Warts are non-cancerous viral growths usually occurring on the hands and feet but which can also affect other locations, such as the genitals or face. One or many warts may appear. They are distinguished from cancerous tumors as they are caused by a viral infection, such as a human papillomavirus, rather than a cancer growth.

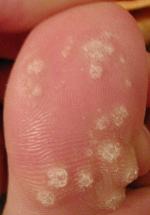
A plantar wart is a wart occurring on the bottom of the foot or toes. Its color is typically similar to that of the skin. Small black dots often occur on the surface. One or more may occur in an area. They may result in pain with pressure such that walking is difficult.

Sebaceous hyperplasia is a disorder of the sebaceous glands in which they become enlarged, producing flesh-colored or yellowish, shiny, often umbilicated bumps. Sebaceous hyperplasia, primarily affecting older patients in high-concentration areas like the face, head, and neck, typically has a 2-4 mm diameter and causes no symptoms. The lesions are often surrounded by telangiectatic blood vessels, also known as "crown vessels," and a central dell, which is in line with the origin of the lesions.

Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma (cSCC), also known as squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin or squamous-cell skin cancer, is one of the three principal types of skin cancer, alongside basal-cell carcinoma and melanoma. cSCC typically presents as a hard lump with a scaly surface, though it may also present as an ulcer. Onset and development often occurs over several months. Compared to basal cell carcinoma, cSCC is more likely to spread to distant areas. When confined to the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin, the pre-invasive or in situ form of cSCC is termed Bowen's disease.
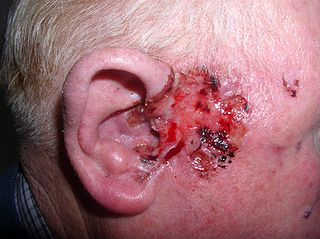
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, basalioma or rodent ulcer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. It may also present as a raised area with ulceration. Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it, but it is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death.

Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin. Actinic keratosis is a disorder of epidermal keratinocytes that is induced by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. These growths are more common in fair-skinned people and those who are frequently in the sun. They are believed to form when skin gets damaged by UV radiation from the sun or indoor tanning beds, usually over the course of decades. Given their pre-cancerous nature, if left untreated, they may turn into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Untreated lesions have up to a 20% risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma, so treatment by a dermatologist is recommended.

Paronychia is an inflammation of the skin around the nail, which can occur suddenly, when it is usually due to the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, or gradually when it is commonly caused by the fungus Candida albicans. The term is from Greek: παρωνυχία from para 'around', onyx 'nail', and the abstract noun suffix -ia.

Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Fingernails may be affected, but it is more common for toenails. Complications may include cellulitis of the lower leg. A number of different types of fungus can cause onychomycosis, including dermatophytes and Fusarium. Risk factors include athlete's foot, other nail diseases, exposure to someone with the condition, peripheral vascular disease, and poor immune function. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on the appearance and confirmed by laboratory testing.
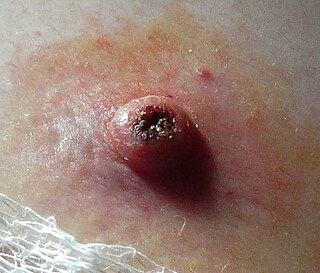
Keratoacanthoma (KA) is a common low-grade rapidly-growing skin tumour that is believed to originate from the hair follicle and can resemble squamous cell carcinoma.
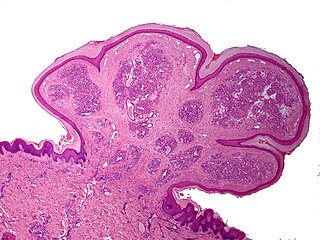
A pyogenic granuloma or lobular capillary hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, skin, or nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head, such as in the thigh.

Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) is a skin condition characterised by warty skin lesions. It results from an abnormal susceptibility to HPV infection (HPV) and is associated with a high lifetime risk of squamous cell carcinomas in skin. It generally presents with scaly spots and small bumps particularly on the hands, feet, face and neck; typically beginning in childhood or in a young adult. The bumps tend to be flat, grow in number and then merge to form plaques. On the trunk, it typically appears like pityriasis versicolor; lesions there being slightly scaly and tan, brown, red or looking pale. On the elbows, it may appear like psoriasis. On the forehead, neck and trunk, the lesions may appear like seborrheic keratosis.

