
Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth using petroleum geology.

Reflection seismology is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite or Tovex blast, a specialized air gun or a seismic vibrator. Reflection seismology is similar to sonar and echolocation. This article is about surface seismic surveys; for vertical seismic profiles, see VSP.

In geophysics and reflection seismology, amplitude versus offset (AVO) or amplitude variation with offset is the general term for referring to the dependency of the seismic attribute, amplitude, with the distance between the source and receiver. AVO analysis is a technique that geophysicists can execute on seismic data to determine a rock's fluid content, porosity, density or seismic velocity, shear wave information, fluid indicators.

A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface pool of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Petroleum reservoirs are broadly classified as conventional and unconventional reservoirs. In conventional reservoirs, the naturally occurring hydrocarbons, such as crude oil or natural gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability, while in unconventional reservoirs, the rocks have high porosity and low permeability, which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in place, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using hydrocarbon exploration methods.
Petrophysics is the study of physical and chemical rock properties and their interactions with fluids.
A petroleum geologist is an earth scientist who works in the field of petroleum geology, which involves all aspects of oil discovery and production. Petroleum geologists are usually linked to the actual discovery of oil and the identification of possible oil deposits, gas caps, or leads. It can be a very labor-intensive task involving several different fields of science and elaborate equipment. Petroleum geologists look at the structural and sedimentary aspects of the stratum/strata to identify possible oil traps or tight shale plays.
Spontaneous potential log, commonly called the self potential log or SP log, is a passive measurement taken by oil industry well loggers to characterise rock formation properties. The log works by measuring small electric potentials between depths with in the borehole and a grounded electrode at the surface. Conductive bore hole fluids are necessary to create a SP response, so the SP log cannot be used in nonconductive drilling muds or air filled holes.

The Sarir Field was discovered in southern Cyrenaica during 1961 and is considered to be the largest oil field in Libya, with estimated oil reserves of 12 Gbbl (1.9 km3). Sarir is operated by the Arabian Gulf Oil Company (AGOCO), a subsidiary of the state-owned National Oil Corporation (NOC).
In petroleum geology, source rock is rock which has generated hydrocarbons or which could generate hydrocarbons. Source rocks are one of the necessary elements of a working petroleum system. They are organic-rich sediments that may have been deposited in a variety of environments including deep water marine, lacustrine and deltaic. Oil shale can be regarded as an organic-rich but immature source rock from which little or no oil has been generated and expelled. Subsurface source rock mapping methodologies make it possible to identify likely zones of petroleum occurrence in sedimentary basins as well as shale gas plays.
In geophysics, seismic inversion is the process of transforming seismic reflection data into a quantitative rock-property description of a reservoir. Seismic inversion may be pre- or post-stack, deterministic, random or geostatistical; it typically includes other reservoir measurements such as well logs and cores.
Heavy oil production is a developing technology for extracting heavy oil in industrial quantities. Estimated reserves of heavy oil are over 6 trillion barrels, three times that of conventional oil and gas.
A synthetic seismogram is the result of forward modelling the seismic response of an input earth model, which is defined in terms of 1D, 2D or 3D variations in physical properties. In hydrocarbon exploration this is used to provide a 'tie' between changes in rock properties in a borehole and seismic reflection data at the same location. It can also be used either to test possible interpretation models for 2D and 3D seismic data or to model the response of the predicted geology as an aid to planning a seismic reflection survey. In the processing of wide-angle reflection and refraction (WARR) data, synthetic seismograms are used to further constrain the results of seismic tomography. In earthquake seismology, synthetic seismograms are used either to match the predicted effects of a particular earthquake source fault model with observed seismometer records or to help constrain the Earth's velocity structure. Synthetic seismograms are generated using specialized geophysical software.

In the oil and gas industry, reservoir modeling involves the construction of a computer model of a petroleum reservoir, for the purposes of improving estimation of reserves and making decisions regarding the development of the field, predicting future production, placing additional wells, and evaluating alternative reservoir management scenarios.
In reflection seismology, a seismic attribute is a quantity extracted or derived from seismic data that can be analysed in order to enhance information that might be more subtle in a traditional seismic image, leading to a better geological or geophysical interpretation of the data. Examples of seismic attributes can include measured time, amplitude, frequency and attenuation, in addition to combinations of these. Most seismic attributes are post-stack, but those that use CMP gathers, such as amplitude versus offset (AVO), must be analysed pre-stack. They can be measured along a single seismic trace or across multiple traces within a defined window.
In reflection seismology, a bright spot is a local high amplitude seismic attribute anomaly that can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons and is therefore known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator. It is used by geophysicists in hydrocarbon exploration.
In reflection seismology, a dim spot is a local low amplitude seismic attribute anomaly that can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons and is therefore known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator. It primarily results from the decrease in acoustic impedance contrast when a hydrocarbon replaces the brine-saturated zone that underlies a shale, decreasing the reflection coefficient.

Hydraulic fracturing in the United Kingdom started in the late 1970s with fracturing of the conventional oil and gas fields near the North Sea. It has been used in about 200 British onshore oil and gas wells since the early 1980s. The technique did not attract attention until licences use were awarded for onshore shale gas exploration in 2008.
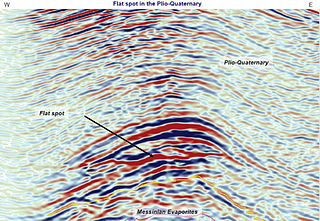
In reflection seismology, a flat spot is a seismic attribute anomaly that appears as a horizontal reflector cutting across the stratigraphy elsewhere present on the seismic image. Its appearance can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons. Therefore, it is known as a direct hydrocarbon indicator and is used by geophysicists in hydrocarbon exploration.
A hydrocarbon indicator (HCI) or direct hydrocarbon indicator (DHI), is an anomalous seismic attribute value or pattern that could be explained by the presence of hydrocarbons in an oil or gas reservoir.

Hydraulic fracturing in Canada was first used in Alberta in 1953 to extract hydrocarbons from the giant Pembina oil field, the biggest conventional oil field in Alberta, which would have produced very little oil without fracturing. Since then, over 170,000 oil and gas wells have been fractured in Western Canada. Hydraulic fracturing is a process that stimulates natural gas or oil in wellbores to flow more easily by subjecting hydrocarbon reservoirs to pressure through the injection of fluids or gas at depth causing the rock to fracture or to widen existing cracks. New hydrocarbon production areas have been opened as hydraulic fracturing stimulating techniques are coupled with more recent advances in horizontal drilling. Complex wells that are many hundreds or thousands of metres below ground are extended even further through drilling of horizontal or directional sections. Massive fracturing has been widely used in Alberta since the late 1970s to recover gas from low-permeability sandstones such as the Spirit River Formation. The productivity of wells in the Cardium, Duvernay, and Viking formations in Alberta, Bakken formation in Saskatchewan, Montney and Horn River formations in British Columbia would not be possible without hydraulic fracturing technology. Hydraulic fracturing has revitalized legacy oilfields. "Hydraulic fracturing of horizontal wells in unconventional shale, silt and tight sand reservoirs unlocks gas, oil and liquids production that until recently was not considered possible." Conventional oil production in Canada was on a decrease since about 2004 but this changed with the increased production from these formations using hydraulic fracturing. Hydraulic fracturing is one of the primary technologies employed to extract shale gas or tight gas from unconventional reservoirs.








