The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines the application programming interface (API), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility with variants of Unix and other operating systems.
The Single UNIX Specification (SUS) is the collective name of a family of standards for computer operating systems, compliance with which is required to qualify for using the "UNIX" trademark. The core specifications of the SUS are developed and maintained by the Austin Group, which is a joint working group of IEEE, ISO JTC 1 SC22 and The Open Group. If an operating system is submitted to The Open Group for certification, and passes conformance tests, then it is deemed to be compliant with a UNIX standard such as UNIX 98 or UNIX 03.
Yacc is a computer program for the Unix operating system developed by Stephen C. Johnson. It is a Look Ahead Left-to-Right (LALR) parser generator, generating a parser, the part of a compiler that tries to make syntactic sense of the source code, specifically a LALR parser, based on an analytic grammar written in a notation similar to Backus–Naur Form (BNF). Yacc is supplied as a standard utility on BSD and AT&T Unix. GNU-based Linux distributions include Bison, a forward-compatible Yacc replacement.

A man page is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system. Topics covered include computer programs, formal standards and conventions, and even abstract concepts. A user may invoke a man page by issuing the man command.
compress is a Unix shell compression program based on the LZW compression algorithm. Compared to more modern compression utilities such as gzip and bzip2, compress performs faster and with less memory usage, at the cost of a significantly lower compression ratio.

In Unix-like and some other operating systems, the pwd command writes the full pathname of the current working directory to the standard output.

uname is a computer program in Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that prints the name, version and other details about the current machine and the operating system running on it.
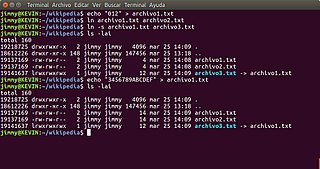
The ln command is a standard Unix command utility used to create a hard link or a symbolic link (symlink) to an existing file or directory. The use of a hard link allows multiple filenames to be associated with the same file since a hard link points to the inode of a given file, the data of which is stored on disk. On the other hand, symbolic links are special files that refer to other files by name.
The archiver, also known simply as ar, is a Unix utility that maintains groups of files as a single archive file. Today, ar is generally used only to create and update static library files that the link editor or linker uses and for generating .deb packages for the Debian family; it can be used to create archives for any purpose, but has been largely replaced by tar for purposes other than static libraries. An implementation of ar is included as one of the GNU Binutils.
In most Unix and Unix-like operating systems, the ps program displays the currently-running processes. A related Unix utility named top provides a real-time view of the running processes.

pax is an archiving utility created by POSIX, defined since 1995. Rather than sort out the incompatible options that have crept up between tar and cpio, along with their implementations across various versions of Unix, the IEEE designed a new archive utility that could support various archive formats with useful options from both archivers. The pax command is available on Unix and Unix-like operating systems and on IBM i, Microsoft Windows NT, and Windows 2000.
In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, iconv is a command-line program and a standardized application programming interface (API) used to convert between different character encodings. "It can convert from any of these encodings to any other, through Unicode conversion."
df is a standard Unix command used to display the amount of available disk space for file systems on which the invoking user has appropriate read access. df is typically implemented using the statfs or statvfs system calls.
nice is a program found on Unix and Unix-like operating systems such as Linux. It directly maps to a kernel call of the same name. nice is used to invoke a utility or shell script with a particular CPU priority, thus giving the process more or less CPU time than other processes. A niceness of -20 is the highest priority and 19 is the lowest priority. The default niceness for processes is inherited from its parent process and is usually 0.

In computing, more is a command to view the contents of a text file one screen at a time. It is available on Unix and Unix-like systems, DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS. Programs of this sort are called pagers. more is a very basic pager, originally allowing only forward navigation through a file, though newer implementations do allow for limited backward movement.
In computing, sleep is a command in Unix, Unix-like and other operating systems that suspends program execution for a specified time.
In Unix-like operating systems, true and false are commands whose only function is to always return with a predetermined exit status. Programmers and scripts often use the exit status of a command to assess success or failure (non-zero) of the command. The true and false commands represent the logical values of command success, because true returns 0, and false returns 1.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, development starting in the 1970s at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
most is a terminal pager program on Unix, OpenVMS, MS-DOS, Windows and Unix-like systems used to view the contents of a text file one screen at a time. Programs of this sort are called pagers. It is similar to more, but has the extended capability of allowing both forward and backward navigation through the file, and can scroll left and right. most also supports multiple windows.
The csplit command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems is a utility that is used to split a file into two or more smaller files determined by context lines.







