Related Research Articles

Tourette syndrome or Tourette's syndrome is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in childhood or adolescence. It is characterized by multiple movement (motor) tics and at least one vocal (phonic) tic. Common tics are blinking, coughing, throat clearing, sniffing, and facial movements. These are typically preceded by an unwanted urge or sensation in the affected muscles known as a premonitory urge, can sometimes be suppressed temporarily, and characteristically change in location, strength, and frequency. Tourette's is at the more severe end of a spectrum of tic disorders. The tics often go unnoticed by casual observers.

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by executive dysfunction occasioning symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate.

The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's disease, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico–basal ganglia–thalamic loop.

Hypergraphia is a behavioral condition characterized by the intense desire to write or draw. Forms of hypergraphia can vary in writing style and content. It is a symptom associated with temporal lobe changes in epilepsy and in Geschwind syndrome. Structures that may have an effect on hypergraphia when damaged due to temporal lobe epilepsy are the hippocampus and Wernicke's area. Aside from temporal lobe epilepsy, chemical causes may be responsible for inducing hypergraphia.

Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), or frontotemporal degeneration disease, or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs broadly present as behavioral or language disorders with gradual onsets. Common signs and symptoms include significant changes in social and personal behavior, apathy, blunting of emotions, and deficits in both expressive and receptive language. Currently, there is no cure for FTD, but there are treatments that help alleviate symptoms.

Hyperfocus is an intense form of mental concentration or visualization that focuses consciousness on a subject, topic, or task. In some individuals, various subjects or topics may also include daydreams, concepts, fiction, the imagination, and other objects of the mind. Hyperfocus on a certain subject can cause side-tracking away from assigned or important tasks.
Cognitive disengagement syndrome (CDS) is an attention syndrome characterised by prominent dreaminess, mental fogginess, hypoactivity, sluggishness, slow reaction time, staring frequently, inconsistent alertness, and a slow working speed.

In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence.
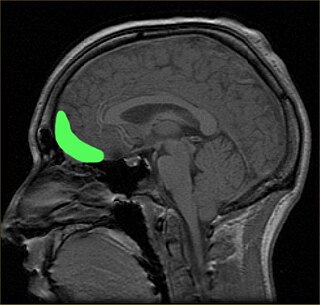
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 12 and 13; in humans it consists of Brodmann area 10, 11 and 47.

Frontal lobe disorder, also frontal lobe syndrome, is an impairment of the frontal lobe of the brain due to disease or frontal lobe injury. The frontal lobe plays a key role in executive functions such as motivation, planning, social behaviour, and speech production. Frontal lobe syndrome can be caused by a range of conditions including head trauma, tumours, neurodegenerative diseases, neurodevelopmental disorders, neurosurgery and cerebrovascular disease. Frontal lobe impairment can be detected by recognition of typical signs and symptoms, use of simple screening tests, and specialist neurological testing.
Cognitive shifting is the mental process of consciously redirecting one's attention from one fixation to another. In contrast, if this process happened unconsciously, then it is referred to as task switching. Both are forms of cognitive flexibility.
An addictive behavior is a behavior, or a stimulus related to a behavior, that is both rewarding and reinforcing, and is associated with the development of an addiction. There are two main forms of addiction: substance use disorders and behavioral addiction. Any activity that activates the reward system in your brain has the potential to cause behavioral addictions. The parallels and distinctions between behavioral addictions and other compulsive behavior disorders like bulimia nervosa and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) are still being researched by behavioral scientists.

In psychology, impulsivity is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically "poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences," which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. Impulsivity can be classified as a multifactorial construct. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. "When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality." Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least two independent components: first, acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and second, choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.
Dysexecutive syndrome (DES) consists of a group of symptoms, usually resulting from brain damage, that fall into cognitive, behavioural and emotional categories and tend to occur together. The term was introduced by Alan Baddeley to describe a common pattern of dysfunction in executive functions, such as planning, abstract thinking, flexibility and behavioural control. It is thought to be Baddeley's hypothesized working memory system and the central executive that are the hypothetical systems impaired in DES. The syndrome was once known as frontal lobe syndrome; however 'dysexecutive syndrome' is preferred because it emphasizes the functional pattern of deficits over the location of the syndrome in the frontal lobe, which is often not the only area affected.

Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental and behavioral disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts and feels the need to perform certain routines (compulsions) repeatedly to relieve the distress caused by the obsession, to the extent where it impairs general function.
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processes. Executive dysfunction can refer to both neurocognitive deficits and behavioural symptoms. It is implicated in numerous psychopathologies and mental disorders, as well as short-term and long-term changes in non-clinical executive control. Executive dysfunction is the mechanism underlying ADHD Paralysis, and in a broader context, it can encompass other cognitive difficulties like planning, organizing, initiating tasks and regulating emotions. It is a core characteristic of ADHD and can elucidate numerous other recognized symptoms.
The biology of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) refers biologically based theories about the mechanism of OCD. Cognitive models generally fall into the category of executive dysfunction or modulatory control. Neuroanatomically, functional and structural neuroimaging studies implicate the prefrontal cortex (PFC), basal ganglia (BG), insula, and posterior cingulate cortex (PCC). Genetic and neurochemical studies implicate glutamate and monoamine neurotransmitters, especially serotonin and dopamine.

