Microsoft Windows, commonly referred to as Windows, is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families, all of which are developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Microsoft Windows families include Windows NT and Windows IoT; these may encompass subfamilies,. Defunct Microsoft Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile and Windows Phone.

Windows Media Player (WMP) is a media player and media library application developed by Microsoft that is used for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is an operating system subfamily developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows Embedded family of products.

Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE) is a version of the Windows XP operating system which was the first version of Windows to include Windows Media Center, designed to serve as a home-entertainment hub. The last version, Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005 Update Rollup 2, was released on October 14, 2005. After that, Windows Media Center was included in certain editions of later Windows versions. It was an optional, paid addition to Windows 8 and then discontinued in Windows 10.
IRIVER is a South Korean consumer electronics brand operated by Dreamus. It markets music and other accessories in its domestic market. Internationally it was best known for its digital audio players and other portable media devices during the 2000s, when it was a competitor of the iPod from Apple. It was created in 1999 by seven former Samsung executives, releasing portable CD players.
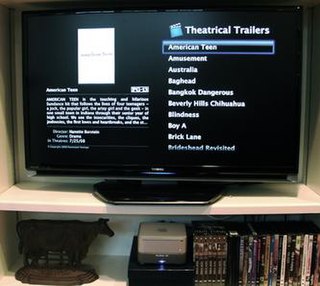
A home theater PC (HTPC) or media center computer is a convergent device that combines some or all the capabilities of a personal computer with a software application that supports video, photo, audio playback, and sometimes video recording functionality. In recent years, other types of consumer electronics, including game consoles and dedicated media devices, have crossed over to manage video and music content. The term "media center" also refers to specialized application software designed to run on standard personal computers.
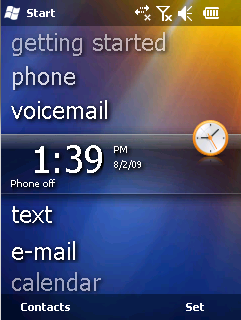
Windows Mobile is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.
Janus is the codename for a portable version of Windows Media DRM for portable devices, whose marketing name is Windows Media DRM for Portable Devices introduced by Microsoft in 2004 for use on portable media devices which store and access content offline. Napster To Go was the first online music store to require the Janus technology. Supporting Janus often implies that the device also make use of the Media Transfer Protocol (MTP).

Windows Media Center (WMC) is a defunct digital video recorder and media player created by Microsoft. Media Center was first introduced to Windows in 2002 on Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE). It was included in Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista, as well as all editions of Windows 7 except Starter and Home Basic. It was also available on Windows 8 Pro and Windows 8.1 Pro as a paid add-on, before being discontinued in Windows 10, although it can reportedly be unofficially reinstalled using a series of Command Prompt commands.

An ultra-mobile PC is a miniature version of a pen computer, a class of laptop whose specifications were launched by Microsoft and Intel in spring 2006. Sony had already made a first attempt in this direction in 2004 with its Vaio U series, which was only sold in Asia. UMPCs are generally smaller than subnotebooks, have a TFT display measuring (diagonally) about 12.7 to 17.8 centimetres, are operated like tablet PCs using a touchscreen or a stylus, and can also have a physical keyboard. There is no clear boundary between subnotebooks and ultra-mobile PCs, but UMPCs commonly have form factors other than the common clamshell laptop design, such as having small keys on either side of the screen, or having a slide-out keyboard.

Zune is a discontinued line of digital media products and services marketed by Microsoft from November 2006 until its discontinuation in June 2012. Zune consisted of a line of portable media players, digital media player software for Windows PCs, a music subscription service known as a "Zune Music Pass", music and video streaming services for the Xbox 360 game console via the Zune Software, music, TV and movie sales, and desktop sync software for Windows Phone. Zune was also the provider of music streaming for United Airlines in-flight, after a partnership in 2010.
The following comparison of portable media players compares general and technical information for notable digital playback devices.
Windows Media Center Extenders are devices that are configured to connect over a computer network to a computer running Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition, Windows Vista Home Premium/Ultimate, Windows 7 Home Premium, or Windows 8 with a Pro pack to stream the computer's media center functions to the Extender device. This allows use of the Media Center and its features on a television receiver or other electronic visual display.

Windows XP visual styles are customizations of the graphical user interface of Windows XP. "Luna", "Royale", "Zune", and "Embedded" are codenames of the official visual styles designed for Windows XP by Microsoft. Since Windows XP, themes include the choice of visual styles as well. By default, "Luna" is preinstalled on Windows XP Home and Professional editions, "Royale" is preinstalled on Windows XP Media Center Edition and "Embedded" is preinstalled on Windows Embedded Standard 2009 and Windows Embedded POSReady 2009. In addition to the preinstalled visual styles, Microsoft has released additional ones for download. Third parties have also released visual styles, though these require modification of core Windows components to work. Visual styles are compatible with all Windows XP editions except Starter Edition.
Zune is a discontinued media management software for Microsoft Windows that functions as a full media player application with a library, an interface to the Zune Marketplace, and as a media streaming server. The software is used to sync with all devices with Zune functionality including the Zune 4, 8, 16, 30, 80, 120, Zune HD, Windows Phone 7, and Microsoft Kin. Zune devices work exclusively with the Zune software, which applies many design principles of Microsoft's Metro design language.
Windows Vista—a major release of the Microsoft Windows operating system—was available in six different product editions: Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate. On September 5, 2006, Microsoft announced the USD pricing for editions available through retail channels; the operating system was later made available to retail on January 30, 2007. Microsoft also made Windows Vista available for purchase and download from Windows Marketplace; it is the first version of Windows to be distributed through a digital distribution platform. Editions sold at retail were available in both Full and Upgrade versions and later included Service Pack 1 (SP1).
Windows XP has been released in several editions since its original release in 2001.
The history of tablet computers and the associated special operating software is an example of pen computing technology, and thus the development of tablets has deep historical roots. The first patent for a system that recognized handwritten characters by analyzing the handwriting motion was granted in 1914. The first publicly demonstrated system using a tablet and handwriting recognition instead of a keyboard for working with a modern digital computer dates to 1956.

Microsoft Tablet PC is a term coined by Microsoft for tablet computers conforming to a set of specifications announced in 2001 by Microsoft, for a pen-enabled personal computer, conforming to hardware specifications devised by Microsoft and running a licensed copy of Windows XP Tablet PC Edition operating system or a derivative thereof.

Linaro is an engineering organization that works on free and open-source software such as the Linux kernel, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), power management, graphics and multimedia interfaces for the ARM family of instruction sets and implementations thereof as well as for the Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA). The company provides a collaborative engineering forum for companies to share engineering resource and funding to solve common problems on ARM software.








