
This article is about transport in Belarus.

Polesia, Polissia, Polesie, or Polesye is a natural and historical region in Eastern Europe, including part of Eastern Poland, the Belarus–Ukraine border region.

Gomel Region, also known as Gomel Oblast or Homyel Voblasts, is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative center is Gomel.

The Dnieper, also called Dnipro, is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately 2,200 km (1,400 mi) long, with a drainage basin of 504,000 square kilometres (195,000 sq mi), it is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth-longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers.

The Pripyat or Prypiat is a river in Eastern Europe, approximately 761 km (473 mi) long. It flows east through Ukraine, Belarus, and Ukraine again, draining into the Dnieper.

Pripyat, also known as Prypiat, is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 1970 as the ninth atomgrad to serve the nearby Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, which is located in the adjacent ghost city of Chernobyl. Pripyat was officially proclaimed a city in 1979 and had grown to a population of 49,360 by the time it was evacuated on the afternoon of 27 April 1986, one day after the Chernobyl disaster.

Belovezhskaya Pushcha National Park is a national park within parts of the Brest Region and Grodno Region in Belarus adjacent to the Polish border. Since 1992 it is a preserved part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Białowieża Forest, the last primeval forest fragment of the European woodlands that once stretched across the European Plain. It is home to a large population of European bison, the continent's heaviest land animals. The border between the two countries runs through the forest with the Białowieża National Park on the Polish side of the border. Since May 2015 there has been a visa-free regime within the forest for hikers and cyclists at the Pierarova-Białowieża border crossing.

The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Zone of Alienation is an officially designated exclusion zone around the site of the Chernobyl nuclear reactor disaster. It is also commonly known as the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, the 30-Kilometre Zone, or The Zone.

The Pinsk Marshes, also known as the Pripet Marshes, the Polesie Marshes, and the Rokitno Marshes, are a vast natural region of wetlands in Polesia, along the forested basin of the Pripyat River and its tributaries from Brest to the west, Mogilev in the northeast, and Kyiv to the southeast. Most of the region is in Belarus, and part is in Ukraine. It is one of the largest wetland areas in Europe.

The Ptsich, or Pcič is a river in Eastern Europe. It flows south through Belarus, taking its source near Minsk, and draining into the Pripyat, being its left tributary. It is 421 kilometres (262 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 9,470 square kilometres (3,660 sq mi).
Oil shale in Belarus is a large, but undeveloped energy resource. While the reserves have been known for decades, they remain unexplored due to oil shale's high ash and sulphur content, low heat of combustion and high cost of extraction and processing. However, depletion of conventional petroleum and natural gas reserves, as well as a high degree of reliance on imported hydrocarbons from Russia, have recently renewed interest in oil shale exploration in the country.

The Belarusian-Ukrainian border is the state border between Belarus and Ukraine with a length of about 1,084 km (674 mi). It starts from the triple junction with Poland to the west and stretches to the triple junction with Russia to the east. The tripoint border at the triple border junction of Belarus, Russia and Ukraine is marked in the form of a monument, while at the other border junction there is a river, the Western Bug that coincides with the border of Poland.

The Polesie State Radioecological Reserve is a radioecological nature reserve in the Polesie region of Belarus, which was created to enclose the territory of Belarus most affected by radioactive fallout from the Chernobyl disaster. The reserve adjoins the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone in Ukraine. The environmental monitoring and countermeasure agency, Bellesrad, oversees the agriculture and forestry in the area.
The protected areas of Belarus are governed by the 1994 law "About the Protected Nature Areas". and its amendments.

The Chernihiv–Ovruch railway is a partially electrified and partially operational single track railway line that stretches between the town of Ovruch and the city of Chernihiv, in northern Ukraine, passing through southern Belarus and the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone. The line is owned by Ukrzaliznytsia alone, with railway stations located in Belarus being leased from the government of Belarus. A portion of the line between railway stations Vilcha and Semykhody has not been in service since the Chernobyl disaster, on 26 April 1986.
Aravichy is an abandoned village in Khoiniki District, Gomel Region, Belarus.
Dzernavichy or Dernovichi is an abandoned village in Narowlya District, Gomel Region, Belarus.

Prypiat-Stokhid National Nature Park was created in 2007 to protect and unify a series of natural complexes of the Pripyat River and Stokhid River valleys in northwestern Ukraine. The park provides protection, research areas, and recreation representative of the meadows and wetlands of the Polissia biosphere region. The park supports two Ramsar wetlands of international importance, and are joined in a cross-boundary Ramsar wetland with Belarus. The park is in the administrative district of Liubeshiv in Volyn Oblast.

Polissia Nature Reserve is a protected nature reserve of Ukraine dedicated to the conservation and scientific study of representative woodland marshes of the Pinsk Marshes in the Polissia region. The reserve is in the administrative districts of Olevsk and Ovruch in Zhytomyr Oblast
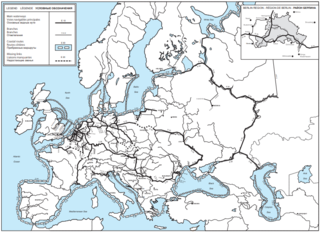
Waterway E40 is a planned navigable transport route that aims to connect the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea.

















