A document type definition (DTD) is a set of markup declarations that define a document type for an SGML-family markup language.

The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

Markup refers to data included in an electronic document which is distinct from the document's content in that it is typically not included in representations of the document for end users, for example on paper or a computer screen, or in an audio stream. Markup is often used to control the display of the document or to enrich its content to facilitate automated processing. A markup language is a set of rules governing what markup information may be included in a document and how it is combined with the content of the document in a way to facilitate use by humans and computer programs. The idea and terminology evolved from the "marking up" of paper manuscripts, which is traditionally written with a red pen or blue pencil on authors' manuscripts.
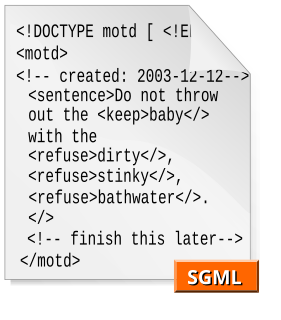
The Standard Generalized Markup Language is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates":

Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.
XSD, a recommendation of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), specifies how to formally describe the elements in an Extensible Markup Language (XML) document. It can be used by programmers to verify each piece of item content in a document, to assure it adheres to the description of the element it is placed in.
An HTML element is a type of HTML document component, one of several types of HTML nodes. HTML document is composed of a tree of simple HTML nodes, such as text nodes, and HTML elements, which add semantics and formatting to parts of document. Each element can have HTML attributes specified. Elements can also have content, including other elements and text.
YAML is a human-readable data-serialization language. It is commonly used for configuration files and in applications where data is being stored or transmitted. YAML targets many of the same communications applications as Extensible Markup Language (XML) but has a minimal syntax which intentionally differs from SGML. It uses both Python-style indentation to indicate nesting, and a more compact format that uses [...] for lists and {...} for maps thus JSON files are valid YAML 1.2.
In computing, RELAX NG is a schema language for XML—a RELAX NG schema specifies a pattern for the structure and content of an XML document. A RELAX NG schema is itself an XML document but RELAX NG also offers a popular compact, non-XML syntax. Compared to other XML schema languages RELAX NG is considered relatively simple.
Extensible Application Markup Language is a declarative XML-based language that Microsoft developed for initializing structured values and objects. It is available under Microsoft's Open Specification Promise.
In web development, "tag soup" is a pejorative for syntactically or structurally incorrect HTML written for a web page. Because web browsers have historically treated HTML syntax or structural errors leniently, there has been little pressure for web developers to follow published standards, and therefore there is a need for all browser implementations to provide mechanisms to cope with the appearance of "tag soup", accepting and correcting for invalid syntax and structure where possible.
OML is an XML format for outlines. It was originally proposed by Ray Grieselhuber. The specification is designed to build upon the concepts found in OPML, with the goal of fixing some of its limitations.
An XML schema is a description of a type of XML document, typically expressed in terms of constraints on the structure and content of documents of that type, above and beyond the basic syntactical constraints imposed by XML itself. These constraints are generally expressed using some combination of grammatical rules governing the order of elements, Boolean predicates that the content must satisfy, data types governing the content of elements and attributes, and more specialized rules such as uniqueness and referential integrity constraints.
The term CDATA, meaning character data, is used for distinct, but related, purposes in the markup languages SGML and XML. The term indicates that a certain portion of the document is general character data, rather than non-character data or character data with a more specific, limited structure.
OmniMark is a fourth-generation programming language used mostly in the publishing industry. It is currently a proprietary software product of Stilo International. As of July 2022, the most recent release of OmniMark was 11.0.
JsonML, the JSON Markup Language is a lightweight markup language used to map between XML and JSON. It converts an XML document or fragment into a JSON data structure for ease of use within JavaScript environments such as a web browser, allowing manipulation of XML data without the overhead of an XML parser.
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
The Office Open XML file formats are a set of file formats that can be used to represent electronic office documents. There are formats for word processing documents, spreadsheets and presentations as well as specific formats for material such as mathematical formulae, graphics, bibliographies etc.
XHTML+RDFa is an extended version of the XHTML markup language for supporting RDF through a collection of attributes and processing rules in the form of well-formed XML documents. XHTML+RDFa is one of the techniques used to develop Semantic Web content by embedding rich semantic markup. Version 1.1 of the language is a superset of XHTML 1.1, integrating the attributes according to RDFa Core 1.1. In other words, it is an RDFa support through XHTML Modularization.



