Related Research Articles

Chloroplasts are organelles that conduct photosynthesis, where the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in plant and algal cells. They then use the ATP and NADPH to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, much amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like Arabidopsis and wheat.
Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations in the cell or outside it. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. This delivery process is carried out based on information contained in the protein itself. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors can lead to diseases.

The dinoflagellates are single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata. Usually considered algae, dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations are distributed depending on sea surface temperature, salinity, or depth. Many dinoflagellates are known to be photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey.

The alveolates are a group of protists, considered a major clade and superphylum within Eukarya, and are also called Alveolata.

The cryptomonads are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.

Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. Paramecia are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and are often very abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, it has been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological processes. Its usefulness as a model organism has caused one ciliate researcher to characterize it as the "white rat" of the phylum Ciliophora.
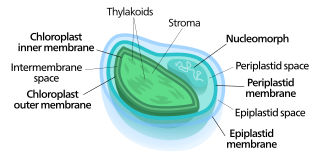
Nucleomorphs are small, vestigial eukaryotic nuclei found between the inner and outer pairs of membranes in certain plastids. They are thought to be vestiges of primitive red and green algal nuclei that were engulfed by a larger eukaryote. Because the nucleomorph lies between two sets of membranes, nucleomorphs support the endosymbiotic theory and are evidence that the plastids containing them are complex plastids. Having two sets of membranes indicate that the plastid, a prokaryote, was engulfed by a eukaryote, an alga, which was then engulfed by another eukaryote, the host cell, making the plastid an example of secondary endosymbiosis.

A theca refers to a sheath or a covering.

The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 220 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.

Paramecium caudatum is a species of unicellular protist in the phylum Ciliophora. They can reach 0.33 mm in length and are covered with minute hair-like organelles called cilia. The cilia are used in locomotion and feeding. The species is very common, and widespread in marine, brackish and freshwater environments.

The genus Ceratium is restricted to a small number of freshwater dinoflagellate species. Previously the genus contained also a large number of marine dinoflagellate species. However, these marine species have now been assigned to a new genus called Tripos. Ceratium dinoflagellates are characterized by their armored plates, two flagella, and horns. They are found worldwide and are of concern due to their blooms.
Geminigera /ˌdʒɛmɪnɪˈdʒɛɹə/ is a genus of cryptophyte from the family Geminigeraceae. Named for its unique pyrenoids, Geminigera is a genus with a single mixotrophic species. It was discovered in 1968 and is known for living in very cold temperatures such as under the Antarctic ice. While originally considered to be part of the genus Cryptomonas, the genus Geminigera was officially described in 1991 by D. R. A. Hill.

Ornithocercus is a genus of planktonic dinoflagellate that is known for its complex morphology that features considerable lists growing from its thecal plates, giving an attractive appearance. Discovered in 1883, this genus has a small number of species currently categorized but is widespread in tropical and sub-tropical oceans. The genus is marked by exosymbiotic bacteria gardens under its lists, the inter-organismal dynamics of which are a current field of research. As they reside only in warm water, the genus has been used as a proxy for climate change and has potential to be an indicator species for environmental change if found in novel environments.
Dinophysis is a genus of dinoflagellates common in tropical, temperate, coastal and oceanic waters. It was first described in 1839 by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.

The Warnowiaceae are a family of athecate dinoflagellates. Members of the family are known as warnowiids. The family is best known for a light-sensitive subcellular structure known as the ocelloid, a highly complex arrangement of organelles with a structure directly analogous to the eyes of multicellular organisms. The ocelloid has been shown to be composed of multiple types of endosymbionts, namely mitochondria and at least one type of plastid.
Durinskia is a genus of dinoflagellate that can be found in freshwater and marine environments. This genus was created to accommodate its type species, Durinskia baltica, after major classification discrepancies were found. While Durinskia species appear to be typical dinoflagellates that are armored with cellulose plates called theca, the presence of a pennate diatom-derived tertiary endosymbiont is their most defining characteristic. This genus is significant to the study of endosymbiotic events and organelle integration since structures and organelle genomes in the tertiary plastids are not reduced. Like some dinoflagellates, species in Durinskia may cause blooms.
Blastodinium is a diverse genus of dinoflagellates and important parasites of planktonic copepods. They exist in either a parasitic stage, a trophont stage, and a dinospore stage. Although morphologically and functionally diverse, as parasites they live exclusively in the intestinal tract of copeods.
Coolia is a marine dinoflagellate genus in the family Ostreopsidaceae. It was first described by Meunier in 1919. There are currently seven identified species distributed globally in tropical and temperate coastal waters. Coolia is a benthic or epiphytic type dinoflagellate: it can be found adhered to sediment or other organisms but it is not limited to these substrates. It can also be found in a freely motile form in the water column. The life cycle of Coolia involves an asexual stage where the cell divides by binary fission and a sexual stage where cysts are produced. Some of the species, for example, Coolia tropicalis and Coolia malayensis, produce toxins that can potentially cause shellfish poisoning in humans.

Haplozoon (/hæploʊ’zoʊən/) are unicellular endo-parasites, primarily infecting maldanid polychaetes. They belong to Dinoflagellata but differ from typical dinoflagellates. Most dinoflagellates are free-living and possess two flagella. Instead, Haplozoon belong to a 5% minority of parasitic dinoflagellates that are not free-living. Additionally, the Haplozoon trophont stage is particularly unique due to an apparent lack of flagella. The presence of flagella or remnant structures is the subject of ongoing research.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Berner, Tamar (1993). Ultrastructure of microalgae (11 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 74–78. ISBN 978-0849363238.
- ↑ Grim, J. N.; Staehelin, L. A. (1984). "The ejectisomes of the flagellate Chilomonas paramecium - Visualization by freeze-fracture and isolation techniques". Journal of Protozoology. 31 (2): 259–267. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02957.x. PMID 6470985.