
Papua New Guinea is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, it shares its only land border with Indonesia to the west and it is directly adjacent to Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The prehistory of Papua New Guinea can be traced to about 50,000–60,000 years ago, when people first migrated towards the Australian continent. The written history began when European navigators first sighted New Guinea in the early part of the 17th century.

Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, which is part of Papua New Guinea. Its land area is 9,300 km2 (3,600 sq mi). The population of the whole province, including nearby islets such as the Carterets, is approximately 300,000. The highest point is Mount Balbi, on the main island, at 2,715 m (8,907 ft).

The flag of Papua New Guinea was adopted on 1 July 1971. In the hoist, it depicts the Southern Cross; in the fly, a Raggiana bird-of-paradise is silhouetted. The design was chosen through a nationwide design competition in early 1971. The winning designer was Susan Karike, who was 15 at the time.

The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the annexation but in 1884 a protectorate was proclaimed over the territory, then called "British New Guinea". There is a certain ambiguity about the exact date on which the entire territory was annexed by the British. The Papua Act 1905 recites that this happened "on or about" 4 September 1888. On 18 March 1902, the Territory was placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia. Resolutions of acceptance were passed by the Commonwealth Parliament, which accepted the territory under the name of Papua.
Sir John Douglas Guise was a Papua New Guinean politician who served as the first governor-general of Papua New Guinea after the country's independence from Australia in 1975. Prior to the independence itself, Guise was a vocal advocate for a peaceful secession from Australia.
The Chief Ministerof Papua and New Guinea was the head of the Australian territorial government of Papua and New Guinea from 1973, when Papua New Guinea was granted self-government, to 1975. Prior to self-government and after the end of the military administration of the jointly administered territory following World War II the head of the executive of the territory was the Administrator. After independence in 1975, the post became the Prime Minister of Papua New Guinea. Michael Somare (1936-2021), was the only occupant of the position, serving from 1972 to 1975, and he remained as Prime Minister after independence.
The House of Assembly of Papua and New Guinea was the legislature of the territory of Papua and New Guinea from 1964 to 1972. Before 1964, the Legislative Council of Papua and New Guinea sat from 1951 to 1964 under the Papua and New Guinea Act 1949. After independence in 1975, the legislature was renamed from the House of Assembly of Papua New Guinea to the National Parliament of Papua New Guinea.

The Supreme Court of Papua New Guinea has been the highest court of Papua New Guinea since 16 September 1975, replacing the pre-Independence Supreme Court and the overseas appellate tribunals from 1902 to 1975 of the High Court of Australia and the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. Judges of the pre-Independence Supreme Court automatically became the first justices of the National Court and accordingly among the pool of judges that were available to be empanelled as a Supreme Court bench.

The Papua Act 1905(Cth) was an Act of the Parliament of Australia which transferred the territory of Papua from Britain to Australia. It formally incorporated Papua as an external territory of Australia and remained in effect until Papua's merger with New Guinea with the passage of the Papua and New Guinea Act 1949.

The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian-administered United Nations trust territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the name of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea. That administrative union was renamed as Papua New Guinea in 1971. Notwithstanding that it was part of an administrative union, the Territory of New Guinea at all times retained a distinct legal status and identity until the advent of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

The states and territories are the second level of government of Australia. The states are administrative divisions that are self-governing polities that are partly sovereign, having ceded some sovereign rights to the federal government. They have their own constitutions, legislatures, executive governments, judiciaries and law enforcement agencies that administer and deliver public policies and programs. Territories can be autonomous and administer local policies and programs much like the states in practice, but are still legally subordinate to the federal government.

The Territory of Papua and New Guinea, officially the Administrative Union of the Territory of Papua and the Territory of New Guinea, was established by an administrative union between the Australian-administered territories of Papua and New Guinea in 1949. In December 1971, the name of the Territory changed to "Papua New Guinea" and in 1975 it became the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.

Sir Michael Thomas Somare was a Papua New Guinean politician. Widely called the "father of the nation", he was the first Prime Minister after independence. At the time of his death, Somare was also the longest-serving prime minister, having been in office for 17 years over three separate terms: from 1975 to 1980; from 1982 to 1985; and from 2002 to 2011. His political career spanned from 1968 until his retirement in 2017. Besides serving as PM, he was minister of foreign affairs, leader of the opposition and governor of East Sepik Province.
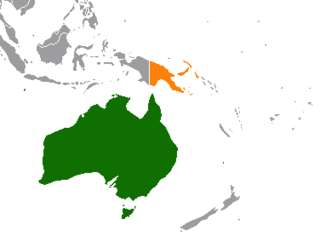
Foreign relations exist between Australia and Papua New Guinea. Papua New Guinea is Australia's closest neighbour and a former colony of Australia. Both nations share the same continent in the Oceania region. Papua New Guinea has developed much closer relations with Australia than with Indonesia, the only country with which it shares a land border. The two countries are Commonwealth realms. In contemporary times, Papua New Guinea is one of the largest recipients of Australian aid. Some critics have pointed to instances where this has led to an outsized Australian influence on Papua New Guinea politics.

The monarchy of Papua New Guinea is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Papua New Guinea. The current Papua New Guinean monarch and head of state, since 8 September 2022, is King Charles III. As sovereign, he is the personal embodiment of the Papua New Guinean Crown. Although the person of the sovereign is equally shared with 14 other independent countries within the Commonwealth of Nations, each country's monarchy is separate and legally distinct. As a result, the current monarch is officially titled King of Papua New Guinea and, in this capacity, he and other members of the royal family undertake public and private functions domestically and abroad as representatives of Papua New Guinea. However, the King is the only member of the royal family with any constitutional role.
Eric Joseph Wright was an Australian general practitioner, medical administrator and public servant. Wright was born in St Leonards, Sydney, New South Wales and died in Lewisham, Sydney, New South Wales. After obtaining his education at Lewisham Public School he joined the department of public health as a medical assistant in 1930. Eric later established a school for medical assistants in Divinukoiari. Due to medical issues, Eric was unable to join the armed forces and instead studied medicine at the University of Sydney. Once Eric had furthered his education he returned to Papua and New Guinea where he then established a private practice. He would eventually marry his receptionist named Shirley May Chan Wong, née Hee. After accomplishing many other things in Papua and New Guinea Eric's health began to deteriorate so he returned to Sydney to be with his family. He was diagnosed with acute myocardial ischaemia and the disease later took his life on 21 December 1979 at Lewisham Hospital.

The Papua New Guinea Independence Act 1975 was an Act passed by the Parliament of Australia. It replaced the Papua and New Guinea Act 1949, and changed the status of the Territory of Papua and New Guinea to that of an independent Papua New Guinea. The Act set 16 September 1975 as date of Papua New Guinea's independence and terminated all remaining sovereign and legislative powers of Australia over the country.

The Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border is the international border between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. The border, which divides the island of New Guinea in half, consists of two straight north–south lines connected by a short section running along the Fly river, totalling 824 km (512 mi). The boundary separates Papua, Highland Papua, and South Papua provinces of Indonesia from Sandaun and Western provinces of Papua New Guinea.











