
Lokasenna is one of the poems of the Poetic Edda. The poem presents flyting between the gods and Loki. It is written in the ljóðaháttr metre, typical for wisdom verse. Lokasenna is believed to be a 10th-century poem.

The word thou is a second-person singular pronoun in English. It is now largely archaic, having been replaced in most contexts by the word you, although it remains in use in parts of Northern England and in Scots. Thou is the nominative form; the oblique/objective form is thee ; the possessive is thy (adjective) or thine ; and the reflexive is thyself. When thou is the grammatical subject of a finite verb in the indicative mood, the verb form typically ends in -(e)st, but in some cases just -t. Some modern or dialect speakers of thou use thee as the subject and conjugate the word with is/was, e.g. thee is, thee was, thee has, thee speaks, thee spoke, thee can, thee could, thee shall. However, this is not considered standard.

The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean before and during the Late Bronze Age collapse. Following the creation of the concept in the 19th century, the Sea Peoples' incursions became one of the most famous chapters of Egyptian history, given its connection with, in the words of Wilhelm Max Müller, "the most important questions of ethnography and the primitive history of classic nations".

The Battle of Kadesh took place in the 13th century BC between the Egyptian Empire led by pharaoh Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire led by king Muwatalli II. Their armies engaged each other at the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs and near the archaeological site of Kadesh, along what is today the Lebanon–Syria border.
The Hittites, also spelled Hethites, were a group of people mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Under the names בני-חת and חתי they are described several times as living in or near Canaan between the time of Abraham and the time of Ezra after the return of the Jews from the Babylonian exile. Their ancestor was Heth.
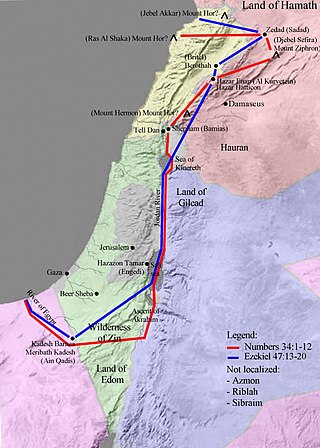
Kadesh or Qadesh or Cades is a place-name that occurs several times in the Hebrew Bible, describing a site or sites located south of, or at the southern border of, Canaan and the Kingdom of Judah in the kingdom of Israel. Many modern academics hold that it was a single site, located at the modern Tel el-Qudeirat, while some academics and rabbinical authorities hold that there were two locations named Kadesh. A related term, either synonymous with Kadesh or referring to one of the two sites, is KadeshBarnea. Various etymologies for Barnea have been proposed, including 'desert of wanderings,' but none have produced widespread agreement.

Menmaatre Ramesses XI reigned from 1107 BC to 1078 BC or 1077 BC and was the tenth and final pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt and as such, was the last king of the New Kingdom period. He ruled Egypt for at least 29 years although some Egyptologists think he could have ruled for as long as 30. The latter figure would be up to 2 years beyond this king's highest known date of Year 10 of the Whm Mswt era or Year 28 of his reign. One scholar, Ad Thijs, has suggested that Ramesses XI could even have reigned as long as 33 years.

Al-Sahifa al-Sajjadiyya is a book of supplications attributed to Ali al-Sajjad, the fourth imam in Shia Islam, and the great-grandson of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad. The oldest prayer manual in Islam, al-Sahifa has been praised as the epitome of Islamic spirituality and the answer to many of today's spiritual questions. In particular, Shia tradition holds the book in great esteem, ranking it behind the Quran, the central religious text of Islam, and Nahj al-Balagha, which is attributed to the fourth Caliph and first Shia imam, Ali ibn Abi Talib. Fifty-four supplications form the core of al-Sahifa, which often also includes an addenda of fourteen supplications and fifteen whispered prayers.

Instruction of Amenemope is a literary work composed in Ancient Egypt, most likely during the Ramesside Period ; it contains thirty chapters of advice for successful living, ostensibly written by the scribe Amenemope son of Kanakht as a legacy for his son. A characteristic product of the New Kingdom "Age of Personal Piety", the work reflects on the inner qualities, attitudes, and behaviors required for a happy life in the face of increasingly difficult social and economic circumstances. It is widely regarded as one of the masterpieces of ancient near-eastern wisdom literature and has been of particular interest to modern scholars because of its similarity to the later biblical Book of Proverbs.
The Prayer of Solomon is a prayer by King Solomon described in 1 Kings 8:22-53 and 2 Chronicles 6:12-42. This prayer is said to have occurred at the dedication of the temple of Solomon, which also became known as the First Temple. The wording and thinking of the prayer have much in common with the language of Deuteronomy.

