Related Research Articles
The Geography of Pakistan is a profound blend of landscapes varying from plains to deserts, forests, and plateaus ranging from the coastal areas of the Indian Ocean in the south to the mountains of the Karakoram, Hindukush, Himalayas ranges in the north. Pakistan geologically overlaps both with the Indian and the Eurasian tectonic plates where its Sindh and Punjab provinces lie on the north-western corner of the Indian plate while Balochistan and most of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa lie within the Eurasian plate which mainly comprises the Iranian Plateau.


The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature spanning parts of West Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It makes up part of the Eurasian Plate, and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate. The plateau is situated between the Zagros Mountains to the west, the Caspian Sea and the Köpet Dag to the north, the Armenian Highlands and the Caucasus Mountains to the northwest, the Strait of Hormuz and the Persian Gulf to the south, and the Indian subcontinent to the east.
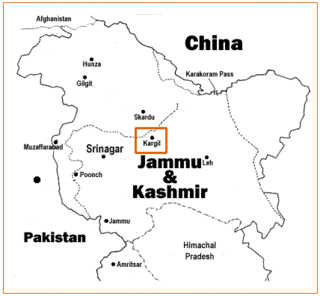
The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC). In India, the conflict is also referred to as Operation Vijay, which was the codename of the Indian military operation in the region. The Indian Air Force acted jointly with the Indian Army to flush out the Pakistan Army and paramilitary troops from vacated Indian positions along the LoC, in what was designated as Operation Safed Sagar.

The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas at about 35.421226°N 77.109540°E, just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. At 76 km (47 mi) long, it is the longest glacier in the Karakoram and second-longest in the world's non-polar areas. It falls from an altitude of 5,753 m (18,875 ft) above sea level at its head at Indira Col on the India–China border down to 3,620 m (11,875 ft) at its terminus. The entire Siachen Glacier, with all major passes, has been under the administration of India as part of the union territory of Ladakh, located in the Kashmir region since 1984. Pakistan maintains a territorial claim over the Siachen Glacier and controls the region west of Saltoro Ridge, lying west of the glacier, with Pakistani posts located 3,000 ft below more than 100 Indian posts on the ridge.

Captain Bana SinghPVC is an Indian soldier and a recipient of the nation's highest gallantry award, the Param Vir Chakra. As a Naib Subedar in the Indian Army, he led the team that wrested control of the highest peak on the Siachen Glacier in Kashmir from Pakistani forces as part of Operation Rajiv. Following his success, India renamed the peak to Bana Post in his honour.
The Battle of Dhalai was a battle fought between India and Pakistan before the formal start 1971 India-Pakistan War for the liberation of Bangladesh. The battle started after an attack by Indian army on Pakistani border outpost (BOP) in East Pakistan on 28 October and lasted until 3 November 1971. Three infantry battalions belonging to 61 Mountain Brigade, one battalion belonging to East Bengal Regiment and 7 Rajputana Rifles supported by an artillery sized brigade of Indian army fought against a battalion sized 12 Frontier Force of Pakistan army.

Operation Meghdoot was the codename for the Indian Armed Forces' operation to seize control of the Siachen Glacier in the then state of Jammu and Kashmir, precipitating the Siachen conflict. Executed in the morning of 13 April 1984 in the highest battlefield in the world, Meghdoot was the first military offensive of its kind. The operation preempted Pakistan's impending Operation Ababeel and was a success, resulting in Indian forces gaining control of the Siachen Glacier in its entirety.

The 2001–2002 India–Pakistan standoff was a military standoff between India and Pakistan that resulted in the massing of troops on both sides of the border and along the Line of Control (LoC) in the region of Kashmir. This was the second major military standoff between India and Pakistan following the successful detonation of nuclear devices by both countries in 1998, the first being the Kargil War of 1999.

