
The Southern Railway (SR), sometimes shortened to 'Southern', was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent. The railway was formed by the amalgamation of several smaller railway companies, the largest of which were the London & South Western Railway (LSWR), the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) and the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR). The construction of what was to become the Southern Railway began in 1838 with the opening of the London and Southampton Railway, which was renamed the London & South Western Railway.

Brighton railway station is the southern terminus of the Brighton Main Line in England, and the principal station serving the city of Brighton, East Sussex. It is 50 miles 49 chains from London Bridge via Redhill.

The West Coastway line is a railway line in England linking the densely populated conurbations of Brighton/Hove/Littlehampton and Southampton/Portsmouth, with 1.3 million people between them. It has short southward branches to Littlehampton and Bognor Regis. Some trains using part of the route operate as direct continuations of passenger services to/from London, particularly those to the branch stations mentioned.
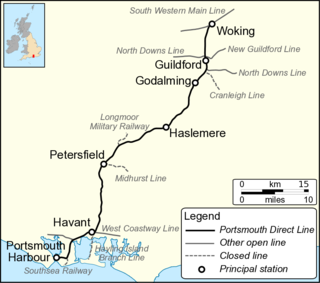
The Portsmouth Direct line is a railway route between Woking in Surrey and Portsmouth Harbour in Hampshire, England. It forms the principal route for passenger trains between London and Portsmouth, and also provides a partial rail link to the Island Line on the Isle of Wight, with passengers disembarking at Portsmouth Harbour before taking the Wightlink catamaran service to Ryde Pier, where the Island Line commences at Ryde Pier Head. The name was derived unofficially, but has entered widespread use for the physical infrastructure between Woking and Portsmouth Harbour, and for the passenger train service from London over the route. The final section of line from Havant to Portsmouth is shared by other passenger routes.
Several ships have been named Innisfallen, the name being derived from the island of Innisfallen in County Kerry and often given to vessels serving the southerly coasts of Ireland. Five served on the Irish Sea route between Cork and Fishguard, from 1896 onwards: two of these were war casualties whilst the remainder have been either scrapped or renamed and sold to new owners.

Fratton railway station is a railway station in the city of Portsmouth, on Portsea Island in the United Kingdom. It was opened in the Fratton area of Portsmouth on 1 July 1885 as an interchange station between the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway and the short-lived Southsea Railway branchline.

Southampton Central railway station is a main line station serving the city of Southampton in Hampshire, southern England. It is on the South West Main Line and also serves the Wessex Main Line and the West Coastway Line. The station is approached from the London direction by passing through Southampton Tunnel and is 79 miles 19 chains (127.5 km) measured from London Waterloo.
Brittany was a 631 GRT passenger ferry built in 1910 for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway. In 1912 she was sold to the London and South Western Railway, passing to the Southern Railway on 1 January 1923. She was renamed Aldershot in 1933. In 1937 she was sold to an Italian owner and renamed Hercules. On 24 November 1941, she was torpedoed and sunk by HMS Triumph.
Duchess of Norfolk was a 381 GRT paddle steamer built in 1911 for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway and London and South Western Railway, who operated a joint service to the Isle of Wight. She was requisitioned by the Royal Navy for use as minesweeper HMS Duchess of Norfolk during the First World War, returning to her owners after the war ended. She passed to the Southern Railway on 1 January 1923.

Brighton was a 1,384 GRT steamship which was built in 1903 for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway and London and South Western Railway. She passed to the Southern Railway on 1 January 1923. In 1930, she was sold to W E Guinness and converted to a private yacht, Roussalka. She was wrecked at Killary Bay on 25 August 1933.

SS Polar Chief was a merchant steamship that was built in England in 1897 and scrapped in Scotland in 1952. In her 55-year career she had previously been called Montcalm, RFA Crenella, Crenella, Rey Alfonso, Anglo-Norse and Empire Chief. Early in the First World War she spent eight months pretending to be the battleship HMS Audacious.

SS (RMS) Empress Queen was a steel paddle steamer, the last of its type ordered by the Isle of Man Steam Packet Company. She was chartered by the Admiralty in 1915 and used for trooping duties until she ran aground off Bembridge, Isle of Wight, England in 1916 and was abandoned.

Belmond British Pullman is a private luxury train that operates day and weekend journeys around Britain and also conveys passengers of the Venice Simplon-Orient-Express (VSOE) between London and Folkestone, as part of their journey to Venice and other European cities.
PS Victoria was a passenger vessel built for the London and South Western Railway and London, Brighton and South Coast Railway in 1881.
PS Duchess of Fife was a passenger vessel built for the London and South Western Railway and London, Brighton and South Coast Railway in 1899.
SS Laura was a passenger vessel built for the London and South Western Railway in 1885.

SS Frederica was a passenger vessel built for the London and South Western Railway in 1890. She later served in the Ottoman Navy as the minelayer Nilufer and was sunk during World War I.

SS Lydia was a passenger vessel built for the London and South Western Railway in 1890.

SS Victoria was a passenger vessel built for the London and South Western Railway in 1896.

The Jubilee class were a group of five passenger and cargo ocean liners built by Harland and Wolff at Belfast, for the White Star Line, specifically for the White Star Line's service from the UK to Australia on the Liverpool–Cape Town–Sydney route. The five ships in order of the dates they entered service were:













