
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually denotes an embassy or high commission, which is the main office of a country's diplomatic representatives to another country; it is usually, but not necessarily, based in the receiving state's capital city. Consulates, on the other hand, are smaller diplomatic missions that are normally located in major cities of the receiving state. As well as being a diplomatic mission to the country in which it is situated, an embassy may also be a nonresident permanent mission to one or more other countries.

The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
China is one of the members of the United Nations and is one of five permanent members of its Security Council. One of the victorious Allies of World War II, the Republic of China (ROC) joined the UN upon its founding in 1945. The subsequent resumption of the Chinese Civil War between the government of Republic of China and the rebel forces of the Chinese Communist Party, led to the latter's victory on the mainland and the establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. Nearly all of Mainland China was soon under its control and the ROC government retreated to the island of Taiwan.

The United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2758 was passed in response to the United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1668 that required any change in China's representation in the UN be determined by a two-thirds vote referring to Article 18 of the UN Charter. The resolution, passed on 25 October 1971, recognized the People's Republic of China as "the only legitimate representative of China to the United Nations" and removed "the representatives of Chiang Kai-shek" from the United Nations.

An apostolic nunciature is a top-level diplomatic mission of the Holy See that is equivalent to an embassy. However, it neither issues visas nor has consulates.

The Soviet Union was a charter member of the United Nations and one of five permanent members of the Security Council. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, its UN seat was transferred to the Russian Federation, one of the many successor states of the USSR.
The United Nations General Assembly has granted observer status to international organizations, entities, and non-member states, to enable them to participate in the work of the United Nations General Assembly, though with limitations. The General Assembly determines the privileges it will grant to each observer, beyond those laid down in a 1986 Conference on treaties between states and international organizations. Exceptionally, the European Union (EU) was in 2011 granted the right to speak in debates, to submit proposals and amendments, the right of reply, to raise points of order and to circulate documents, etc. As of May 2011, the EU is the only international organization to hold these enhanced rights, which has been likened to the rights of full membership, short of the right to vote.

The G4 nations, comprising Brazil, Germany, India, and Japan, are four countries which support each other's bids for permanent seats on the United Nations Security Council. Unlike the G7, where the common denominator is the economy and long-term political motives, the G4's primary aim is the permanent member seats on the Security Council. Each of these four countries have figured among the elected non-permanent members of the council since the UN's establishment. Their economic and political influence has grown significantly in the last decades, reaching a scope comparable to the permanent members (P5). However, the G4's bids are often opposed by the Uniting for Consensus movement, and particularly their economic competitors or political rivals.
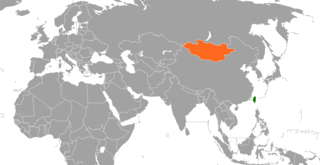
At its establishment in 1912, the Republic of China claimed to be the successor state to the entirety of the Qing empire, which included Outer Mongolia. The Republic of China did not recognize Outer Mongolia until 1945; neither country exchanged diplomats between 1946 and 1949. At the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, Mongolia recognized the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China retreated to the island of Taiwan. The Republic of China continued to show Mongolia as part of its territory on official maps until 2002 when they recognized Mongolia as an independent country, and informal relations were established between the two sides.
The Ambassador of Iran to the United Nations is the leader of the delegation of Iran to the United Nations. The position is more formally known as the "Permanent Representative of the Islamic Republic of Iran to the United Nations”, with the rank and status of Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary, and Representative of Iran in the United Nations Security Council.

The Permanent Mission of France to the United Nations is the diplomatic mission of the French Republic to the United Nations in New York. As such, it reports to the Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs.

The permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the five sovereign states to whom the UN Charter of 1945 grants a permanent seat on the UN Security Council: China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States.

The Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States represents the interests of Taiwan in the United States in the absence of formal diplomatic relations, functioning as a de facto embassy. Its counterpart in Taiwan is the office of the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT) in Taipei.
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania joined the United Nations on 14 December 1955, and has participated in several UN peacekeeping operations. The current Representative of Albania in the UN is Mr. Ferit Hoxha. Albania is a non-permanent member of the 15-country UN Security Council for the two-year term (2022–2023).

The Permanent Mission of India to the United Nations is the formal title of the Indian delegation to the United Nations (UN). India was among the founding members of the United Nations and signed the Declaration by United Nations on 1 January 1942. India also participated in the United Nations Conference on International Organization and Diwan Bahadur Sir Arcot Ramasamy Mudaliar signed the United Nations Charter on India's behalf.
The Permanent Mission of Afghanistan to the United Nations is the formal title of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan delegation to the United Nations (UN). Afghanistan officially joined the United Nations on 19 November 1946 as the Kingdom of Afghanistan.

Zhang Jun is a Chinese diplomat who has served as the Permanent Representative of China to the United Nations since July 2019. In March 2020, May 2021, August 2022 and November 2023, he became President of the United Nations Security Council by assuming the monthly rotating role among Council members according to alphabetical order in the English language.

The Permanent Mission of North Korea to the United Nations is the diplomatic mission of North Korea to the United Nations (UN) in New York.


















