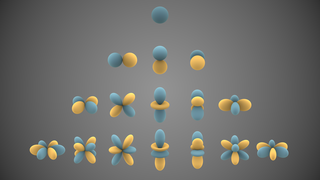In mathematical physics and mathematics, the Pauli matrices are a set of three 2 × 2 complex matrices which are Hermitian, involutory and unitary. Usually indicated by the Greek letter sigma, they are occasionally denoted by tau when used in connection with isospin symmetries.

In mathematics and physics, Laplace's equation is a second-order partial differential equation named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who first studied its properties. This is often written as

In mathematics, Legendre polynomials, named after Adrien-Marie Legendre (1782), are a system of complete and orthogonal polynomials with a vast number of mathematical properties and numerous applications. They can be defined in many ways, and the various definitions highlight different aspects as well as suggest generalizations and connections to different mathematical structures and physical and numerical applications.
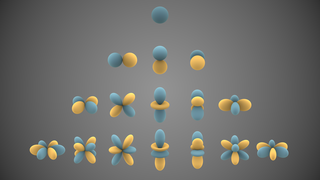
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields.

The Mie solution to Maxwell's equations describes the scattering of an electromagnetic plane wave by a homogeneous sphere. The solution takes the form of an infinite series of spherical multipole partial waves. It is named after Gustav Mie.

In quantum mechanics, a particle in a spherically symmetric potential is a system with a potential that depends only on the distance between the particle and a center. This is how isolated atoms are described, and plays a central role as a first approximation to the formation of chemical bonds.
In mathematics, the Helmholtz equation is the eigenvalue problem for the Laplace operator. It corresponds to the linear partial differential equation
A multipole expansion is a mathematical series representing a function that depends on angles—usually the two angles used in the spherical coordinate system for three-dimensional Euclidean space, . Similarly to Taylor series, multipole expansions are useful because oftentimes only the first few terms are needed to provide a good approximation of the original function. The function being expanded may be real- or complex-valued and is defined either on , or less often on for some other .
In mathematics, the Hankel transform expresses any given function f(r) as the weighted sum of an infinite number of Bessel functions of the first kind Jν(kr). The Bessel functions in the sum are all of the same order ν, but differ in a scaling factor k along the r axis. The necessary coefficient Fν of each Bessel function in the sum, as a function of the scaling factor k constitutes the transformed function. The Hankel transform is an integral transform and was first developed by the mathematician Hermann Hankel. It is also known as the Fourier–Bessel transform. Just as the Fourier transform for an infinite interval is related to the Fourier series over a finite interval, so the Hankel transform over an infinite interval is related to the Fourier–Bessel series over a finite interval.
The electromagnetic wave equation is a second-order partial differential equation that describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves through a medium or in a vacuum. It is a three-dimensional form of the wave equation. The homogeneous form of the equation, written in terms of either the electric field E or the magnetic field B, takes the form:
In physics, spherical multipole moments are the coefficients in a series expansion of a potential that varies inversely with the distance R to a source, i.e., as Examples of such potentials are the electric potential, the magnetic potential and the gravitational potential.
In physics, the Green's function for Laplace's equation in three variables is used to describe the response of a particular type of physical system to a point source. In particular, this Green's function arises in systems that can be described by Poisson's equation, a partial differential equation (PDE) of the form
In physics, the Laplace expansion of potentials that are directly proportional to the inverse of the distance, such as Newton's gravitational potential or Coulomb's electrostatic potential, expresses them in terms of the spherical Legendre polynomials. In quantum mechanical calculations on atoms the expansion is used in the evaluation of integrals of the inter-electronic repulsion.
In physics and mathematics, the solid harmonics are solutions of the Laplace equation in spherical polar coordinates, assumed to be (smooth) functions . There are two kinds: the regular solid harmonics, which are well-defined at the origin and the irregular solid harmonics, which are singular at the origin. Both sets of functions play an important role in potential theory, and are obtained by rescaling spherical harmonics appropriately:
In mathematics, vector spherical harmonics (VSH) are an extension of the scalar spherical harmonics for use with vector fields. The components of the VSH are complex-valued functions expressed in the spherical coordinate basis vectors.

In mathematics, a Coulomb wave function is a solution of the Coulomb wave equation, named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. They are used to describe the behavior of charged particles in a Coulomb potential and can be written in terms of confluent hypergeometric functions or Whittaker functions of imaginary argument.
In fluid dynamics, the Oseen equations describe the flow of a viscous and incompressible fluid at small Reynolds numbers, as formulated by Carl Wilhelm Oseen in 1910. Oseen flow is an improved description of these flows, as compared to Stokes flow, with the (partial) inclusion of convective acceleration.
Multipole radiation is a theoretical framework for the description of electromagnetic or gravitational radiation from time-dependent distributions of distant sources. These tools are applied to physical phenomena which occur at a variety of length scales - from gravitational waves due to galaxy collisions to gamma radiation resulting from nuclear decay. Multipole radiation is analyzed using similar multipole expansion techniques that describe fields from static sources, however there are important differences in the details of the analysis because multipole radiation fields behave quite differently from static fields. This article is primarily concerned with electromagnetic multipole radiation, although the treatment of gravitational waves is similar.
Partial-wave analysis, in the context of quantum mechanics, refers to a technique for solving scattering problems by decomposing each wave into its constituent angular-momentum components and solving using boundary conditions.
In pure and applied mathematics, quantum mechanics and computer graphics, a tensor operator generalizes the notion of operators which are scalars and vectors. A special class of these are spherical tensor operators which apply the notion of the spherical basis and spherical harmonics. The spherical basis closely relates to the description of angular momentum in quantum mechanics and spherical harmonic functions. The coordinate-free generalization of a tensor operator is known as a representation operator.