C–H bonds to be thought of as a functional group in the streamlining of organic synthesis.
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are a major class of non-heme iron proteins that catalyse a wide range of reactions. These reactions include hydroxylation reactions, demethylations, ring expansions, ring closures, and desaturations. Functionally, the αKG-dependent hydroxylases are comparable to cytochrome P450 enzymes. Both use O2 and reducing equivalents as cosubstrates and both generate water.









