
Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States, reckoned from the geographic center of the U.S.. In Oceania, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia.

Guam is a U.S. territory in the western Pacific Ocean, at the boundary of the Philippine Sea. It is the southernmost and largest member of the Mariana Islands archipelago, which is itself the northernmost group of islands in Micronesia. The closest political entity is the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), another U.S. territory. Guam shares maritime boundaries with CNMI to the north and the Federated States of Micronesia to the south. It is located approximately one quarter of the way from the Philippines to Hawaii. Its location and size make it strategically important. It is the only island with both a protected harbor and land for multiple airports between Asia and Hawaii, on an east–west axis, and between Papua New Guinea and Japan, on a north–south axis.

The United States territory of Guam has no railways or freeways, nor does it have a merchant marine. The largest port is Apra Harbor, which serves almost all commercial traffic including cruise, cargo and fishing vessels. There are smaller harbors located on the island which serve recreational boaters. Roads are primarily paved by a coral/oil mixture that, when it gets wet, tends to have oil float to the surface, making the roads dangerous. This is one of the reasons the speed limit on most of the island is 35 mph. But, during road repair or maintenance, a different mixture of asphalt that is not as slippery is used. Its main commercial airport is the Antonio B. Won Pat International Airport.

Hagåtña is the capital village of the United States territory of Guam. From the 18th through mid-20th century, it was Guam's population center, but today it is the second smallest of the island's 19 villages in both area and population. However, it remains one of the island's major commercial districts in addition to being the seat of government.

Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwater to the north and the Orote Peninsula in the south. Naval Base Guam and the Port of Guam are the two major users of the harbor. It is also a popular recreation area for boaters, surfers, scuba divers, and other recreationalists.

Edward David Taussig was a decorated Rear Admiral in the United States Navy. He is best remembered for being the officer to claim Wake Island after the Spanish–American War, as well as accepting the physical relinquishment of Guam by its Spanish governor following the Treaty of Paris in which Spain ceded Guam to the United States following nearly 300 years of colonial rule. Taussig briefly served as Governor of Guam. He was the first of a four-generational family of United States Naval Academy graduates including his son, Vice Admiral Joseph K. Taussig (1877–1947), grandson Captain Joseph K. Taussig Jr. (1920–1999), and great-grandson, Captain Joseph K. Taussig USMC (1945–).

The Capture of Guam was a bloodless engagement between the United States and Spain during the Spanish–American War. The U.S. Navy sent a single cruiser, USS Charleston, to capture the island of Guam, then under Spanish control. However, the Spanish garrison on the island had no knowledge of the war and no real ability to resist the American forces. They surrendered without resistance and the island passed into American control. The event was the only conflict of the Spanish–American War on Guam.

The Republican Party of Guam, commonly referred to as Guam GOP, is a political party in Guam affiliated with the United States Republican Party.

Hågat is a village in the United States territory of Guam. It is located south of Apra Harbor on the island's western shore. The village's population has decreased since the island's 2010 census.
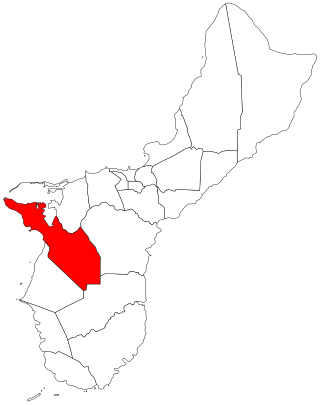
Sånta Rita-Sumai, formerly Santa Rita and encompassing the former municipality of Sumay, is a village located on the southwest coast of the United States territory of Guam with hills overlooking Apra Harbor. According to the 2020 census it has a population of 6,470, which is up slightly from 6,084 in 2010 but down from 11,857 in 1990. Santa Rita is the newest village in Guam, having been established after the Second World War.

Piti is a village located on the central west coast of the United States territory of Guam. It contains northern and eastern coastlines of Apra Harbor, including Cabras Island, which has the commercial Port of Guam and the island's largest power plants. Piti was a pre-Spanish CHamoru village and, after Spanish colonization, became the primary port town on Guam. The town was largely destroyed during the 1944 liberation of Guam and the population relocated during the wartime construction of Apra Harbor.

Humåtak is a village on the southwestern coast of the United States territory of Guam. The month of March in the Chamorro language is "Umatalaf," or "to catch guatafi," which is believed to be the root word of Umatac. The village's population has decreased since the island's 2010 census, and it is by far the least populated village on the island.
The Guam Department of Education (GDOE), formerly the Guam Public School System, is a school district that serves the United States territory of Guam. The school district can be thought of as analogous to the school districts of other cities and communities in the United States, but in some manners, it can also be thought of as analogous to the state education agencies of other states and territories.

