
The Workers' Party is a major centre-left political party in Singapore and is one of the three contemporary political parties represented in Parliament, alongside the governing People's Action Party (PAP) and opposition Progress Singapore Party (PSP). It is currently the largest opposition party in Parliament. It is also one of the two oldest parties active in the country, having contested every parliamentary election since 1959, the other being the PAP. The WP has been the only political party other than the PAP with elected Members of Parliament (MPs) since the 1991 general election.

Barisan Sosialis was a political party in Singapore. It was formed on 29 July 1961 and officially registered on 13 August 1961 by left-wing members of the People's Action Party (PAP) who had been expelled from the PAP. The prominent founding members of the Barisan were Lee Siew Choh and Lim Chin Siong. It became the biggest opposition party in Singapore in the 1960s and the 1980s.

The Democratic Progressive Party is an opposition political party in Singapore.
The Labour Front is a defunct political party in Singapore that operated from 1955 to 1960.

Lim Chin Siong was a Singaporean politician and union leader active in Singapore in the 1950s and 1960s. He was one of the founders of the governing People's Action Party (PAP), which has governed the country continuously since independence. Lim also used his popularity to galvanise many trade unions in support of the PAP.

Lim Yew Hock was a Singaporean-born Malaysian politician and diplomat who served as Chief Minister of Singapore between 1956 and 1959. He was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Cairnhill between 1959 and 1963 and previously a Member of the Legislative Council and later Legislative Assembly between 1948 and 1963. He was the 2nd de facto Leader of the Opposition between 1959 and 1963. He and his family elected to take up Malaysian citizenship after Singapore's independence from Malaysia.

The Central Provident Fund Board (CPFB), commonly known as the CPF Board or simply the Central Provident Fund (CPF), is a compulsory comprehensive savings and pension plan for working Singaporeans and permanent residents primarily to fund their retirement, healthcare, education and housing needs in Singapore.

The history of the modern state of Singapore dates back to its founding in the early 19th century; however, evidence suggests that a significant trading settlement existed on the island in the 14th century. The last ruler of the Kingdom of Singapura, Parameswara, was expelled by the Majapahit or the Siamese before he founded Malacca. Singapore then came under the Malacca Sultanate and subsequently the Johor Sultanate. In 1819, British statesman Stamford Raffles negotiated a treaty whereby Johor will allow the British to locate a trading port on the island, ultimately leading to the establishment of the Crown colony of Singapore in 1867. Important reasons for the rise of Singapore were its nodal position at the tip of the Malay Peninsula flanked by the Pacific and Indian Oceans, the presence of a natural sheltered harbour, as well as its status as a free port.

General elections were held in Singapore on 30 May 1959. They were held under the new constitution and were the first in which all 51 seats in the Legislative Assembly were filled by election. This was the first election victory for the People's Action Party (PAP), as they won a landslide victory with 43 seats. The party has remained in power ever since.
The Colony of Singapore was a Crown colony of the United Kingdom that encompassed what is modern-day Singapore from 1946 to 1958. During this period, Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands were also administered from Singapore. It was created after the dissolution of the Straits Settlements shortly after the Japanese occupation of Singapore ended in 1945. The power of the British Government was vested in the governor of Singapore. The colony eventually gained partial internal self-governance in 1955. It lasted until the establishment of the State of Singapore in 1958, with full internal self-governance granted in 1959.

The self-governance of Singapore was carried out in several stages. Since the founding of Singapore in 1819, Singapore had been under the colonial rule of the United Kingdom. The first local elections on a limited scale for several positions in the government of Singapore started in 1948 following an amendment to the Constitution of Singapore.

The Legislative Assembly of the State of Singapore was the legislature of the Government of Singapore from 1955 to 1965 and is the predecessor of the Parliament of Singapore. The Rendel Constitution, proposed in 1953, sought to give the local population more self-governance as the Merdeka independence movement grew. The Constitution took effect upon the conclusion of the 1955 general election, creating the new Legislative Assembly to replace the Legislative Council of Singapore. In contrast to the Legislative Council, the majority of seats in the Legislative Assembly in 1955 were allotted by election rather than appointment by the British colonial government. 25 seats were elected and 7 were appointed. The British colonial government still reserved significant power, such as that of veto and control of certain aspects of the government.

Howe Yoon Chong was a Singaporean politician and civil servant who served as Minister for Defence between 1979 and 1982, and Minister for Health between 1982 and 1985. A member of the governing People's Action Party (PAP), he was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Potong Pasir SMC between 1979 and 1984.
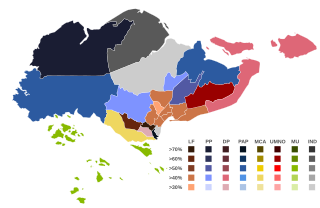
General elections were held in Singapore on 2 April 1955 to elect members to the 25 elected seats in the Legislative Assembly. Nomination day was on 28 February 1955.

General elections were held in Singapore on 22 December 1984. President Devan Nair dissolved parliament on 4 December 1984 on the advice of Prime Minister Lee Kuan Yew. The result was a victory for the People's Action Party, which won 77 of the 79 seats, marking the first time since 1963 that at least one opposition candidate was elected to parliament in a general election, although the first presence of an opposition MP was in the 1981 Anson by-election.

Foo Mee Har is a Malaysian-born Singaporean politician and businesswoman. A member of the governing People's Action Party (PAP), she has been the Member of Parliament (MP) representing the Ayer Rajah–Gek Poh division of West Coast GRC since 2011.
The National Trades Union Congress (NTUC) spearheads the labour movement of Singapore, which represents almost a million workers in the country across more than 70 unions, affiliated associations and related organisations. Singapore runs on a tripartism model which aims to offers competitive advantages for the country by promoting economic competitiveness, harmonious government-labour-management relations and the overall progress of the nation.
The following lists events that happened during 1955 in Singapore.

The reserves of the Government of Singapore is a collection of assets, after subtracting for liabilities, owned by the Government of Singapore and the entities listed in the fifth schedule of the Constitution, such as the Central Provident Fund (CPF), Housing and Development Board (HDB) and Temasek Holdings amongst others. This also includes the Official Foreign Reserves (OFR) accumulated by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and the assets managed by GIC Private Limited (GIC). Liabilities held by the Government include MAS-issued bonds such as Singapore Government Securities (SGS) and Government-issued Special Singapore Government Securities (SSGS) that are exclusively purchased by CPF with monies from CPF account holders.
















