
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents, both liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. When this loss includes flatus (gas), it is referred to as anal incontinence. FI is a sign or a symptom, not a diagnosis. Incontinence can result from different causes and might occur with either constipation or diarrhea. Continence is maintained by several interrelated factors, including the anal sampling mechanism, and incontinence usually results from a deficiency of multiple mechanisms. The most common causes are thought to be immediate or delayed damage from childbirth, complications from prior anorectal surgery, altered bowel habits. An estimated 2.2% of community-dwelling adults are affected. However, reported prevalence figures vary. A prevalence of 8.39% among non-institutionalized U.S adults between 2005 and 2010 has been reported, and among institutionalized elders figures come close to 50%.
In anatomy, a fistula is an abnormal connection joining two hollow spaces, such as blood vessels, intestines, or other hollow organs to each other, often resulting in an abnormal flow of fluid from one space to the other. An anal fistula connects the anal canal to the perianal skin. An anovaginal or rectovaginal fistula is a hole joining the anus or rectum to the vagina. A colovaginal fistula joins the space in the colon to that in the vagina. A urinary tract fistula is an abnormal opening in the urinary tract or an abnormal connection between the urinary tract and another organ. An abnormal communication between the bladder and the uterus is called a vesicouterine fistula, while if it is between the bladder and the vagina it is known as a vesicovaginal fistula, and if between the urethra and the vagina: a urethrovaginal fistula. When occurring between two parts of the intestine, it is known as an enteroenteral fistula, between the small intestine and the skin as an enterocutaneous fistula, and between the colon and the skin as a colocutaneous fistula.

Lymphogranuloma venereum is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the invasive serovars L1, L2, L2a, L2b, or L3 of Chlamydia trachomatis.
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segment of the bowel, it functions to regulate release of excrement by two muscular sphincter complexes. The anus is the aperture at the terminal portion of the anal canal.
Proctitis is an inflammation of the anus and the lining of the rectum, affecting only the last 6 inches of the rectum.

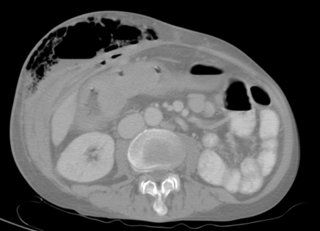
Anal fistula is a chronic abnormal communication between the anal canal and the perianal skin. An anal fistula can be described as a narrow tunnel with its internal opening in the anal canal and its external opening in the skin near the anus. Anal fistulae commonly occur in people with a history of anal abscesses. They can form when anal abscesses do not heal properly.
A phlegmon is a localized area of acute inflammation of the soft tissues. It is a descriptive term which may be used for inflammation related to a bacterial infection or non-infectious causes. Most commonly, it is used in contradistinction to a "walled-off" pus-filled collection (abscess), although a phlegmon may progress to an abscess if untreated. A phlegmon can localize anywhere in the body. The Latin term phlegmōn is from Ancient Greek φλέγω (phlégō) 'burn'.

An anoscopy is an examination using a small, rigid, tubular instrument called an anoscope. This is inserted a few inches into the anus in order to evaluate problems of the anal canal. Anoscopy is used to diagnose hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and some cancers.

The rectal venous plexus is the venous plexus surrounding the rectum. It consists of an internal and an external rectal plexus. It is drained by the superior, middle, and inferior rectal veins. It forms a portosystemic (portocaval) anastomosis. This allows rectally administered medications to bypassing first pass metabolism.

Anorectal abscess is an abscess adjacent to the anus. Most cases of perianal abscesses are sporadic, though there are certain situations which elevate the risk for developing the disease, such as diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, chronic corticosteroid treatment and others. It arises as a complication of paraproctitis. Ischiorectal, inter- and intrasphincteric abscesses have been described.
Lateral internal sphincterotomy is an operation performed on the internal anal sphincter muscle for the treatment of chronic anal fissure. The internal anal sphincter is one of two muscles that comprise the anal sphincter which controls the passage of feces. The procedure helps by lowering the resting pressure of the internal anal sphincter, which improves blood supply to the fissure and allows faster healing. The procedure has been shown to be very effective, with 96% of fissures healing at a median of 3 weeks in one trial.

The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about 4 centimetres (1.6 in) long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin rectumintestinum, meaning straight intestine.
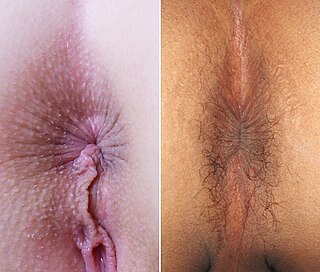
In humans, the anus is the external opening of the rectum, located inside the intergluteal cleft and separated from the genitals by the perineum. Two sphincters control the exit of feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. It is located behind the perineum which is located behind the vulva or scrotum.
Rectal pain is the symptom of pain in the area of the rectum. A number of different causes (68) have been documented.
Rectal discharge is intermittent or continuous expression of liquid from the anus. Normal rectal mucus is needed for proper excretion of waste. Otherwise, this is closely related to types of fecal incontinence but the term rectal discharge does not necessarily imply degrees of incontinence. Types of fecal incontinence that produce a liquid leakage could be thought of as a type of rectal discharge.
Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome or SRUS is a chronic, benign disorder of the rectal mucosa. It commonly occurs with varying degrees of rectal prolapse. The condition is thought to be caused by different factors, such as long term constipation, straining during defecation, and dyssynergic defecation. Treatment is by normalization of bowel habits, biofeedback, and other conservative measures. In more severe cases various surgical procedures may be indicated. The condition is relatively rare, affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 people per year. It affects mainly adults aged 30–50. Females are affected slightly more often than males. The disorder can be confused clinically with rectal cancer or other conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, even when a biopsy is done.
Anismus or dyssynergic defecation is the failure of normal relaxation of pelvic floor muscles during attempted defecation. It can occur in both children and adults, and in both men and women. It can be caused by physical defects or it can occur for other reasons or unknown reasons. Anismus that has a behavioral cause could be viewed as having similarities with parcopresis, or psychogenic fecal retention.
Obstructed defecation syndrome is a major cause of functional constipation, of which it is considered a subtype. It is characterized by difficult and/or incomplete emptying of the rectum with or without an actual reduction in the number of bowel movements per week. Normal definitions of functional constipation include infrequent bowel movements and hard stools. In contrast, ODS may occur with frequent bowel movements and even with soft stools, and the colonic transit time may be normal, but delayed in the rectum and sigmoid colon.

Anorectal disorders include conditions involving the anorectal junction as seen in the image. They are painful but common conditions like hemorrhoids, tears, fistulas, or abscesses that affect the anal region. Most people experience some form of anorectal disorder during their lifetime. Primary care physicians can treat most of these disorders, however, high-risk individuals include those with HIV, roughly half of whom need surgery to remedy the disorders. Likelihood of malignancy should also be considered in high risk individuals. This is why it is important to perform a full history and physical exam on each patient. Because these disorders affect the rectum, people are often embarrassed or afraid to confer with a medical professional.











