
A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent stems, lianas, or runners. The word vine can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in wicker work.

Toxicodendron radicans, commonly known as eastern poison ivy or poison ivy, is an allergenic flowering plant that occurs in Asia and eastern North America. The species is well known for causing urushiol-induced contact dermatitis, an itchy, irritating, and sometimes painful rash, in most people who touch it. The rash is caused by urushiol, a clear liquid compound in the plant's sap. The species is variable in its appearance and habit, and despite its common name, it is not a true ivy (Hedera), but rather a member of the cashew and pistachio family (Anacardiaceae). T. radicans is commonly eaten by many animals and the seeds are consumed by birds, but poison ivy is most often thought of as an unwelcome weed. It is a different species from western poison ivy, T. rydbergii, which has similar effects.
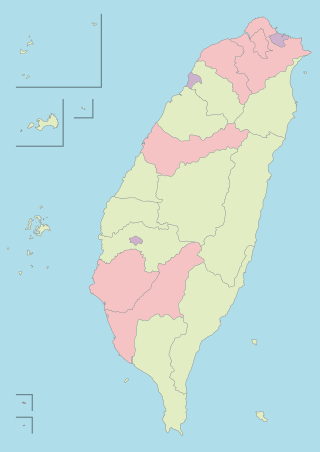
An autonomous municipality or city, previously provincial city, is a de jure second-level administrative division unit in the Republic of China (Taiwan).
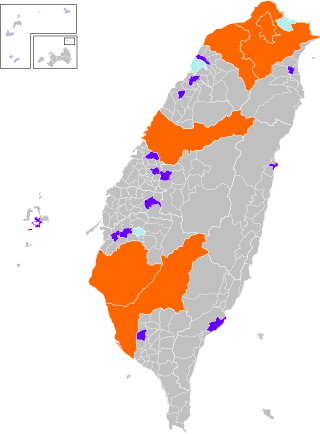
A county-administered city is a third-level administrative division in the Republic of China (Taiwan) below a county, which in turn is below of a province. Under the administrative structure of the ROC, it is at the same level as a township or a district. Such cities are under the jurisdiction of counties. It is also the lowest-level city in Taiwan, below a city and a special municipality. There are 14 county-administered cities currently under ROC control.
Ivy without qualifiers usually means plants in the genus Hedera in the family Araliaceae.

Hedera, commonly called ivy, is a genus of 12–15 species of evergreen climbing or ground-creeping woody plants in the family Araliaceae, native to Western Europe, Central Europe, Southern Europe, Macaronesia, northwestern Africa and across central-southern Asia east to Japan and Taiwan. Several species are cultivated as climbing ornamentals, and the name ivy especially denotes common ivy, known in North America as "English ivy", which is frequently planted to clothe brick walls.

Parthenocissus quinquefolia, known as Virginia creeper, Victoria creeper, five-leaved ivy, or five-finger, is a species of flowering vine in the grape family, Vitaceae. It is native to eastern and central North America, from southeastern Canada and the eastern United States west to Manitoba and Utah, and south to eastern Mexico and Guatemala.

Parthenocissus, is a genus of tendril climbing plants in the grape family, Vitaceae. It contains about 12 species native to the Himalaya, eastern Asia and North America. Several are grown for ornamental use, notably P. henryana, P. quinquefolia and P. tricuspidata.

The free area of the Republic of China, also known as the "Taiwan Area of the Republic of China", the "Tai-Min Area " or simply the "Taiwan Area", is a term used by the government of the Republic of China (Taiwan) to refer to the territories under its actual control. As a legal term written in the Additional articles of the ROC constitution and Cross-Strait Act.

Parthenocissus inserta, also known as thicket creeper, false Virginia creeper, woodbine, or grape woodbine, is a woody vine native to North America, in southeastern Canada and a large area of the United States, from Maine west to Montana and south to New Jersey and Missouri in the east, and Texas to Arizona in the west. It is present in California, but it may be an introduced species that far west. It is introduced in Europe.
Japanese ivy may refer to:
The recorded history of Taipei began with the Han Chinese settling of the Taipei Basin in 1709, leading up to the formation of the national capital of Taiwan and high-tech industry hub and that is now Taipei City. Other notable dates include the 1895 annexation of Taiwan by Japan, during which Taipei began to grow more rapidly, and in the 1950s, the USA's provision of financial assistance to the Republic of China government, after which the city continued on a path of fast structural and industrial growth.

Parthenocissus dalzielii is a creeper related to the grapevine family. It is a native plant of East and South-east Asia.
Differing literary and colloquial readings for certain Chinese characters are a common feature of many Chinese varieties, and the reading distinctions for these linguistic doublets often typify a dialect group. Literary readings are usually used in loanwords, names, literary works, and in formal settings, while colloquial/vernacular readings are usually used in everyday vernacular speech.

Nippoptilia vitis is a moth of the family Pterophoridae, that is known from Japan, Korea, Taiwan, China and Thailand.

The Wistaria Tea House, the Wisteria House, or Wistaria House is a historical teahouse in Daan District, Taipei, Taiwan. The establishment is situated in a Japanese-style wooden house built in the 1920s on Xinsheng South Road. The teahouse is named after the three wisteria vines planted in the front courtyard forming a shaded area leading to the entrance of the building. The teahouse, with its circa 1930s decor, was reopened to much fanfare after a long needed renovation in 2008.

Dendrocnide meyeniana or the poisonous wood nettle is a species of tree in the family Urticaceae, native to the thickets and secondary forests of Taiwan and the Philippines. The specific epithet meyeniana honors Franz Meyen, who collected the type specimen in Manila during his world cruise.

Ampelopsis glandulosa, with common names creeper, porcelain berry, Amur peppervine, and wild grape, is an ornamental plant, native to temperate areas of Asia including China, Japan, India, Nepal, Myanmar, Vietnam, and the Philippines. It is generally similar to, and potentially confused with, grape species and other Ampelopsis species.

























