
Kalamazoo/Battle Creek International Airport is a county-owned public airport in Kalamazoo, Kalamazoo County, Michigan, US, 3 miles (4.8 km) southeast of Downtown Kalamazoo. The airport is located approximately 20 miles (32 km) west of the city of Battle Creek. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2023-27, in which it is categorized as a non-hub primary commercial service facility.

Capital Airlines was an airline serving the eastern, southern, southeastern, and midwestern United States. Capital's headquarters were located at Washington National Airport across the Potomac river from Washington, D.C., where crew training and aircraft overhauls were also accomplished. In the 1950s Capital was the fifth largest United States domestic carrier by passenger count after the Big Four air carriers.
Eastern Air Lines Flight 66 was a regularly scheduled flight from New Orleans to New York City that crashed on June 24, 1975 while on approach to New York's John F. Kennedy International Airport, killing 113 of the 124 people on board. The crash was determined to be caused by wind shear caused by a microburst, but the failure of the airport and the flight crew to recognize the severe weather hazard was also a contributing factor.

American Airlines Flight 320 was a scheduled flight between Chicago Midway International Airport and New York City's LaGuardia Airport. On February 3, 1959, the Lockheed L-188 Electra performing the flight crashed into the East River during its descent and approach to LaGuardia Airport, killing 65 of the 73 people on board. Weather conditions in the area were poor, which meant that the crew had to descend through dense clouds and fog. The aircraft flew lower than the pilots intended and it crashed into the icy river 4,900 feet (1,500 m) short of the runway at a speed of 140 knots. American Airlines had been flying the newly-developed Lockheed Electra in commercial service for only about two weeks before the accident.

USAir Flight 1016 was a regularly scheduled flight in the southeastern United States, between Columbia, South Carolina, and Charlotte, North Carolina. On July 2, 1994, the flight encountered heavy thunderstorms and microburst-induced windshear while attempting to land, and crashed into heavy trees and a private residence near the airport. The crash and ensuing fire caused 37 fatalities and seriously injured twenty others.

Eastern Air Lines Flight 512 was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Charlotte, North Carolina, to New York City that crashed on November 30, 1962, killing 25 of the 51 people on board. The aircraft, a Douglas DC-7B operated by Eastern Air Lines, crashed at Idlewild Airport in heavy fog while attempting to perform a go-around. One of the plane's wings struck the ground and the plane crashed into soft sand in a marsh about 200 yards (180 m) from the runway, where it burst into flames. Emergency crews responded, but rescuers were delayed by the thick fog and the soft terrain. An investigation launched after the crash found that the probable cause of the accident was that the pilots had made critical mistakes during the go-around that prevented the aircraft from gaining altitude.

American Airlines Flight 157, a Douglas DC-6, departed on November 29, 1949, from New York City bound for Mexico City with 46 passengers and crew. After one engine failed in mid-flight, a series of critical mistakes by the flight crew caused the pilot to lose control of the plane during the final approach to a routine stopover at Love Field in Dallas, Texas. The airliner slid off the runway and struck a parked airplane, a hangar, and a flight school before crashing into a business across from the airport. 26 passengers and two flight attendants died. The pilot, co-pilot, flight engineer, and 15 passengers survived.

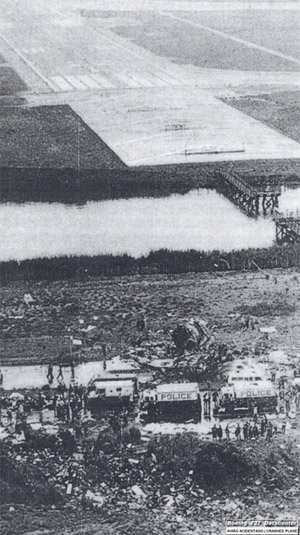
American Airlines Flight 383 was a nonstop flight from New York City to Cincinnati on November 8, 1965. The aircraft was a Boeing 727, with 57 passengers, and 5 crew on board. The aircraft crashed on final approach to the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport located in Hebron, Kentucky, United States. Only three passengers and one flight attendant survived the crash.

Eastern Air Lines Flight 212 was a controlled flight into terrain accident of a McDonnell Douglas DC-9 during approach to Charlotte Douglas International Airport in North Carolina. The incident occurred on September 11, 1974, killing 72 of the 82 people on board. The scheduled flight was from Charleston Municipal Airport to Chicago O'Hare, with an intermediate stop in Charlotte.

