The Altai Mountains, also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia and Eastern Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the Sayan Mountains in the northeast, and gradually becomes lower in the southeast, where it merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert. It spans from about 45° to 52° N and from about 84° to 99° E.

Bayan-Ölgii is the westernmost of the 21 aimags (provinces) of Mongolia. The country's only Muslim and Kazakh-majority aimag, it was established in August 1940. Its capital is Ölgii.

The Tawan Bogd is a mountain massif in Mongolia, near the triple border with China and Russia. Its highest peak, the Khüiten Peak, is the highest point of Mongolia at 4374 meters above sea level.
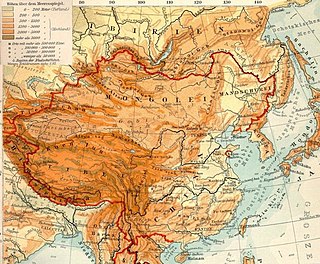
The Mongolian Plateau is an inland plateau in Asia that lies between 37°46′-53°08′N and 87°40′-122°15′E and has an area of approximately 3,200,000 square kilometres (1,200,000 sq mi). It is bounded by the Greater Hinggan Mountains in the east, the Yin Mountains to the south, the Altai Mountains to the west, and the Sayan and Khentii mountains to the north. The plateau includes the Gobi Desert as well as dry steppe regions. It has an elevation of roughly 1,000 to 1,500 meters, with the lowest point in Hulunbuir and the highest point in the Altai.

The retreat of glaciers since 1850 is well documented and is one of the effects of climate change. The retreat of mountain glaciers provide evidence for the rise in global temperatures since the late 19th century. Examples include mountain glaciers in western North America, Asia, the Alps in central Europe and tropical and subtropical regions of South America and Africa. Since glacial mass is affected by long-term climatic changes, e.g., precipitation, mean temperature, and cloud cover, glacial mass changes are one of the most sensitive indicators of climate change. Retreat of glaciers is also a major reason for sea level rise. Excluding peripheral glaciers of ice sheets, the total cumulated global glacial losses over the 26-year period from 1993 to 2018 were likely 5500 gigatons, or 210 gigatons per yr.

Khüiten Peak, also known in China as Friendship Peak, is a mountain peak in the Altai Range. The international border between China and Mongolia runs across its summit point, which, at 4,356 metres (14,291 ft), is the highest point in the Altais and the highest in both Mongolia and Altay Prefecture in Western China. The peak is covered in snow year-round.
South Central Siberia is a geographical region north of the point where Russia, China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia come together.

Altai Tavan Bogd National Park is a national park in Bayan-Ölgii Province of western Mongolia. The park includes the Mongolian side of the Tavan Bogd massif, which is divided by the triple border with Russia and China in the Altai Mountains.

The Rock Paintings of Tsagaan Salaa are located in western Mongolia. Site is inside Altai Tavan Bogd National Park and was approved as part of a larger Petroglyphic Complexes of the Mongolian Altai World Heritage Site along with The Upper Tsagaan Gol Complex in 2011.

Tavan Bogd Group is a Mongolian conglomerate with 14 subsidiaries and four affiliates in trades and services, manufacturing, financial services and mining supplies along with restaurant, tourism and hospitality businesses in Mongolia. Established in 1995, Tavan Bogd Group is one of the largest corporations in Mongolia, officially representing some of the world’s best-known brands such as Toyota, Hitachi Construction Machinery, Colgate-Palmolive, Toto, L'Occitane en Provence, KFC, Pizza Hut, Bridgestone, Heinz, Funai, Xerox and Double A. In addition, Tavan Bogd Group sells luxury cashmere products through Gobi Cashmere, which currently operates about 140 boutique stores in 40 countries.

Tsambagarav is a mountain between Khovd Province and Bayan-Ölgii Province in western Mongolia, it is a mountain of the Altai Mountains range. It has two peaks, its highest peak "Tsast Uul" has an elevation of 4,193 metres (13,757 ft) and another peak same named "Tsambagarav" (48.655196,90.847063). The mountain is the stand-alone eternally snow-capped mountain of the Mongol Altai and the regional sacred mountain in Mongolia.
Malchin Peak is the one of five peaks of the Tavan Bogd mountain on the Mongolia-Russian border. The Peak towers at the elevation of 4,050 m (13,287 ft). It is the only one of the five peaks of Tavan Bogd that can be climbed without specialized mountain climbing equipment.
Nairamdal Peak or Friendship Peak is the one of five peaks of the Tavan Bogd mountain and it marks the border tripoint between Russia, Mongolia, and China. The Peak towers at the elevation of 4,082 m (13,392 ft).

Khoton Lake is a freshwater lake in Altai Tavan Bogd National Park in Bayan-Ölgii Province, western Mongolia.

The wildlife of Mongolia consists of flora, fauna and funga found in the harsh habitats dictated by the diverse climatic conditions found throughout the country. In the north, there are salty marshes and fresh-water sources. The centre has desert steppes. In the south, there are semi deserts as well as the hot Gobi desert in the south, the fifth-largest desert in the world.
An earthquake occurred in southern Mongolia on December 4, 1957, measuring 7.8–8.1 and assigned XII (Extreme) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. Surface faulting was observed in the aftermath with peak vertical and horizontal scarp reaching 9 m (30 ft). Because of the extremely sparse population in the area, this event, despite its magnitude, was not catastrophic. However, 30 people died and the towns of Dzun Bogd, Bayan-leg and Baruin Bogd were completely destroyed.

The Altai alpine meadow and tundra ecoregion is a terrestrial ecoregion covering the higher elevation of the Altai Mountains at the center of the "X" formed by the borders separating Russia, Kazakhstan, China, and Mongolia. The mountain peaks are the farthest north in Central Asia, separating the plains of Siberia to the north from the hot, dry deserts to the south. Altitudes above 2,400 meters display characteristics of tundra, with patches of alpine meadows and some trees immediately below the treeline. The ecoregion is in the montane grasslands and shrublands biome, and the Palearctic realm, with a humid continental climate. It covers an area of 90,132 square kilometres (34,800 sq mi).

Khurgan Lake is a lake located in the district of Tsengel, in the Bayan-Ölgii Province of western Mongolia.

Dayan Lake is a lake located the district of Sagsai, in the Bayan-Ölgii Province of western Mongolia. It is recognized by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area since 2009. It is located in the Altai Tavan Bogd National Park.