The Siachen conflict, sometimes referred to as the Siachen Glacier conflict or the Siachen War, was a military conflict between India and Pakistan over the disputed 1,000-square-mile (2,600 km2) Siachen Glacier region in Kashmir. The conflict was started in 1984 by India's successful capture of the Siachen Glacier as part of Operation Meghdoot, and continued with Operation Rajiv in 1987. India took control of the 70-kilometre-long (43 mi) Siachen Glacier and its tributary glaciers, as well as all the main passes and heights of the Saltoro Ridge immediately west of the glacier, including Sia La, Bilafond La, and Gyong La. Pakistan controls the glacial valleys immediately west of the Saltoro Ridge. A cease-fire went into effect in 2003, but both sides maintain a heavy military presence in the area. The conflict has resulted in thousands of deaths, mostly due to natural hazards. External commentators have characterized it as pointless, given the perceived uselessness of the territory, and indicative of bitter stubbornness on both sides.
Skiwy Małe is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Siemiatycze, within Siemiatycze County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. It lies approximately 10 kilometres (6 mi) north-west of Siemiatycze and 76 km (47 mi) south of the regional capital Białystok.

The Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) divides current positions of Indian and Pakistani military posts and troops across the entire 110 kilometres (68 mi) long front line in the disputed region of Siachen Glacier. AGPL generally runs along the Saltoro Mountains range, beginning from the northernmost point of the (LOC) at Point NJ 9842 and ending in the north on the Indira Ridge at the India-China-Pakistan LAC tripoint near Sia Kangri about 4 km (2.5 mi) northwest of Indira Col West, with peaks in excess of 7,000 m (23,000 ft) and temperatures ranging to around −55 °C (−67 °F). India gained control of 1,000 square miles (2,600 km2) of disputed territory in 1984 because of its military operations in Siachen. A cease-fire was announced in 2003.
NJ9842, also called NJ 980420, is the northernmost demarcated point of the India-Pakistan cease fire line in Kashmir known as the Line of Control (LoC). The India–Pakistan AGPL, begins from the NJ9842 on LoC and ends near the Indira Ridge at the trijunction of areas controlled by China, India, and Pakistan.

Kuza Bandai is a well developed village in Swat Valley of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is known for its natural environment and also known as an area crossed by Alexander the Great. Later, after the Lal Masjid battle, Kuza Bandai and Bara Bandai became sympathetic to the Taliban movement. The village consists of Yusufzai Pakhtun tribes. It is one of Pakistan's Provincially Administered Tribal Areas (PATA).
Indira Col West is a mountain pass at 5,988 metres (19,646 ft)) altitude on the Indira Ridge of Siachen Muztagh in Karakoram Range. It is on the border between Indian-controlled Siachen Glacier and the Chinese-controlled Trans-Karakoram Tract, close to the tripoint of India, Pakistan, and China. The India-Pakistan Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) in the Siachen area ends near the pass. It is possible to ascend the pass from both the north and south sides controlled by China and India respectively.

Chorbat Valley is a section of the Shyok river valley divided between Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan and Indian-administered Ladakh. The Pakistan-administered portion is in the Khaplu tehsil of Ghanche District in Gilgit–Baltistan, and the Indian-administered portion is in the Nubra tehsil, Leh district of Ladakh. Chorbat stretches from the edge of Khaplu to the Chalunka village of Nubra.

The Kargil War Memorial, also known as Dras War Memorial, is a war memorial built by the Indian Army in the town of Dras, near Kargil city in Kargil district of Ladakh, India, commemorating the 1999 Kargil War between India and Pakistan. The memorial is located on the Srinagar-Leh National Highway 1D, about 5 km from the city centre across the Tiger Hill, Kargil.
Operation Rajiv was the codename for an Indian Army operation that aimed to capture a high point along the Actual Ground Position Line (AGPL) on the Siachen Glacier in June 1987. Prior to this operation, the area had been under the control of Pakistani forces, who had established a post on the peak, designated Quaid Post. Following India's successful capture of the peak, the post was renamed to Bana Top after Naib Subedar Bana Singh, who led the operation. Since Operation Rajiv in 1987, India continues to hold this post, which lies just to the south of the strategic Bilafond La mountain pass, also controlled by India. Alongside the higher-altitude installations, India has also established posts on the slopes at lower heights in this sector.
Point 5353 is a mountain peak on the Line of Control dividing the Indian- and Pakistani-administered portions of Kashmir in the vicinity of Dras in the Kargil district. It is the highest peak along the Marpo La ridge and dominates the entire area on both the sides of the Line of Control.
Yaldor Sub Sector was the scene of some of the major infiltration by Pakistani Northern Light Infantry battalions and some of the major battles of Kargil War were fought here.
References
- 1 2 "Pakistan still occupies key Drass point". www.thehindubusinessline.com.
- 1 2 3 Newslaundry. "Newslaundry – Sabki Dhulai".