
Masonry is the craft of building a structure with brick, stone, or similar material, including mortar plastering which are often laid in, bound and pasted together by mortar; the term masonry can also refer to the building units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks and building stone such as marble, granite, and limestone, cast stone, concrete blocks, glass blocks, and adobe. Masonry is generally a highly durable form of construction. However, the materials used, the quality of the mortar and workmanship, and the pattern in which the units are assembled can substantially affect the durability of the overall masonry construction. A person who constructs masonry is called a mason or bricklayer. These are both classified as construction trades.

The Washington Monument is an obelisk on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., built to commemorate George Washington, a Founding Father of the United States, victorious commander-in-chief of the Continental Army from 1775 to 1783 in the American Revolutionary War, and the first President of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Standing east of the Reflecting Pool and the Lincoln Memorial, the monument, made of marble, granite, and bluestone gneiss, is both the world's tallest predominantly stone structure and the world's tallest obelisk, standing 554 feet 7+11⁄32 inches (169.046 m) tall, according to the U.S. Geodetic Survey measurements in 2013–2014. It is the tallest monumental column in the world if all are measured above their pedestrian entrances. It was the world's tallest structure between 1884 and 1889, after which it was overtaken by the Eiffel Tower, in Paris. Previously, the tallest structure was the Cologne Cathedral.

Drywall is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or without additives, typically extruded between thick sheets of facer and backer paper, used in the construction of interior walls and ceilings. The plaster is mixed with fiber ; plasticizer, foaming agent; and additives that can reduce mildew, flammability, and water absorption.

Brickwork is masonry produced by a bricklayer, using bricks and mortar. Typically, rows of bricks called courses are laid on top of one another to build up a structure such as a brick wall.

In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the ground or more rarely, water, transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep. Foundation engineering is the application of soil mechanics and rock mechanics in the design of foundation elements of structures.

A concrete block, also known as a cinder block in North American English, breeze block in British English, concrete masonry unit (CMU), or by various other terms, is a standard-size rectangular block used in building construction. The use of blockwork allows structures to be built in the traditional masonry style with layers of staggered blocks.

Ashlar is finely dressed stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruvius as opus isodomum, or less frequently trapezoidal. Precisely cut "on all faces adjacent to those of other stones", ashlar is capable of very thin joints between blocks, and the visible face of the stone may be quarry-faced or feature a variety of treatments: tooled, smoothly polished or rendered with another material for decorative effect.

Repointing is the process of renewing the pointing, which is the external part of mortar joints, in masonry construction. Over time, weathering and decay cause voids in the joints between masonry units, usually in bricks, allowing the undesirable entrance of water. Water entering through these voids can cause significant damage through frost weathering and from salt dissolution and deposition. Repointing is also called pointing, or pointing up, although these terms more properly refer to the finishing step in new construction.

Murus Dacicus is a construction method for defensive walls and fortifications developed in ancient Dacia sometime before the Roman conquest. It is a mix between traditional construction methods particular to Dacian builders and methods imported from Greek and Roman architecture and masonry, and – although somewhat similar construction techniques were used before, during and long after the period – it has peculiarities that make it unique.

A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two "skins" separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can slowly draw rainwater or even humidity into the wall. One function of the cavity is to drain water through weep holes at the base of the wall system or above windows. The weep holes allow wind to create an air stream through the cavity that exports evaporated water from the cavity to the outside. Usually, weep holes are created by separating several vertical joints approximately two meters apart at the base of each story. Weep holes are also placed above windows to prevent dry rot of wooden window frames. A cavity wall with masonry as both inner and outer skins is more commonly referred to as a double wythe masonry wall.

Damp proofing in construction is a type of moisture control applied to building walls and floors to prevent moisture from passing into the interior spaces. Dampness problems are among the most frequent problems encountered in residences.
Opus quadratum is an ancient Roman construction technique, in which squared blocks of stone of the same height were set in parallel courses, most often without the use of mortar. The Latin author Vitruvius describes the technique.

Masonry veneer walls consist of a single non-structural external layer of masonry, typically made of brick, stone or manufactured stone. Masonry veneer can have an air space behind it and is technically called "anchored veneer". A masonry veneer attached directly to the backing is called "adhered veneer". The innermost element is structural, and may consist of masonry, concrete, timber or metal frame.

A weep, a weep hole, or a weep-brick is a small opening that allows water to drain from within an assembly. Weeps are located at the bottom of the object to allow for drainage; the weep hole must be sized adequately to overcome surface tension.
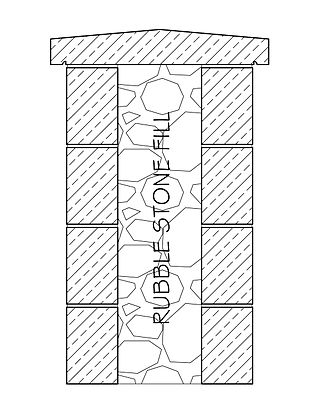
Rubble masonry or rubble stone is rough, uneven building stone not laid in regular courses. It may fill the core of a wall which is faced with unit masonry such as brick or ashlar. Some medieval cathedral walls have outer shells of ashlar with an inner backfill of mortarless rubble and dirt.
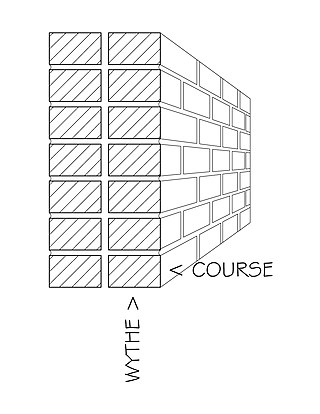
A course is a layer of the same unit running horizontally in a wall. It can also be defined as a continuous row of any masonry unit such as bricks, concrete masonry units (CMU), stone, shingles, tiles, etc.

A rainscreen is an exterior wall detail where the siding stands off from the moisture-resistant surface of an air/water barrier applied to the sheathing to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation. The rainscreen is the cladding or siding itself but the term rainscreen implies a system of building. Ideally the rainscreen prevents the wall air/water barrier from getting wet but because of cladding attachments and penetrations water is likely to reach this point, and hence materials are selected to be moisture tolerant and integrated with flashing. In some cases a rainscreen wall is called a pressure-equalized rainscreen wall where the ventilation openings are large enough for the air pressure to nearly equalize on both sides of the rain screen, but this name has been criticized as being redundant and is only useful to scientists and engineers.

Burg Krems is a castle in Styria, Austria. Burg Krems is 330 metres (1,080 ft) above sea level.

The Prison of Anemas is a large Byzantine building attached to the walls of the city of Constantinople. It is traditionally identified with the prisons named after Michael Anemas, a Byzantine general who rose in unsuccessful revolt against Emperor Alexios I Komnenos and was the first person to be imprisoned there. The prison features prominently in the last centuries of the Byzantine Empire, when four Byzantine emperors were imprisoned there.

Domes first appeared in South Asia during medieval period when it was constructed with stone, brick and mortar, and iron dowels and cramps. Centering was made from timber and bamboo. The use of iron cramps to join together adjacent stones was known in Ancient India, and was used at the base of domes for hoop reinforcement. The synthesis of styles created by this introduction of new forms to the Hindu tradition of trabeate construction created a distinctive architecture.



