A squamous cell papilloma is a generally benign papilloma that arises from the stratified squamous epithelium of the skin, lip, oral cavity, tongue, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, cervix, vagina or anal canal. Squamous cell papillomas are typically associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) while sometimes the cause is unknown.

Atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) of the skin is a low-grade malignancy related to malignant fibrous histiocytoma, which it resembles histologically. Atypical fibroxanthoma manifests as a hard, pink or red papule or nodule that grows over the course of several months and may bleed or ulcerate. They typically occur on the head and neck. Atypical fibroxanthoma is usually asymptomatic.
Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp presents with pustules, erosions, and crusts on the scalp of primarily older Caucasian females, and on biopsy, has a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with or without foreign body giant cells and pilosebaceous atrophy.
Pincer nails are a toenail disorder in which the lateral edges of the nail slowly approach one another, compressing the nailbed and underlying dermis. It occurs less often in the fingernails than toenails, and there usually are no symptoms.
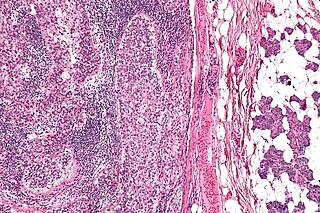
Sebaceous carcinoma, also known as sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGc), sebaceous cell carcinoma, and meibomian gland carcinoma is an uncommon malignant cutaneous tumor. Most are typically about 1.4 cm at presentation. SGc originates from sebaceous glands in the skin and, therefore, may originate anywhere in the body where these glands are found. SGc can be divided into 2 types: periocular and extraocular. The periocular region is rich in sebaceous glands making it a common site of origin. The cause of these lesions in the vast majority of cases is unknown. Occasional cases may be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome. SGc accounts for approximately 0.7% of all skin cancers, and the incidence of SGc is highest in Caucasian, Asian, and Indian populations. Due to the rarity of this tumor and variability in clinical and histological presentation, SGc is often misdiagnosed as an inflammatory condition or a more common neoplasm. SGc is commonly treated with wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery, and the relative survival rates at 5 and 10 years are 92.72 and 86.98%, respectively.
Malalignment of the nail plate, also known as congenital malalignment of the great toenails or congenital malalignment syndrome, is a congenital malalignment of the nail of the great toe, and is often misdiagnosed although it is a common condition. It most commonly affects the hallucices. The nail might be discolored and develop infections. If the misaligned nail becomes embedded in the lateral nail fold it can cause pain, inflammation and erythema.
Actinic granuloma (AG) was first described by O'Brien in 1975 as a rare granulomatous disease. Lesions appear on sun-exposed areas, usually on the face, neck, and scalp, with a slight preference for middle-aged women. They are typically asymptomatic, single or multiple, annular or polycyclic lesions measuring up to 6 cm in diameter, with slow centrifugal expansion, an erythematous elevated edge, and a hypopigmented, atrophic center.
Pseudoepitheliomatous keratotic and micaceous balanitis, (PKMB) is a cutaneous condition characterized by skin lesions on the glans penis that are wart-like with scaling. It can present as a cutaneous horn. PKMB is usually asymptomatic, with occasional irritation, burning sensation, fissuring, or maceration.
Laser-assisted drug delivery (LADD) is a drug delivery technique commonly used in the dermatology field that involves lasers. As skin acts as a protective barrier to the environment, the absorption of topical products through the epidermis is limited; thus, different drug delivery modalities have been employed to improve the efficacy of these treatments. The use of lasers in LADD has been shown to enhance the penetration of drugs transdermal, leading to a higher absorption rate, limited systemic effects, and reduced duration of treatment. Although this technique has evolved in the past decade due to its efficacy through scientific research and clinical practice, there remain some limitations regarding the safety aspect that needs to be taken into consideration.














