
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery to end users or its storage, using for example, the pumped-storage method.
An energy crisis or energy shortage is any significant bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In literature, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, in particular, those that supply national electricity grids or those used as fuel in industrial development. Population growth has led to a surge in the global demand for energy in recent years. In the 2000s, this new demand – together with Middle East tension, the falling value of the US dollar, dwindling oil reserves, concerns over peak oil, and oil price speculation – triggered the 2000s energy crisis, which saw the price of oil reach an all-time high of $147.30 per barrel ($926/m3) in 2008.

Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include the production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse of energy that would otherwise be wasted. Energy conservation and efficiency measures reduce the demand for energy development, and can have benefits to society with improvements to environmental issues.

In economics, the Jevons paradox occurs when technological progress increases the efficiency with which a resource is used, but the falling cost of use induces increases in demand enough that resource use is increased, rather than reduced. Governments typically assume that efficiency gains will lower resource consumption, ignoring the possibility of the paradox arising.

Roger A. Pielke Jr. is an American political scientist and professor, and was the director of the Sports Governance Center within the Department of Athletics at the Center for Science and Technology Policy Research at the University of Colorado Boulder.

The Hype About Hydrogen: Fact and Fiction in the Race to Save the Climate is a book by Joseph J. Romm, published in 2004 by Island Press and updated in 2005. The book has been translated into German as Der Wasserstoff-Boom. Romm is an expert on clean energy, advanced vehicles, energy security, and greenhouse gas mitigation.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal, oil, or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.

The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy industry is a crucial part of the infrastructure and maintenance of society in almost all countries.

Robert Bryce is an American author and journalist based in Austin, Texas. His articles on energy, politics, and other topics have appeared in numerous publications, including the New York Times,Washington Post,Wall Street Journal,Forbes, Real Clear Energy,Counterpunch, and National Review.
An integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) is a technology using a high pressure gasifier to turn coal and other carbon based fuels into pressurized gas—synthesis gas (syngas). It can then remove impurities from the syngas prior to the electricity generation cycle. Some of these pollutants, such as sulfur, can be turned into re-usable byproducts through the Claus process. This results in lower emissions of sulfur dioxide, particulates, mercury, and in some cases carbon dioxide. With additional process equipment, a water-gas shift reaction can increase gasification efficiency and reduce carbon monoxide emissions by converting it to carbon dioxide. The resulting carbon dioxide from the shift reaction can be separated, compressed, and stored through sequestration. Excess heat from the primary combustion and syngas fired generation is then passed to a steam cycle, similar to a combined cycle gas turbine. This process results in improved thermodynamic efficiency, compared to conventional pulverized coal combustion.

United States energy independence is the concept of eliminating or substantially reducing import of petroleum to satisfy the nation's need for energy. Some proposals for achieving energy independence would permit imports from the neighboring nations of Canada and Mexico, in which case it would be called North American energy independence. Energy independence is espoused by those who want to leave the US unaffected by global energy supply disruptions and would restrict reliance upon politically unstable states for its energy security.

Energy independence is independence or autarky regarding energy resources, energy supply and/or energy generation by the energy industry.

Greenhouse Solutions with Sustainable Energy is a 2007 book by Australian academic Mark Diesendorf. The book puts forward a set of policies and strategies for implementing the most promising clean energy technologies by all spheres of government, business and community organisations. Greenhouse Solutions with Sustainable Energy suggests that a mix of efficient energy use, renewable energy sources and natural gas offers a clean and feasible energy future for Australia.

A gas-fired power plant, sometimes referred to as gas-fired power station, natural gas power plant, or methane gas power plant, is a thermal power station that burns natural gas to generate electricity. Gas-fired power plants generate almost a quarter of world electricity and are significant sources of greenhouse gas emissions. However, they can provide seasonal, dispatchable energy generation to compensate for variable renewable energy deficits, where hydropower or interconnectors are not available. In the early 2020s batteries became competitive with gas peaker plants.

Fossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels to zero, to reduce deaths and illness from air pollution, limit climate change, and strengthen energy independence. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition, but is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies.
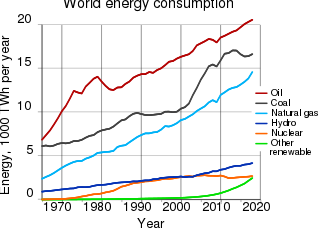
The environmental impact of the energy industry is significant, as energy and natural resource consumption are closely related. Producing, transporting, or consuming energy all have an environmental impact. Energy has been harnessed by human beings for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire for light, heat, cooking and for safety, and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources. Scientific consensus on some of the main human activities that contribute to global warming are considered to be increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, causing a warming effect, global changes to land surface, such as deforestation, for a warming effect, increasing concentrations of aerosols, mainly for a cooling effect.

Gusher of Lies: The Dangerous Delusions of Energy Independence is a book by Robert Bryce which was released in 2008 and is published by PublicAffairs.

Pipe Dreams: Greed, Ego, and the Death of Enron is a book by Robert Bryce and published in 2002 by PublicAffairs with an introduction by Molly Ivins.

The Hartwell Paper called for a reorientation of climate policy after the perceived failure in 2009 of the UNFCCC climate conference in Copenhagen. It was a response to the United Nations' Kyoto Protocol, a previous international agreement meant to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The paper was published in May 2010 by the London School of Economics in cooperation with the University of Oxford. The authors are 14 natural and social scientists from Asia, Europe and North America, including Mike Hulme, Roger A. Pielke (Jr), Nico Stehr and Steve Rayner, who met under the Chatham House Rule.


















