
Ophichthidae is a family of fish in the order Anguilliformes, commonly known as the snake eels. The term "Ophichthidae" comes from Greek ophis ("serpent") and ichthys ("fish"). Snake eels are also burrowing eels. They are named for their physical appearance, as they have long, cylindrical, snake-like bodies. This family is found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate waters. They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from coastal shallows and even rivers, to depths below 800 m (2,600 ft). Most species are bottom dwellers, hiding in mud or sand to capture their prey of crustaceans and small fish, but some are pelagic.

The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses and others.

Longneck eels or neck eels are a family, Derichthyidae, of eels. They are pelagic fishes, found in the middle and depths of most oceans. The name comes from Greek deres meaning "neck" and ichthys meaning "fish".

Nettastomatidae, the duckbill eels or witch eels are a family of eels. The name is from νῆττα and στόμα.
Anguilloidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Anguilliformes, the eels.

The speckled moray eel is a moray eel found in the eastern Pacific Ocean, around the Galapagos Islands and along the Central American coast from Costa Rica to Colombia. It is also found in the Gulf of California. It reaches a length of about 170 cm.

Enchelycore is a genus of moray eels in the family Muraenidae. Enchelycore species are generally small to medium-sized eels, most ranging from 2 to 3 feet in length, with the largest being the Mosaic Moray, which reaches a length of 6 feet (180 cm). Members of the genus feature distinctive, curved jaws that prevent them from fully closing their mouth and aids them in catching, and holding on to prey. Enchelycore species can also feature extremely bright colors and ornate markings.

The wolf eel is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Anarhichadidae, the wolf fishes. It is found in the North Pacific Ocean. Despite its common name and resemblance, it is not a true eel. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Anarrhichthys.

The Heterenchelyidae or mud eels are a small family of eels native to the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and eastern Pacific.
Myroconger is the only genus of eels, the thin eels, in the family Myrocongridae. Very little is known about the group.

Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 20 families, 164 genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators.
Kaupichthys is a genus of eels in the family Chlopsidae.
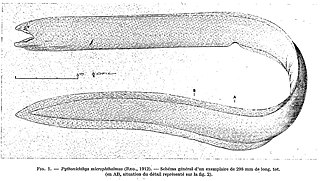
Pythonichthys is a genus of eels of the family Heterenchelyidae that occur in tropical waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean off of Panama and in the Atlantic Ocean near the Caribbean Sea and the west coast of Africa. It contains the following described species:

Moringua is a genus of eels of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Moringuidae, the spaghetti eels. These eels occur in shallow tropical and subtropical waters.

Pisodonophis is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae. It currently contains the following species:
Panturichthys fowleri, commonly known as Fowler's shortfaced eel, is an eel in the family Heterenchelyidae. It was described by Adam Ben-Tuvia in 1953, originally under the genus Lophenchelys. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from a single specimen collected from Israel, in the Mediterranean Sea. The holotype specimen was discovered dwelling at a depth range of 27–55 metres.
Panturichthys isognathus is an eel in the family Heterenchelyidae. It was described by Max Poll in 1953. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Gulf of Guinea in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, where it predominates south of the equator. It is a demersal fish that typically dwells at a depth range of 40–150 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 32.5 centimetres.
The slender shortfaced eel is an eel in the family Heterenchelyidae. It was described by Ernst Ehrenbaum in 1915, originally under the genus Heterenchelys. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Benin to Angola in the Gulf of Guinea, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Males can reach a maximum total length of 149 centimetres.
The Mauritanian shortface eel is an eel in the family Heterenchelyidae. It was described by Jacques Pellegrin in 1913. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, where it is distributed from Morocco to Guinea. It typically dwells at a depth range of 30–1000 metres, habituating muddy substrates on the African continental shelf. Males can reach a maximum total length of 84 centimetres.

Muraenoidei is a suborder of mainly marine ray-finned fishes velonging to the order Anguilliformes, the eels. The eels in this suborder are distributed in the tropical and temperate seas around the world.












