
The Brassicales are an order of flowering plants, belonging to the eurosids II group of dicotyledons under the APG II system. One character common to many members of the order is the production of glucosinolate compounds. Most systems of classification have included this order, although sometimes under the name Capparales.

Millets are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.

Meliaceae, the mahogany family, is a flowering plant family of mostly trees and shrubs in the order Sapindales.

Sorghum or broomcorn is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Sorghum bicolor is grown as a cereal for human consumption and as animal fodder.

Manihot esculenta, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca, is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions as an annual crop for its edible starchy tuberous root. Cassava is predominantly consumed in boiled form, but substantial quantities are processed to extract cassava starch, called tapioca, which is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. The Brazilian farofa, and the related garri of West Africa, is an edible coarse flour obtained by grating cassava roots, pressing moisture off the obtained grated pulp, and finally drying it.
Muthi is a traditional medicine practice in Southern Africa as far north as Lake Tanganyika.

Rooibos, or Aspalathus linearis, is a broom-like member of the plant family Fabaceae that grows in South Africa's fynbos biome.

Montane grasslands and shrublands are a biome defined by the World Wildlife Fund. The biome includes high elevation grasslands and shrublands around the world. The term "montane" in the name of the biome refers to "high elevation", rather than the ecological term that denotes the region below the treeline.

Okra, Abelmoschus esculentus, known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions around the world for its edible green seed pods, okra is featured in the cuisines of many countries.

Pedaliaceae, the pedalium family or sesame family, is a flowering plant family classified in the order Lamiales. The family includes sesame, the source of sesame seeds.

Yam is the common name for some plant species in the genus Dioscorea that form edible tubers.

Olacaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Santalales. They are woody plants, native throughout the tropical regions of the world. As of July 2021, the circumscription of the family varies; some sources maintain a broad family, others split it into seven segregate families.

Silene undulata is a plant native to the Eastern Cape of South Africa.

PPC Ltd, a supplier of cement, lime (material) and related products in southern Africa. It has 11 cement factories and a lime manufacturing facility in six African countries including South Africa, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Rwanda and Zimbabwe. The company is headquartered in Sandton (Johannesburg).
Murex is a genus of medium to large sized predatory tropical sea snails.

The Stellenbosch University Botanical Garden located in the historical center of Stellenbosch is the oldest university botanical garden in South Africa. The Garden is relatively small and houses an enormous diversity of plants, both indigenous to South Africa and introduced species. It is open to the public.

The Manie van der Schijff Botanical Garden was formally established in 1934 and is managed by the University of Pretoria. Although the garden was originally established to support research and the conservation of indigenous plants, the garden is open to the public.
The South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI) is an organisation tasked with research and dissemination of information on biodiversity, and legally mandated to contribute to the management of the country's biodiversity resources.

Kewa is a genus of flowering plants, consisting of eight species of succulent sub-woody plants, native to eastern and southern Africa, including Saint Helena and Madagascar. These are small shrubs or herbs that form cushions and have edible, acid-tasting leaves. Kewa is the only genus in the family Kewaceae.
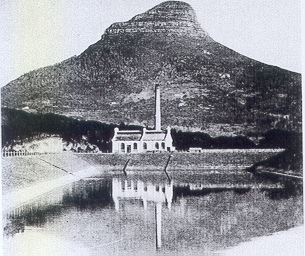
The Graaff Electric Lighting Works power station is a decommissioned Hydro-electric and steam power plant located in Cape Town, South Africa at the site of the Molteno Dam.
















