Related Research Articles

An oath of office is an oath or affirmation a person takes before assuming the duties of an office, usually a position in government or within a religious body, although such oaths are sometimes required of officers of other organizations. Such oaths are often required by the laws of the state, religious body, or other organization before the person may actually exercise the powers of the office or organization. It may be administered at an inauguration, coronation, enthronement, or other ceremony connected with the taking up of office itself, or it may be administered privately. In some cases it may be administered privately and then repeated during a public ceremony.

The Pledge of Allegiance is a patriotic recited verse that promises allegiance to the flag of the United States and the republic of the United States of America. The first version, with a text different from the one used at present, was written in 1885 by Captain George Thatcher Balch, a Union Army officer in the Civil War who later authored a book on how to teach patriotism to children in public schools. In 1892, Francis Bellamy revised Balch's verse as part of a magazine promotion surrounding the World's Columbian Exposition, which celebrated the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' arrival in the Americas. Bellamy, the circulation manager for The Youth's Companion magazine, helped persuade then-president Benjamin Harrison to institute Columbus Day as a national holiday and lobbied Congress for a national school celebration of the day. The magazine sent leaflets containing part of Bellamy's Pledge of Allegiance to schools across the country and on October 21, 1892, over 10,000 children recited the verse together.

"Lupang Hinirang", originally titled in Spanish as "Marcha Nacional Filipina", and commonly and informally known by its incipit "Bayang Magiliw", is the national anthem of the Philippines. Its music was composed in 1898 by Julián Felipe, and the lyrics were adopted from the Spanish poem "Filipinas", written by José Palma in 1899.

The coat of arms of the Philippines features the eight-rayed sun of the Philippines with each ray representing the eight provinces which were placed under martial law by Governor-General Ramón Blanco Sr. during the Philippine Revolution, and the three five-pointed stars representing the three major island groups of Luzon, the Visayas, and Mindanao.

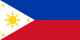
The national flag of the Philippines is a horizontal bicolor flag with equal bands of royal blue and crimson red, with a white, equilateral triangle at the hoist. In the center of the triangle is a golden-yellow sun with eight primary rays, each representing a province. At each vertex of the triangle is a five-pointed, golden-yellow star, each of which representing one of the country's three main island groups—Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The white triangle at the hoist represents liberty, equality, and fraternity. A unique feature of this flag is its usage to indicate a state of war if it is displayed with the red side on top, which is effectively achieved by flipping the flag upside-down.

The president of the Philippines is the head of state, head of government and chief executive of the Philippines. The president leads the executive branch of the Philippine government and is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Philippines.

The Boy Scouts of the Philippines (BSP) is the national scouting organization of the Philippines in the World Organization of the Scout Movement. The Scout movement was first introduced in the Philippines on 1910 during the American Occupation. It was "granted Recognition as a Member Organisation of the Boy Scouts International Conference...with effect from October 31, 1936" by virtue of certification signed by J. S. Wilson, Olave Baden-Powell, and Daniel Spry.
The Patriotic Oath is one of two national pledges of the Philippines, the other being the Pledge of Allegiance to the Flag. It is commonly recited at flag ceremonies of schools—especially public schools—immediately after singing the Philippine national anthem but before reciting the Pledge of Allegiance to the Flag.

The Aerospace Cadets of the Philippines or ACP program is a co-educational youth program oriented in aerospace technology, whose aim is to promote national enthusiasm in aviation among the youth and to train them to meet the requirements for leadership and civic service through aerospace education and military training.
The national symbols of the Philippines consist of symbols that represent Philippine traditions and ideals and convey the principles of sovereignty and national solidarity of the Filipino people. Some of these symbols namely the national flag, the Great Seal, the coat of arms and the national motto are stated in the Flag and Heraldic Code of the Philippines, which is also known as Republic Act 8491. In the Constitution of the Philippines, the Filipino language is stated as the national language of the Philippines. Aside from those stated symbols in the Constitution and in Republic Act 8491, there are only six official national symbols of the Philippines enacted through law, namely sampaguita as national flower, narra as national tree, the Philippine eagle as national bird, Philippine pearl as national gem, arnis as national martial art and sport and the Filipino Sign Language as the national sign language. Thus, there is a total of twelve official national symbols passed through Philippine laws.

The inauguration of the president of the Republic of the Philippines is a ceremony marking the commencement of the six-year term of a president of the Philippines, who is both head of state and head of government. The inauguration is performed on June 30, as mandated by the 1987 Constitution. Under the older 1935 Constitution, the date was December 30, which is also Rizal Day; the last inauguration held on the older date was Ferdinand Marcos' second one on December 30, 1969. The most recent public presidential inauguration ceremony was that of President Bongbong Marcos, who began his six-year term in office on Thursday, June 30, 2022.

The flag of the president of the Philippines or the presidential standard of the Philippines consists of the presidential coat of arms on a blue background. While having the same design as the presidential seal since 1947, the flag has a separate history, and the designs on the flag and seal have at different times influenced each other.
The Oath of Allegiance is an oath administered to and recited by immigrants who wish to accede to the citizenship of the Republic of the Philippines. The current oath, based on the United States Oath of Allegiance, was first enshrined in Commonwealth Act No. 473, the Revised Naturalization Law of 1939, with the modern version enshrined in Republic Act No. 9225, the Citizenship Retention and Re-acquisition Act of 2003.
Philippine Air Force Citizenship Advancement Training is a citizenship advancement training program in the Philippines. It is comparable to the Aerospace Cadets of the Philippines both are under the command hierarchy of the Philippine Air Force.

Maka-Diyos, Maka-tao, Makakalikasan at Makabansa is the national motto of the Philippines. Derived from the last four lines of the Pledge of Allegiance to the Philippine Flag, it was adopted on February 12, 1998 with the passage of Republic Act No. 8491, the Flag and Heraldic Code of the Philippines, during the presidency of Fidel V. Ramos. Its adoption came twelve years after the abolition of the country's previous motto, "Isang Bansa, Isang Diwa", which was adopted during the presidency of Ferdinand Marcos in 1979.

Isang Bansa, Isang Diwa was the national motto of the Philippines from 1978 to 1986, during the presidency of President Ferdinand Marcos. It was adopted on June 9, 1978 by virtue of Presidential Decree No. 1413. The motto has been criticized and has been denounced as "the slogan of a fascist regime".

The Independence Flagpole or the Philippine National Flagpole is a 45.72 m (150.0 ft) flagpole located near the Rizal Monument in Rizal Park in Manila, Philippines. It is the highest flagpole in the country.

The Great Seal of the Philippines is used to authenticate official documents of the government of the Philippines.

Ebralinag v Division Superintendent was a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the Philippines which established and tolerated freedom of religion. It involved 25 pupils from Asturias, Cebu and 43 pupils from the towns of Daanbantayan, Pinamungajan, Taburan and Carcar, Cebu, who are Jehovah's Witnesses, that were expelled for refusing to sing the national anthem and salute the flag and recite the patriotic pledge as required by Republic Act No. 1265 and Department Order No.8 of 1955. The Supreme Court ruling of this decision overturned Supreme Court's ruling of Gerona v Secretary of Education.
References
- ↑ "Executive Order No. 343, June 12, 1996" – via Supreme Court E-Library.
- 1 2 3 4 "Flag and Heraldic Code of the Philippines" – via Supreme Court E-Library.
- ↑ "Executive Order No. 343, s. 1996". Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines. 12 June 1996. Retrieved 15 October 2021.
- ↑ "Panunumpa sa Watawat". tagaloglang.com. ENGLISH TRANSLATION OF PLEDGE. Retrieved June 16, 2022.