Manuel Flores "Carson" Leon Guerrero was a Guamanian politician who is the sixth Appointed Governor of Guam from March 1963 to July 1969. He was appointed to the office after the term of Bill Daniel. He was a member of the Democratic Party of Guam and was the first of native Chamorro descent to rise to the highest office in the territory.

USS Lipan (AT-85) was a Navajo-class fleet tug constructed for the United States Navy during World War II. Her purpose was to aid ships, usually by towing, on the high seas or in combat or post-combat areas, plus "other duties as assigned." She served in the Pacific Ocean during World War II and the Korean War. She was awarded two battle stars for World War II and four battle stars for the Korean War.

Cabras Island was historically a low-lying finger of land off the coast of Piti, Guam that formed part of the northern protective arm of Apra Harbor. Shortly after the 1944 Battle of Guam it was connected by a causeway to the mainland and extended by the Glass Breakwater, and is now typically referred to simply as Cabras. Cabras houses both the Port of Guam and the primary Guam Power Authority generators supplying Guam. It lends its name to both a small vessel Cabras Marina, near the mainland, and the large vessel Cabras Channel, connecting the port to the deeper waters of the middle harbor.

Agat Bay is a bay on the west coast of Guam. Its northern boundary is the Orote Peninsula, occupied entirely by Naval Base Guam, which itself lies within the village of Sånta Rita-Sumai. The bay stretches south along the coast of the village of Hågat to Facpi Point. With a length of some seven kilometers, the bay stretches for nearly one fifth of the west coast of Guam. The Asan Invasion Beach of the 1944 Battle of Guam is commemorated by the Agat Unit of War in the Pacific National Historical Park, which spans surce and subsurface areas from Apaca Point to Bangi Point. The NRHP-listed Agat World War II Amtrac is submerged off Agat Cemetery.
José Sisto, also called José Sisto Rodrigo and José Sixto, was twice Governor of Guam, first after overthrowing Francisco Martínez Portusach, and again after being legitimately placed in the position by the United States government. He served as Spanish administrator of the Public Treasury in Guam until the United States captured the island during the Spanish–American War. When Martínez was named Commissioner, Sisto quickly staged a coup d'état and claimed the position as the highest ranking Spanish official on the island. He began arming native guards and commandeering ammunition, but was briefly overthrown by Venancio Roberto and other pro-American elements on December 31, 1898, but was officially put into power by officers of the United States Navy only two days later after they decided he held a legitimate claim to the position. His second term was brief, and he officially relinquished control on February 1, 1899 after learning that the United States had obtained Guam.

Guam, one of the external territories of the United States of America confirmed its first case of the COVID-19 pandemic on March 15, 2020, and the first death on March 22. The Government of Guam ordered the general lockdown of the island in mid-March. Governor Lou Leon Guerrero announced the implementation of a four-step "Pandemic Condition of Readiness" (PCOR) on April 30, 2020. Travelers to Guam from designated high-risk areas must provide a recent negative COVID-19 test or undergo mandatory quarantine in a government-approved facility. Guam moved from PCOR 1 to PCOR 2 on May 10, allowing some business activity with restrictions, and then to PCOR 3 on July 20. An outbreak in mid-August was not controlled for several months, resulting in the 7-day rolling test positivity rate to spike above 15% in early October 2020, as well as infections in both the Governor and Lieutenant Governor. Guam announced a return to the lockdown conditions of PCOR 1 on August 14 to control the outbreak, which was not loosened to PCOR 2 until January 15, 2021. It was further relaxed to PCOR 3 on February 21, 2021. From December 2020 to July 2021 cases stayed very low until a surge in August 2021 largely as a result of the delta variant. By October 2021, 90% of the population was vaccinated.

Sumay, also Sumai, was a village on the United States territory of Guam. It was located on the north coast of the Orote Peninsula along Apra Harbor. It was inhabited by Chamorro people before contact with Europeans. Sumay became a prosperous port town serving whalers and other sailors in the 1800s and the second most populous settlement on Guam after Hagåtña, the capital of the Spanish Mariana Islands. Following the Capture of Guam by the United States in 1898, the village was the site of Marine Barracks Guam. In the early 1900s, it was a link for two firsts connecting the United States and Asia: the first submarine communications cable for telegraph and the China Clipper, the first air service. After the Japanese invasion of Guam in 1941, the residents were evicted and the village turned into a Japanese military garrison. Sumay was leveled during the U.S. liberation of the island in 1944. The U.S. military prohibited the residents from returning, relocating them to the hills of nearby Sånta Rita-Sumai. In 1948, the U.S. military exercised eminent domain and took all private and commercial property at Sumay. Its former location is now on Naval Base Guam.



















