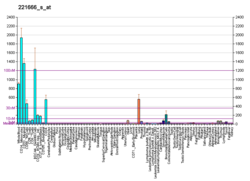
Function
This gene encodes an adaptor protein that is composed of two protein–protein interaction domains: a N-terminal PYRIN-PAAD-DAPIN domain (PYD) and a C-terminal caspase-recruitment domain (CARD). The PYD and CARD domains are members of the six-helix bundle death domain-fold superfamily that mediates assembly of large signaling complexes in the inflammatory and apoptotic signaling pathways via the activation of caspase. In normal cells, this protein is localized to the cytoplasm; however, in cells undergoing apoptosis, it forms ball-like aggregates near the nuclear periphery.
PYCARD can occur in four different isoforms. Isoform 1, often referred to as canonical PYCARD, and isoform 2 are the activatory isoforms. They co-localize with nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) and caspase-1. Unlike isoform 1, isoform 2 is involved in direct IL-1β processing regulation. Isoform 3 is an inhibitory isoform, so that it only co-localizes with caspase-1, but not with NLRs. Isoform 4 is not able to act as an adaptor protein in NLR signalling and its role remains elusive. [6]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.