Related Research Articles

Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) is a neurological condition involving severe damage to the myelin sheath of nerve cells in the pons. It is predominately iatrogenic (treatment-induced), and is characterized by acute paralysis, dysphagia, dysarthria, and other neurological symptoms.

A phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE), thereby preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) by the respective PDE subtype(s). The ubiquitous presence of this enzyme means that non-specific inhibitors have a wide range of actions, the actions in the heart, and lungs being some of the first to find a therapeutic use.
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those with absence seizures, partial seizures, and generalized seizures. They can be given intravenously or by mouth, and the tablet forms exist in both long- and short-acting formulations.
Myelitis is inflammation of the spinal cord which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Inflammation in the spinal cord, can cause the myelin and axon to be damaged resulting in symptoms such as paralysis and sensory loss. Myelitis is classified to several categories depending on the area or the cause of the lesion; however, any inflammatory attack on the spinal cord is often referred to as transverse myelitis.
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken by mouth.

Dizocilpine (INN), also known as MK-801, is a noncompetitive antagonist of the N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a glutamate receptor, discovered by a team at Merck in 1982. Glutamate is the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter. The channel is normally blocked with a magnesium ion and requires depolarization of the neuron to remove the magnesium and allow the glutamate to open the channel, causing an influx of calcium, which then leads to subsequent depolarization. Dizocilpine binds inside the ion channel of the receptor at several of PCP's binding sites thus preventing the flow of ions, including calcium (Ca2+), through the channel. Dizocilpine blocks NMDA receptors in a use- and voltage-dependent manner, since the channel must open for the drug to bind inside it. The drug acts as a potent anti-convulsant and probably has dissociative anesthetic properties, but it is not used clinically for this purpose because of the discovery of brain lesions, called Olney's lesions (see below), in laboratory rats. Dizocilpine is also associated with a number of negative side effects, including cognitive disruption and psychotic-spectrum reactions. It inhibits the induction of long term potentiation and has been found to impair the acquisition of difficult, but not easy, learning tasks in rats and primates. Because of these effects of dizocilpine, the NMDA receptor pore-blocker ketamine is used instead as a dissociative anesthetic in human medical procedures. While ketamine may also trigger temporary psychosis in certain individuals, its short half-life and lower potency make it a much safer clinical option. However, dizocilpine is the most frequently used non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist in animal models to mimic psychosis for experimental purposes.

Zonisamide, sold under the brand name Zonegran, is a medication used to treat the symptoms of epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. Chemically it is a sulfonamide. It serves as an anticonvulsant used primarily as an adjunctive therapy in adults with Parkinson's disease, partial-onset seizures; infantile spasm, mixed seizure types of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, myoclonic and generalized tonic clonic seizure. Despite this it is also sometimes used as a monotherapy for partial-onset seizures.

Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. In renal physiology, when blood is filtered by the kidney, the filtrate passes through the tubules of the nephron, allowing for exchange of salts, acid equivalents, and other solutes before it drains into the bladder as urine. The metabolic acidosis that results from RTA may be caused either by insufficient secretion of hydrogen ions into the latter portions of the nephron or by failure to reabsorb sufficient bicarbonate ions from the filtrate in the early portion of the nephron. Although a metabolic acidosis also occurs in those with chronic kidney disease, the term RTA is reserved for individuals with poor urinary acidification in otherwise well-functioning kidneys. Several different types of RTA exist, which all have different syndromes and different causes. RTA is usually an incidental finding based on routine blood draws that show abnormal results. Clinically, patients may present with vague symptoms such as dehydration, mental status changes, or delayed growth in adolescents.

Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.
Apnea of prematurity is defined as cessation of breathing by a premature infant that lasts for more than 20 seconds and/or is accompanied by hypoxia or bradycardia. Apnea is traditionally classified as either obstructive, central, or mixed. Obstructive apnea may occur when the infant's neck is hyperflexed or conversely, hyperextended. It may also occur due to low pharyngeal muscle tone or to inflammation of the soft tissues, which can block the flow of air though the pharynx and vocal cords. Central apnea occurs when there is a lack of respiratory effort. This may result from central nervous system immaturity, or from the effects of medications or illness. Many episodes of apnea of prematurity may start as either obstructive or central, but then involve elements of both, becoming mixed in nature.
Alternating hemiplegia of childhood is an ultra-rare neurological disorder named for the transient episodes, often referred to as "attacks", of hemiplegia from which those with the disorder suffer. It typically presents before the age of 18 months. These hemiplegic attacks can cause anything from mild weakness to complete paralysis on one or both sides of the body, and they can vary greatly in duration. Attacks may also alternate from one side of the body to the other, or alternate between affecting one or both sides during a single attack. Besides hemiplegia, symptoms of the disorder include an extremely broad range of neurological and developmental impairments which are not well understood. Normally, hemiplegia and other associated symptoms cease completely with sleep, but they may recur upon waking.
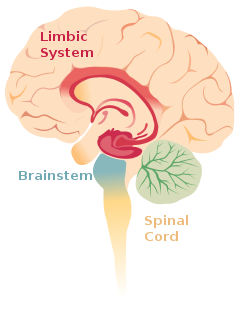
Limbic encephalitis is a form of encephalitis, a disease characterized by inflammation of the brain. Limbic encephalitis is caused by autoimmunity: an abnormal state where the body produces antibodies against itself. Some cases are associated with cancer and some are not. Although the disease is known as "limbic" encephalitis, it is seldom limited to the limbic system and post-mortem studies usually show involvement of other parts of the brain. The disease was first described by Brierley and others in 1960 as a series of three cases. The link to cancer was first noted in 1968 and confirmed by later investigators.