On March 29, 2001, a chartered Gulfstream III business jet operated by Avjet from Los Angeles, California, to Aspen, Colorado, crashed into the ground while on final approach. All three crew members and 15 passengers on board perished.

Eastern Air Lines Flight 537, registration N88727, was a Douglas DC-4 aircraft en route from Boston, Massachusetts, to Washington, D.C., via intermediate points on November 1, 1949. NX-26927 was a Lockheed P-38 Lightning being test-flown for acceptance by the government of Bolivia by Erick Rios Bridoux of the Bolivian Air Force. The two aircraft collided in mid-air at an altitude of 300 feet about half a mile southwest of the threshold of Runway 3 at Washington National Airport, killing all 55 aboard the DC-4 and seriously injuring the pilot of the P-38. At the time it was the deadliest airliner incident in United States history.

On July 1, 1965 Continental Airlines Flight 12 overran the runway while attempting to land at Kansas City Municipal Airport. No one was killed or seriously injured, but the accident forced discussions about runway safety in Kansas City and resulted in construction of a new airport, Kansas City International Airport, which opened in 1972. The accident also led to widespread implementation of runway grooving, which improves braking in wet landing conditions.

Western Airlines Flight 2605, nicknamed the "Night Owl", was an international scheduled passenger flight from Los Angeles, California, to Mexico City, Mexico. On October 31, 1979, at 5:42 a.m. CST (UTC−06:00), the McDonnell Douglas DC-10 operating the flight crashed at Mexico City International Airport in fog after landing on a runway that was closed for maintenance. Of the 89 people on board, 72 were killed, in addition to a maintenance worker who died when the plane struck his vehicle.

On July 10, 1991, a L'Express Airlines Beechcraft C99, flying as Flight 508 originating in New Orleans, and in transit from Mobile to Birmingham, crashed while attempting to make an ILS approach to Runway 5 at Birmingham Municipal Airport in Birmingham, Alabama. The plane crashed in the Fairview area near Five Points West in the Ensley neighborhood and subsequently injured four persons on the ground, as well as destroying two homes. Of the 15 occupants on board, there were 13 fatalities. The cause of the crash was attributed to the captain's decision to attempt an instrument approach into severe thunderstorms resulting in a loss of control of the airplane. To date it is the deadliest commercial aviation accident in Alabama history.

Aeroflot Flight 3352 was a regularly scheduled Aeroflot flight from Krasnodar to Novosibirsk, with an intermediate landing in Omsk. While landing at Omsk Airport on Thursday, 11 October 1984, the aircraft crashed into maintenance vehicles on the runway, killing 174 people on board and four on the ground. While a chain of mistakes in airport operations contributed to the accident, its major cause was an air traffic controller falling asleep on duty. As of 2022, this remains the deadliest aviation accident on Russian territory. It was also the deadliest aviation accident involving a Tupolev Tu-154 at the time until the crash of Aeroflot Flight 5143 nine months later; as of 2023, it still ranks as the second-deadliest accident involving a Tupolev Tu-154. The tragedy was kept secret for twenty years, until Komsomolskaya Pravda published an article in 2004.

American Airlines Flight 723 was a scheduled American Airlines flight from Boston Airport in Massachusetts, to Chicago Midway Airport in Illinois. On September 16, 1953, a Convair 240 propliner flying this route crashed while attempting to land at Albany Airport in upstate New York, killing all 28 people on board.

AIRES Flight 8250 was a domestic scheduled passenger flight that on 16 August 2010 crashed on landing at night in poor weather on the Colombian island of San Andrés, killing two of the 131 people on board. The aircraft, an AIRES-operated Boeing 737-700, was arriving from the Colombian capital Bogotá when it heavily touched down short of the runway, breaking up in three sections.
Northeast Airlines Flight 285 was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Boston's Logan International Airport to New York's LaGuardia Airport with stops in Hyannis, Nantucket, Martha's Vineyard, and New Bedford that crashed on September 15, 1957, while trying to land at New Bedford. Seven passengers and two crew members were killed in the crash and three passengers later died from injuries. It was Northeast's second fatal crash of the year and was followed by another deadly crash the following year.

Northwest Orient Airlines Flight 324 was a military charter flight from Haneda Airport to McChord Air Force Base. On the morning of January 19, 1952, the flight crashed into Hecate Strait in British Columbia, Canada, while making an emergency landing at Sandspit Airport. All three crew members and 33 of the 40 passengers were killed, making the flight the third-deadliest aviation accident in Canada at the time.




















