
BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties, and electrical insulation. A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other polyester films under different brand names. In the UK and US, the best-known trade names are Mylar, Melinex, Lumirror and Hostaphan.

Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins.

In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening ("curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, and is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent. Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network.
PCT, P.C.T. or pct may refer to:

Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT resists solvents, shrinks very little during forming, is mechanically strong, is heat-resistant up to 150 °C, and can be treated with flame retardants to make it noncombustible. It was developed by Britain's Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI).

A plasticizer is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.

Although PET is used in several applications,, as of 2022 only bottles are collected at a substantial scale. The main motivations have been either cost reduction or recycle content of retail goods. An increasing amount is recycled back into bottles, the rest goes into fibres, film, thermoformed packaging and strapping. After sorting, cleaning and grinding, 'bottle flake' is obtained, which is then processed by either:

Terephthalic acid is an organic compound with formula C6H4(CO2H)2. This white solid is a commodity chemical, used principally as a precursor to the polyester PET, used to make clothing and plastic bottles. Several million tons are produced annually. The common name is derived from the turpentine-producing tree Pistacia terebinthus and phthalic acid.
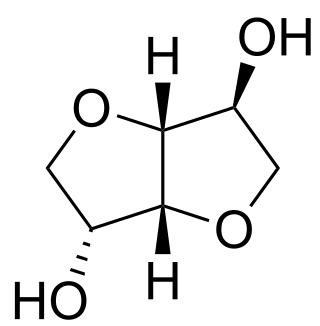
Isosorbide is a bicyclic chemical compound from the group of diols and the oxygen-containing heterocycles, containing two fused furan rings. The starting material for isosorbide is D-sorbitol, which is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of D-glucose, which is in turn produced by hydrolysis of starch. Isosorbide is discussed as a plant-based platform chemical from which biodegradable derivatives of various functionality can be obtained.

Polyethylene naphthalate is a polyester derived from naphthalene-2,6-dicarboxylic acid and ethylene glycol. As such it is related to poly(ethylene terephthalate), but with superior barrier properties.

Powder coating is a type of coating that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. Unlike conventional liquid paint which is delivered via an evaporating solvent, powder coating is typically applied electrostatically and then cured under heat or with ultraviolet light. The powder may be a thermoplastic or a thermoset polymer. It is usually used to create a hard finish that is tougher than conventional paint. Powder coating is mainly used for coating of metals, such as household appliances, aluminium extrusions, drum hardware, automobiles, and bicycle frames. Advancements in powder coating technology like UV-curable powder coatings allow for other materials such as plastics, composites, carbon fiber, and MDF to be powder coated due to the minimum heat and oven dwell time required to process these components.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in plants and insects, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. Synthetic polyesters are used extensively in clothing.

A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, and ink. The size ranges from very small bottles to large carboys. Consumer blow molded containers often have integral handles or are shaped to facilitate grasping.
PBAT is a biodegradable random copolymer, specifically a copolyester of adipic acid, 1,4-butanediol and terephthalic acid. PBAT is produced by many different manufacturers and may be known by the brand names ecoflex, Wango,Ecoworld, Eastar Bio, and Origo-Bi. It is also called poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and sometimes polybutyrate-adipate-terephthalate or even just "polybutyrate". It is generally marketed as a fully biodegradable alternative to low-density polyethylene, having many similar properties including flexibility and resilience, allowing it to be used for many similar uses such as plastic bags and wraps. It is depicted as a block co-polymer here due to the common synthetic method of first synthesizing two copolymer blocks and then combining them. However, it is important to note that the actual structure of the polymer is a random co-polymer of the blocks shown.
A thermoset polymer matrix is a synthetic polymer reinforcement where polymers act as binder or matrix to secure in place incorporated particulates, fibres or other reinforcements. They were first developed for structural applications, such as glass-reinforced plastic radar domes on aircraft and graphite-epoxy payload bay doors on the Space Shuttle.
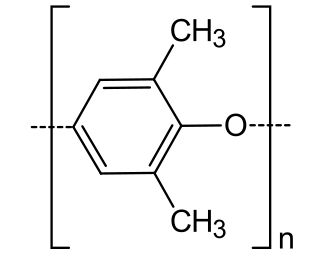
Poly(p-phenylene oxide) (PPO), poly(p-phenylene ether) (PPE), often referred to simply as polyphenylene oxide, is a high-temperature thermoplastic. It is rarely used in its pure form due to difficulties in processing. It is mainly used as blend with polystyrene, high impact styrene-butadiene copolymer or polyamide. PPO is a registered trademark of SABIC Innovative Plastics B.V. under which various polyphenylene ether resins are sold.

Cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM) is a mixture of isomeric organic compounds with formula C6H10(CH2OH)2. It is a colorless low-melting solid used in the production of polyester resins. Commercial samples consist of a mixture of cis and trans isomers. It is a di-substituted derivative of cyclohexane and is classified as a diol, meaning that it has two OH functional groups. Commercial CHDM typically has a cis/trans ratio of 30:70.

Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is a thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family. PBS is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester with properties that are comparable to polypropylene.

Aluminium diethyl phosphinate is a chemical compound with formula Al(C
4H
10O
2P)3. It decomposes above 300 °C.
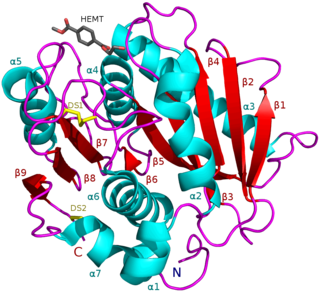
PETases are an esterase class of enzymes that catalyze the breakdown (via hydrolysis) of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic to monomeric mono-2-hydroxyethyl terephthalate (MHET). The idealized chemical reaction is:

