Biotin deficiency is a nutritional disorder which can become serious, even fatal, if allowed to progress untreated. It can occur in people of any age, ancestry, or gender. Biotin is part of the B vitamin family. Biotin deficiency rarely occurs among healthy people because the daily requirement of biotin is low, many foods provide adequate amounts of it, intestinal bacteria synthesize small amounts of it, and the body effectively scavenges and recycles it in the kidneys during production of urine. However, deficiencies can be caused by consuming raw egg whites over a period of weeks to months. Egg whites contain high levels of avidin, a protein that binds biotin strongly. When cooked, avidin is partially denatured and binding to biotin is reduced. However one study showed that 30-40% of the avidin activity was still present in the white after frying or boiling. Genetic disorders such as biotinidase deficiency, multiple carboxylase deficiency, and holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency can also lead to inborn or late-onset forms of biotin deficiency. In all cases – dietary, genetic, or otherwise – supplementation with biotin is the primary method of treatment.

Anterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes, basal ganglia, anterior fornix and anterior corpus callosum.
Carbonic anhydrase IX is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA9 gene. It is one of the 14 carbonic anhydrase isoforms found in humans and is a transmembrane dimeric metalloenzyme with an extracellular active site that facilitates acid secretion in the gastrointestinal tract. CA IX is overexpressed in many types of cancer including clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) as well as carcinomas of the cervix, breast and lung where it promotes tumor growth by enhancing tumor acidosis.
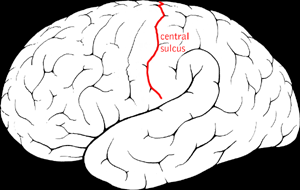
Benign Rolandic epilepsy or benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BCECTS) is the most common epilepsy syndrome in childhood. Most children will outgrow the syndrome, hence the label benign. The seizures, sometimes referred to as sylvian seizures, start around the central sulcus of the brain.
Thyroid disease in pregnancy can affect the health of the mother as well as the child before and after delivery. Thyroid disorders are prevalent in women of child-bearing age and for this reason commonly present as a pre-existing disease in pregnancy, or after childbirth. Uncorrected thyroid dysfunction in pregnancy has adverse effects on fetal and maternal well-being. The deleterious effects of thyroid dysfunction can also extend beyond pregnancy and delivery to affect neurointellectual development in the early life of the child. Due to an increase in thyroxine binding globulin, an increase in placental type 3 deioidinase and the placental transfer of maternal thyroxine to the fetus, the demand for thyroid hormones is increased during pregnancy. The necessary increase in thyroid hormone production is facilitated by high human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentrations, which bind the TSH receptor and stimulate the maternal thyroid to increase maternal thyroid hormone concentrations by roughly 50%. If the necessary increase in thyroid function cannot be met, this may cause a previously unnoticed (mild) thyroid disorder to worsen and become evident as gestational thyroid disease. Currently, there is not enough evidence to suggest that screening for thyroid dysfunction is beneficial, especially since treatment thyroid hormone supplementation may come with a risk of overtreatment. After women give birth, about 5% develop postpartum thyroiditis which can occur up to nine months afterwards.This is characterized by a short period of hyperthyroidism followed by a period of hypothyroidism; 20–40% remain permanently hypothyroid.

Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin. The majority of affected individuals experience significant intellectual and physical problems, although this is not always the case. The clinical features of AGS can mimic those of in utero acquired infection, and some characteristics of the condition also overlap with the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Following an original description of eight cases in 1984, the condition was first referred to as 'Aicardi–Goutières syndrome' (AGS) in 1992, and the first international meeting on AGS was held in Pavia, Italy, in 2001.
Cerebellar agenesis is a rare condition in which a brain develops without the cerebellum. The cerebellum controls smooth movement, and when it does not develop, the rest of the brain must compensate, which it cannot do completely. The condition is not fatal on its own, but people born without a cerebellum experience severe developmental delays, language deficits, and neurological abnormalities. As children with cerebellar agenesis get older, their movements usually improve. It can co-exist with other severe malformations of the central nervous system, like anencephaly, holoprosencephaly, and microencephaly.
In ophthalmology, apraxia of lid opening (ALO) is an inability to initiate voluntary opening of the eyelid following a period of eyelid closure, with normal function at other times. Manual lifting of the eyelid often resolves the problem and the lid is able to stay open.
References
- ↑ Hayman, M.; Harvey, A. S.; Hopkins, I. J.; Kornberg, A. J.; Coleman, L. T.; Shield, L. K. (1998). "Paroxysmal tonic upgaze: A reappraisal of outcome". Annals of Neurology. 43 (4): 514–520. doi:10.1002/ana.410430416. PMID 9546334. S2CID 32875120.
- ↑ Quade A, Thiel A, Kurth I, Holtgrewe M, Elbracht M, Beule D, Eggermann K, Scholl UI, Häusler M (2019) Paroxysmal tonic upgaze: A heterogeneous clinical condition responsive to carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Eur J Paediatr Neurol
- ↑ Quade A, Thiel A, Kurth I, Holtgrewe M, Elbracht M, Beule D, Eggermann K, Scholl UI, Häusler M (2019) Paroxysmal tonic upgaze: A heterogeneous clinical condition responsive to carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Eur J Paediatr Neurol
- ↑ "PTU: A Summary" . Retrieved 11 June 2013.