
Mercury is the first planet from the Sun and the smallest in the Solar System. In English, it is named after the Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), god of commerce and communication, and the messenger of the gods. Mercury is classified as a terrestrial planet, with roughly the same surface gravity as Mars. The surface of Mercury is heavily cratered, as a result of countless impact events that have accumulated over billions of years. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of 1,550 km (960 mi) and one-third the diameter of the planet. Similarly to the Earth's Moon, Mercury's surface displays an expansive rupes system generated from thrust faults and bright ray systems formed by impact event remnants.

Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second-largest in the Solar System, larger than any of the dwarf planets of the Solar System. It is the only moon known to have a dense atmosphere, and is the only known object in space other than Earth on which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found.

Rhea is the second-largest moon of Saturn and the ninth-largest moon in the Solar System, with a surface area that is comparable to the area of Australia. It is the smallest body in the Solar System for which precise measurements have confirmed a shape consistent with hydrostatic equilibrium. It was discovered in 1672 by Giovanni Domenico Cassini.

Shackleton is an impact crater that lies at the lunar south pole. The peaks along the crater's rim are exposed to almost continual sunlight, while the interior is perpetually in shadow. The low-temperature interior of this crater functions as a cold trap that may capture and freeze volatiles shed during comet impacts on the Moon. Measurements by the Lunar Prospector spacecraft showed higher than normal amounts of hydrogen within the crater, which may indicate the presence of water ice. The crater is named after Antarctic explorer Ernest Shackleton.

Chao Meng-Fu is a 167 km (104 mi) diameter crater on Mercury named after the Chinese painter and calligrapher Zhao Mengfu (1254–1322). Due to its location near Mercury's south pole and the planet's small axial tilt, an estimated 40% of the crater lies in permanent shadow. This combined with bright radar echoes from the location of the crater leads scientists to suspect that it may shelter large quantities of ice protected against sublimation into the near-vacuum by the constant −171 °C (−276 °F) temperatures.

The geology of Mercury is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mercury. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term geology is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography.

The Mare Australe quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Mare Australe quadrangle is also referred to as MC-30. The quadrangle covers all the area of Mars south of 65°, including the South polar ice cap, and its surrounding area. The quadrangle's name derives from an older name for a feature that is now called Planum Australe, a large plain surrounding the polar cap. The Mars polar lander crash landed in this region.

Almost all water on Mars today exists as ice, though it also exists in small quantities as vapor in the atmosphere. What was thought to be low-volume liquid brines in shallow Martian soil, also called recurrent slope lineae, may be grains of flowing sand and dust slipping downhill to make dark streaks. While most water ice is buried, it is exposed at the surface across several locations on Mars. In the mid-latitudes, it is exposed by impact craters, steep scarps and gullies. Additionally, water ice is also visible at the surface at the north polar ice cap. Abundant water ice is also present beneath the permanent carbon dioxide ice cap at the Martian south pole. More than 5 million km3 of ice have been detected at or near the surface of Mars, enough to cover the whole planet to a depth of 35 meters (115 ft). Even more ice might be locked away in the deep subsurface.
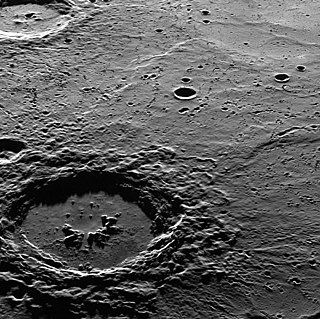
Hokusai is a rayed impact crater on Mercury, which was discovered in 1991 by ground-based radar observations conducted at Goldstone Observatory. The crater was initially known as feature B. Its appearance was so dissimilar to other impact craters that it was once thought to be a shield volcano. However improved radar images by the Arecibo Observatory obtained later in 2000–2005 clearly showed that feature B is an impact crater with an extensive ray system. The bright appearance of rays in the radio images indicates that the crater is geologically young; fresh impact ejecta has a rough surface, which leads to strong scattering of radio waves.

Debussy is a rayed impact crater on Mercury, which was discovered in 1969 by low resolution ground-based radar observations obtained by the Goldstone Observatory. Later in 1990–2005 it was imaged in more detail by the Arecibo Observatory. The crater was initially known as the feature A. The bright appearance of rays in the radar images indicates that the crater is geologically young, because fresh and rough surfaces of young impact craters are good scatterers of radio waves.

Despréz is a crater on Mercury with a diameter of 47.05 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1979. Despréz is named for the French composer Josquin des Prez, who lived from 1440 to 1521.

A permanently shadowed crater is a depression on a body in the Solar System within which lies a point that is always in darkness.
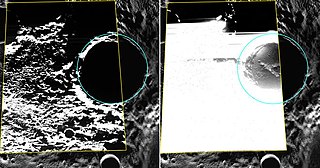
Kandinsky is a deep crater on Mercury, located near the planet's north pole. It was named by the IAU in 2012 for Russian painter Wassily Kandinsky.

Tolkien is one of the northernmost craters on Mercury, located in the Borealis quadrangle at 88.82 N, 211.08 W. It is 50 km in diameter. It was named after the South African born British writer J. R. R. Tolkien. The name was approved by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature on August 6, 2012. Since Tolkien is very close to the north pole, and Mercury has almost no axial tilt, Tolkien receives very little sunlight. S band radar data from the Arecibo Observatory collected between 1999 and 2005 indicates a radar-bright area covers the entire floor of Tolkien, which is probably indicative of a water ice deposit.

Vonnegut is a crater on Mercury, near the north pole. It was named by the IAU in 2017 after the American author Kurt Vonnegut. Part of Vonnegut's 1959 novel The Sirens of Titan takes place on Mercury. The crater was referred to as e5 in scientific literature prior to naming.

Yoshikawa is a crater on Mercury, near the north pole. It was named by the IAU in 2012 after the Japanese novelist Eiji Yoshikawa.

Tryggvadóttir is a crater on Mercury. The north pole of Mercury is located next to its northern rim. It was named by the IAU in 2012 after the Icelandic artist Nína Tryggvadóttir.

Chesterton is a crater on Mercury, near the north pole. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 2012, after the English author G. K. Chesterton.

Remarque is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on December 16, 2013. Remarque is named for the German author Erich Maria Remarque.

Morrison is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in September 2022. Morrison is named for the American author Toni Morrison, who lived from 1931 to 2019.





