Inhibitory control, also known as response inhibition, is a cognitive process – and, more specifically, an executive function – that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses and natural, habitual, or dominant behavioral responses to stimuli in order to select a more appropriate behavior that is consistent with completing their goals. Self-control is an important aspect of inhibitory control. For example, successfully suppressing the natural behavioral response to eat cake when one is craving it while dieting requires the use of inhibitory control.
Executive functions are a cognitive apparatus that controls and manages cognitive processes. Norman and Shallice (1980) proposed a model on executive functioning of attentional control that specifies how thought and action schemata become activated or suppressed for routine and non-routine circumstances. Schemas, or scripts, specify an individual's series of actions or thoughts under the influence of environmental conditions. Every stimulus condition turns on the activation of a response or schema. The initiation of appropriate schema under routine, well-learned situations is monitored by contention scheduling which laterally inhibits competing schemas for the control of cognitive apparatus. Under unique, non-routine procedures controls schema activation. The SAS is an executive monitoring system that oversees and controls contention scheduling by influencing schema activation probabilities and allowing for general strategies to be applied to novel problems or situations during automatic attentional processes.
The delayed-maturation theory of obsessive–compulsive disorder suggests that obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) can be caused by delayed maturation of the frontal striatal circuitry or parts of the brain that make up the frontal cortex, striatum, or integrating circuits. Some researchers suspect that variations in the volume of specific brain structures can be observed in children that have OCD. It has not been determined if delayed-maturation of this frontal circuitry contributes to the development of OCD or if OCD is the ailment that inhibits normal growth of structures in the frontal striatal, frontal cortex, or striatum. However, the use of neuroimaging has equipped researchers with evidence of some brain structures that are consistently less adequate and less matured in patients diagnosed with OCD in comparison to brains without OCD. More specifically, structures such as the caudate nucleus, volumes of gray matter, white matter, and the cingulate have been identified as being less developed in people with OCD in comparison to individuals that do not have OCD. However, the cortex volume of the operculum (brain) is larger and OCD patients are also reported to have larger temporal lobe volumes; which has been identified in some women patients with OCD. Further research is needed to determine the effect of these structural size differences on the onset and degree of OCD and the maturation of specific brain structures.
References
- 1 2 Helm-Estabrooks N (2004). "The problem of perseveration". Semin Speech Lang. 25 (4): 289–90. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-837241 . PMID 15599818.
- 1 2 "Perseveration". Psych Central.com. Archived from the original on 2012-10-16.
- 1 2 "Perseveration - Define Perseveration at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.com. Archived from the original on 2012-08-14.
- 1 2 Dictionary of Biological Psychology - p.595
- ↑ "Perseverate | Define Perseverate at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.reference.com. Archived from the original on 2014-01-30. Retrieved 2014-03-03.
- 1 2 "Psychiatric Glossary of Terms in Psychiatry". priory.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-07.
- ↑ Iversen, Susan D.; Mishkin, Mortimer (1970). "Perseverative interference in monkeys following selective lesions of the inferior prefrontal convexity". Experimental Brain Research. 11 (4): 376–86. doi:10.1007/BF00237911. PMID 4993199. S2CID 11685677.
- ↑ http://academic.oup.com/brain/article-pdf/130/3/816/778818/awl347.pdf [ bare URL PDF ]
- 1 2 Misdiagnosis And Dual Diagnoses Of Gifted Children And Adults: Adhd, Bipolar... - Webb, p.50-51]: Notes prior research into "hyperfocus" in ADHD, identifies it with "flow" in gifted children, observes that what is called hyperfocus in such cases "seems to be a less medical-sounding description of perseveration. Thus the apparent ability to concentrate in certain limited situations does not exclude the diagnosis of ADD/ADHD."
- ↑ Taking Charge of Adult ADHD, Barkley R. - p.61-62 "One track Mind"
- ↑ Meaux, Julie B. (2000). "Stop, look, and listen: the challenge for children with ADHD". Issues in Comprehensive Pediatric Nursing. 23 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1080/01460860050121394. PMID 11011659. S2CID 19944681.
- ↑ Miranda, Monica Carolina; Barbosa, Thais; Muszkat, Mauro; Rodrigues, Camila Cruz; Sinnes, Elaine Girão; Coelho, Luzia Flavia S; Rizzuti, Sueli; Palma, Sonia Maria Mota; Bueno, Orlando Francisco Amodeo (2012). "Performance patterns in Conners' CPT among children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and dyslexia". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria. 70 (2): 91–6. doi: 10.1590/S0004-282X2012000200004 . PMID 22311211.
- ↑ Gyula, Demeter; Mihály, Racsmány; Katalin, Csigó; András, Harsányi; Attila, Németh; László, Döme (2013). "Ép rövid távú memória és károsodott végrehajtó funkciók kényszerbetegségben" [Intact short-term memory and impaired executive functions in obsessive compulsive disorder]. Ideggyógyászati Szemle (in Hungarian). 66 (1–2): 35–41. PMID 23607228. Archived from the original on 2015-07-04.
- ↑ Pediatric Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder~differential at eMedicine
- ↑ Ridley, R.M.; et al. (1981). "An involvement of dopamine in higher order choice mechanisms in the monkey". Psychopharmacology. 72 (2): 173–177. doi:10.1007/bf00431652. PMID 6782607. S2CID 33346412.
- ↑ Zelazo PD, Müller U, Frye D, et al. (2003). "The development of executive function in early childhood". Monogr Soc Res Child Dev. 68 (3): vii–137. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5834.2003.06803010.x. PMID 14723273.
- ↑ Sharon, Tanya; DeLoache, Judy S. (2003). "The role of perseveration in children's symbolic understanding and skill". Developmental Science. 6 (3): 289–96. doi:10.1111/1467-7687.00285. S2CID 332017.