
Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates metamorphism deep in the Earth's crust. Kyanite is also known as disthene or cyanite.

In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.

Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula KAl2(AlSi3O10)(F,OH)2, or (KF)2(Al2O3)3(SiO2)6(H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavage yielding remarkably thin laminae (sheets) which are often highly elastic. Sheets of muscovite 5 meters × 3 meters (16.5 feet × 10 feet) have been found in Nellore, India.

A pencil is a writing or drawing implement with a solid pigment core in a protective casing that reduces the risk of core breakage, and keeps it from marking the user's hand.

Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic rock. Foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering, but instead is in planes perpendicular to the direction of metamorphic compression.

Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite to anorthite endmembers (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium and calcium atoms can substitute for each other in the mineral's crystal lattice structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or "record-groove" effect.

A penciller is an artist who works on the creation of comic books, graphic novels, and similar visual art forms, with a focus on the initial pencil illustrations, usually in collaboration with other artists, who provide inks, colors and lettering in the book, under the supervision of an editor.

Anhydrite, or anhydrous calcium sulfate, is a mineral with the chemical formula CaSO4. It is in the orthorhombic crystal system, with three directions of perfect cleavage parallel to the three planes of symmetry. It is not isomorphous with the orthorhombic barium (baryte) and strontium (celestine) sulfates, as might be expected from the chemical formulas. Distinctly developed crystals are somewhat rare, the mineral usually presenting the form of cleavage masses. The Mohs hardness is 3.5, and the specific gravity is 2.9. The color is white, sometimes greyish, bluish, or purple. On the best developed of the three cleavages, the lustre is pearly; on other surfaces it is glassy. When exposed to water, anhydrite readily transforms to the more commonly occurring gypsum, (CaSO4·2H2O) by the absorption of water. This transformation is reversible, with gypsum or calcium sulfate hemihydrate forming anhydrite by heating to around 200 °C (400 °F) under normal atmospheric conditions. Anhydrite is commonly associated with calcite, halite, and sulfides such as galena, chalcopyrite, molybdenite, and pyrite in vein deposits.

Henry Clifton Sorby was an English microscopist and geologist. His major contribution was the development of techniques for studying iron and steel with microscopes. This paved the way for the mass production of steel.

Cleavage, in mineralogy and materials science, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in the crystal, which create smooth repeating surfaces that are visible both in the microscope and to the naked eye. If bonds in certain directions are weaker than others, the crystal will tend to split along the weakly bonded planes. These flat breaks are termed "cleavage". The classic example of cleavage is mica, which cleaves in a single direction along the basal pinacoid, making the layers seem like pages in a book. In fact, mineralogists often refer to "books of mica".

Cleavage is the narrow depression or hollow between the breasts of a woman. The superior portion of cleavage may be accentuated by clothing such as a low-cut neckline that exposes the division, and often the term is used to describe the low neckline itself, instead of the term décolletage. Joseph Breen, head of the U.S. film industry's Production Code Administration, coined the term in its current meaning when evaluating the 1943 film The Outlaw, starring Jane Russell. The term was explained in Time magazine on August 5, 1946. It is most commonly used in the parlance of Western female fashion to refer to necklines that reveal or emphasize décolletage.
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage ends with the formation of the blastula, or of the blastocyst in mammals.
Edwin Pouncey, also known by the nom de plumeSavage Pencil, is an English comics artist, musician, and music journalist.
Nikolsky's sign is a clinical dermatological sign, named after Pyotr Nikolsky (1858–1940), a Russian physician who trained and worked in the Russian Empire. The sign is present when slight rubbing of the skin results in exfoliation of the outermost layer. A typical test would be to place the eraser of a pencil on the roof of a lesion and spin the pencil in a rolling motion between the thumb and forefinger. If the lesion is opened, then the Nikolsky's sign is present/positive.

Foliation in geology refers to repetitive layering in metamorphic rocks. Each layer can be as thin as a sheet of paper, or over a meter in thickness. The word comes from the Latin folium, meaning "leaf", and refers to the sheet-like planar structure. It is caused by shearing forces, or differential pressure. The layers form parallel to the direction of the shear, or perpendicular to the direction of higher pressure. Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are typically formed in the absence of significant differential pressure or shear. Foliation is common in rocks affected by the regional metamorphic compression typical of areas of mountain belt formation.
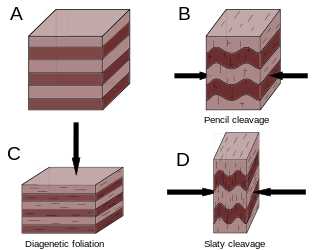
Cleavage, in structural geology and petrology, describes a type of planar rock feature that develops as a result of deformation and metamorphism. The degree of deformation and metamorphism along with rock type determines the kind of cleavage feature that develops. Generally, these structures are formed in fine grained rocks composed of minerals affected by pressure solution.
In the field of mineralogy, fracture is the texture and shape of a rock's surface formed when a mineral is fractured. Minerals often have a highly distinctive fracture, making it a principal feature used in their identification.

Plymouth Sound, Shores and Cliffs is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) around the Plymouth Sound, a large area of water where the River Plym and Tamar meet. It stretches across the two ceremonial counties of Devon and Cornwall and the unitary authority area of Plymouth. It contains fossils of plants and sea creatures and its cliffs show a timeline of the Middle to Early Devonian period hundreds of millions of years ago

The Spiralia are a morphologically diverse clade of protostome animals, including within their number the molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths and other taxa. The term Spiralia is applied to those phyla that exhibit canonical spiral cleavage, a pattern of early development found in most members of the Lophotrochozoa.















