Related Research Articles

Morphine is a pain medication of the opiate family that is found naturally in a dark brown, resinous form, from the poppy plant. It can be taken orally or injected; it is also often smoked. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to increase feelings of pleasure and warm relaxation and to reduce pain, and is often abused for this purpose. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Morphine can be administered by mouth, by injection into a muscle, by injection under the skin, intravenously, injection into the space around the spinal cord, or rectally. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine are available as MS-Contin, Kadian, and other brand names as well as generically.

Hydromorphone, also known as dihydromorphinone, and sold under the brand name Dilaudid among others, is an opioid used to treat moderate to severe pain. Typically, long-term use is only recommended for pain due to cancer. It may be used by mouth or by injection into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. Effects generally begin within half an hour and last for up to five hours.

Desmethylprodine or 1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionoxypiperidine is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1940s by researchers at Hoffmann-La Roche. Desmethylprodine has been labeled by the DEA as a Schedule I drug in the United States. It is an analog of pethidine (meperidine) a Schedule II drug. Chemically, it is a reversed ester of pethidine which has about 70% of the potency of morphine. Unlike its derivative prodine, it was not reported to exhibit optical isomerism. It was reported to have 30 times the activity of pethidine and a greater analgesic effect than morphine in rats, and it was demonstrated to cause central nervous system stimulation in mice.

Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines, the prodines, bemidones and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues.

Levorphanol is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is one of two enantiomers of the compound racemorphan.

Dipropanoylmorphine is an opiate derivative, the 3,6-dipropanoyl ester of morphine. It was developed in 1972 as an analgesic. It is rarely used in some countries for the relief of severe pain such as that caused by terminal cancer, as an alternative to diamorphine (heroin) and morphine. The drug was first synthesised circa or about 1875 in Great Britain along with many other esters of morphine, all of which were shelved at the time, some of which were later developed such as heroin (1898), acetylpropionylmorphine (1923), dibenzoylmorphine, and so on. The name of this drug is also given as 3,6-dipropanoylmorphine and its 6-mono-acetylated homologue is also a longer-acting heroin-like drug, as are 3,6-diformylmorphine and 6-formylmorphine.

Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR4 gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system.
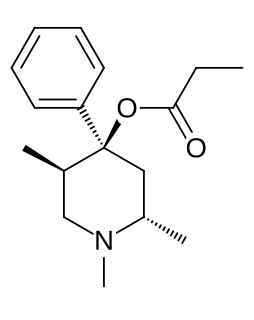
Trimeperidine (Promedol) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of prodine. It was developed in the early 1950s in the USSR during research into the related drug pethidine.

Pheneridine is a 4-Phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).

Sameridine is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).

Desomorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid commercialized by Roche, with powerful, fast-acting effects, such as sedation and analgesia. It was first discovered and patented by a German team working for Knoll in 1920 but was not generally recognized. It was later synthesized in 1932 by Lyndon Frederick Small. Small also successfully patented it in 1934 in the United States. Desomorphine was used in Switzerland under the brand name Permonid and was described as having a fast onset and a short duration of action, with relatively little nausea compared to equivalent doses of morphine. Dose-by-dose it is eight to ten times more potent than morphine.

Allylnorpethidine (WIN-7681) is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine).
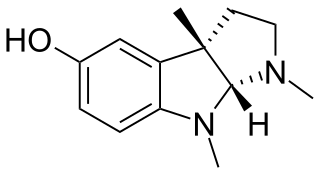
Eseroline is a drug which acts as an opioid agonist. It is a metabolite of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor physostigmine but unlike physostigmine, the acetylcholinesterase inhibition produced by eseroline is weak and easily reversible, and it produces fairly potent analgesic effects mediated through the μ-opioid receptor. This mixture of activities gives eseroline an unusual pharmacological profile, although its uses are limited by side effects such as respiratory depression and neurotoxicity.

3-( ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) is a research drug that was developed by Merck & Co. as a selective allosteric antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. Identified through structure-activity relationship studies on an older mGluR5 antagonist MPEP, MTEP has subsequently itself acted as a lead compound for newer and even more improved drugs.
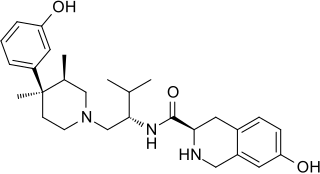
JDTic is a selective, long-acting ("inactivating") antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR). JDTic is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative, distantly related structurally to analgesics such as pethidine and ketobemidone, and more closely to the MOR antagonist alvimopan. In addition, it is structurally distinct from other KOR antagonists such as norbinaltorphimine. JDTic has been used to create crystal structures of KOR [ PDB: 4DJH, 6VI4].

Opiate is a term classically used in pharmacology to mean a substance derived from opium. Opioid, a more modern term, is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America.
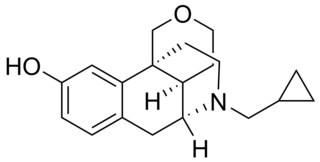
Proxorphan (INN), also known as proxorphan tartate (USAN), is an opioid analgesic and antitussive drug of the morphinan family that was never marketed. It acts preferentially as a κ-opioid receptor partial agonist and to a lesser extent as a μ-opioid receptor partial agonist.
Peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonists (PAMORAs) are a class of chemical compounds that are used to reverse adverse effects caused by opioids interacting with receptors outside the central nervous system (CNS), mainly those located in the gastrointestinal tract. PAMORAs are designed to specifically inhibit certain opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract and with limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Therefore, PAMORAs do not affect the analgesic effects of opioids within the central nervous system.

LS-115509 is an opioid analgesic related to the 4-phenylpiperidine family. It is comparable to drugs such as prodine and pheneridine, but is distinguished by the presence of an ether group and furan ring at the piperidine 4-position, which are not found in other drugs of this class. In animal studies, it has around 2-3x the potency of morphine depending on what assay is used. Like prodine, it has two stereocenters and four possible enantiomers, but the activity of these has not been tested separately.
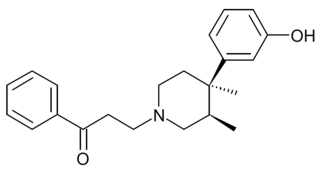
LY-88329 is an opioid receptor ligand related to medicines such as pethidine. It has high affinity to the μ-opioid receptor, but unlike structurally related drugs such as 3-methylfentanyl and OPPPP, LY-88329 is a potent opioid antagonist. In animal studies it blocks the effects of morphine and has anorectic action.
References
- ↑ Janssen, PA (April 1962). "A Review of the Chemical Features Associated with Strong Morphine-Like Activity". British Journal of Anaesthesia . 34 (4): 260–268. doi: 10.1093/bja/34.4.260 . PMID 14451235.