Ancient Egyptian literature was written with the Egyptian language from ancient Egypt's pharaonic period until the end of Roman domination. It represents the oldest corpus of Egyptian literature. Along with Sumerian literature, it is considered the world's earliest literature.

Psalm 69 is the 69th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in English in the King James Version: "Save me, O God; for the waters are come in unto my soul". It is subtitled: "To the chief musician, upon Shoshannim, a Psalm of David". The Book of Psalms is part of the third section of the Hebrew Bible, and a book of the Christian Old Testament. In the slightly different numbering system used in the Greek Septuagint version of the Bible and in the Latin Vulgate, this psalm is Psalm 68. In Latin, it is known as "Salvum me fac Deus". It has 36 verses.

The alma mater of the University of Pittsburgh was adopted soon after the University changed its name in 1908 from the Western University of Pennsylvania to its current moniker. Lyrics were written by George M. P. Baird, class of 1909 and were set to the tune of what was then the Austrian National Anthem. A new tune for the "Alma Mater" hymn was composed by Charles W. Scovel, class of 1883, but it was not widely adopted and was either lost or became obscure.

Salome appears in the apocryphal Gospel known as the Gospel of James as an associate of the unnamed midwife at the Nativity of Jesus, and is regularly depicted with the midwife in Eastern Orthodox icons of the Nativity of Jesus, though she has long vanished from most Western depictions. Salome herself is clearly distinguished from "the midwife" in this infancy gospel attributed to James the Just, also known as the Protevangelion of James. The passage in Chapter XIX and XX reads, in the edition and translation by M. R. James:
(Ch XIX, 3) And the midwife went forth of the cave and Salome met her. And she said to her: Salome, Salome, a new sight have I to tell thee. A virgin hath brought forth, which her nature alloweth not. And Salome said: As the Lord my God liveth, if I make not trial and prove her nature I will not believe that a virgin hath brought forth.
(XX. 1) And the midwife went in and said unto Mary: Order thyself, for there is no small contention arisen concerning thee. And Salome made trial and cried out and said: Woe unto mine iniquity and mine unbelief, because I have tempted the living God, and lo, my hand falleth away from me in fire. And she bowed her knees unto the Lord, saying: O God of my fathers, remember that I am the seed of Abraham and Isaac and Jacob: make me not a public example unto the children of Israel, but restore me unto the poor, for thou knowest, Lord, that in thy name did I perform my cures, and did receive my hire of thee. 3 And lo, an angel of the Lord appeared, saying unto her: Salome, Salome, the Lord hath hearkened to thee: bring thine hand near unto the young child and take him up, and there shall be unto thee salvation and joy. 4 And Salome came near and took him up, saying: I will do him worship, for a great king is born unto Israel. And behold immediately Salome was healed: and she went forth of the cave justified. And lo, a voice saying: Salome, Salome, tell none of the marvels which thou hast seen, until the child enter into Jerusalem.

Psalm 40 is the 40th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in English in the King James Version: "I waited patiently for the LORD". The Book of Psalms is part of the third section of the Hebrew Bible, and a book of the Christian Old Testament. In the slightly different numbering system used in the Greek Septuagint and Latin Vulgate translations of the Bible, this psalm is Psalm 39. In Latin, it is known by the incipit, "Expectans expectavi Dominum". It is described by the Jerusalem Bible as a "song of praise and prayer for help".

Psalm 139 is the 139th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in English in the King James Version: "O Lord, thou hast searched me, and known me". In Latin, it is known as "Domine probasti me et cognovisti me". The psalm is a hymn psalm. Attributed to David, it is known for its affirmation of God's omnipresence. Alexander Kirkpatrick states that "the consciousness of the intimate personal relation between God and man which is characteristic of the whole Psalter reaches its climax here".
Kumayl bin Ziyad an-Nakha'i was among the most loyal companions of Imam Ali Ibn Abi Talib. Moreover, Kumayl occupies a prominent position in Shia Islam. Converting to Islam during the time of Islamic prophet Muhammad, he rose to a position of prominence during the caliphates of Uthman and Ali. In the caliphate of Ali, Kumayl flourished and served him in the most disciplined of ways. However, he is recognized for his pious and humble nature as well as preserving Imam Ali's teachings. Kumayl is best known for the du'a (supplication) of Prophet Khidr, which is commonly known by the name du'a Kumayl.

The Begatting of the President is a satirical album narrated by Orson Welles, summarising the presidency of Lyndon B. Johnson and the election of 1968, leading up to the election of Richard Nixon, delivered in the style of Biblical verse.

The Prayer of Thanksgiving is a Hermetic Gnostic prayer text preserved in Coptic, Greek and Latin.
















