
Pachydactylus is a genus of insectivorous geckos, lizards in the family Gekkonidae. The genus is endemic to Africa, and member species are commonly known as thick-toed geckos. The genus also displays rich speciation, having 58 distinct species identified when compared to other closely related gecko genera like Rhoptropus, most of which have emerged since 35Ma. It has been suggested that the reason for this rich speciation not from adaptive radiation nor nonadaptive radiation, but that the genus represents a clade somewhere between the two drivers of speciation. P. bibronii geckos have been used by NASA as animal models for experimentation.

Chondrodactylus bibronii, commonly known as Bibron's thick-toed gecko, Bibron's sand gecko, or simply Bibron's gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to southern Africa. C. bibronii has been used as an animal model in bioastronautic research examining the effects of spaceflight on the morphology and physiology of vertebrates.
Choleoeimeria is a genus of alveolate parasites that infect the biliary tracts of reptiles. Morphologically they are similar to the Eimeria, to whom they are closely related. The genus was described in 1989 by Paperna and Landsberg.
Pachydactylus austeni, also known commonly as Austen's thick-toed gecko or Austen's gecko, is a species of small thick-toed gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is indigenous to the western coast of South Africa.

Pachydactylus geitje, also known commonly as the ocellated gecko, the ocellated thick-toed gecko and the Cradock thick-toed gecko, is a tiny species of thick-toed gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is indigenous to the Western Cape of South Africa.

Pachydactylus atorquatus, also known commonly as the Augrabies gecko and Good's gecko, is a species of thick-toed gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to southern Africa.
Vivian Frederick Maynard FitzSimons, born in Pietermaritzburg, was a notable herpetologist in South Africa. Also, he contributed to the collection of spermatophyte samples for the National Herbarium which has become part of the South African National Biodiversity Institute at the Pretoria National Botanical Garden. In 1937, together with Anna Amelia Obermeyer, he collected some of the earliest plant specimens from the Eastern Highlands of Rhodesia.
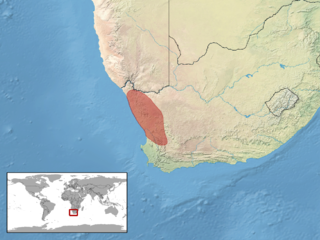
Pachydactylus labialis, commonly known as the Calvinia thick-toed gecko, Western Cape gecko, or Western Cape thick-toed gecko, is a gecko species endemic to the Western and Northern Cape in South Africa, often found taking shelter under stones.

Pachydactylus vansoni, commonly known as Van Son's gecko or Van Son's thick-toed gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to Southern Africa.

Turner's thick-toed gecko is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to southern Africa.
Chondrodactylus fitzsimonsi, also known commonly as the button-scaled gecko, FitzSimons' thick-toed gecko, Fitzsimons's thick-toed gecko, and FitzSimons' tubercled gecko, is a species of gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to southwestern Africa.
Wahlberg's Kalahari gecko, also known commonly as the Kalahari ground gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to southern Africa.
Pachydactylus acuminatus is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae, a family also known as the typical geckos. The species P. acuminatus is endemic to Namibia. It was once believed to be a subspecies of Weber's thick-toed gecko but was lifted to species status in 2006.
Pachydactylus barnardi, also known commonly as Barnard's rough gecko or Barnard's thick-toed gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is indigenous to Southern Africa.
Pachydactylus haackei, also known commonly as Haacke's gecko or Haacke's thick-toed gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to Southern Africa.
Monica's gecko, also known commonly as Monica's thick-toed gecko, is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to southern Africa.
Werner's thick-toed gecko is a species of lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to Namibia.

Monopeltis capensis, also known commonly as the Cape spade-snouted worm lizard, the Cape wedge-snouted worm lizard, the Cape worm lizard, and the South African shield-snouted amphisbaenian, is a species of amphisbaenian in the family Amphisbaenidae. The species is native to southern Africa.








