
Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft from one star system, solitary star, or planetary system to another. Interstellar travel is expected to prove much more difficult than interplanetary spaceflight due to the vast difference in the scale of the involved distances. Whereas the distance between any two planets in the Solar System is less than 30 astronomical units (AU), stars are typically separated by hundreds of thousands of AU, causing these distances to typically be expressed instead in light-years. Because of the vastness of these distances, non-generational interstellar travel based on known physics would need to occur at a high percentage of the speed of light; even so, travel times would be long, at least decades and perhaps millennia or longer.
Beam-powered propulsion, also known as directed energy propulsion, is a class of aircraft or spacecraft propulsion that uses energy beamed to the spacecraft from a remote power plant to provide energy. The beam is typically either a microwave or a laser beam and it is either pulsed or continuous. A continuous beam lends itself to thermal rockets, photonic thrusters and light sails, whereas a pulsed beam lends itself to ablative thrusters and pulse detonation engines.

A fusion rocket is a theoretical design for a rocket driven by fusion propulsion that could provide efficient and sustained acceleration in space without the need to carry a large fuel supply. The design requires fusion power technology beyond current capabilities, and much larger and more complex rockets.

A starship, starcraft, or interstellar spacecraft is a theoretical spacecraft designed for traveling between planetary systems.

A generation ship, or generation starship, is a hypothetical type of interstellar ark starship that travels at sub-light speed. Since such a ship might require hundreds to thousands of years to reach nearby stars, the original occupants of a generation ship would grow old and die, leaving their descendants to continue traveling.
Starwisp is a hypothetical unmanned interstellar probe design proposed by the late Robert L. Forward. It is propelled by a microwave sail, similar to a solar sail in concept, but powered by microwaves from a human-made source. It would fly through the target system without slowing down.

Laser propulsion is a form of beam-powered propulsion where the energy source is a remote laser system and separate from the reaction mass. This form of propulsion differs from a conventional chemical rocket where both energy and reaction mass come from the solid or liquid propellants carried on board the vehicle.

Project Daedalus was a study conducted between 1973 and 1978 by the British Interplanetary Society to design a plausible uncrewed interstellar probe. Intended mainly as a scientific probe, the design criteria specified that the spacecraft had to use existing or near-future technology and had to be able to reach its destination within a human lifetime. Alan Bond led a team of scientists and engineers who proposed using a fusion rocket to reach Barnard's Star 5.9 light years away. The trip was estimated to take 50 years, but the design was required to be flexible enough that it could be sent to any other target star.
MagBeam is the name given to an ion propulsion system for space travel initially proposed by Professor Robert Winglee of the Earth and Space Sciences Department at the University of Washington for the October 2004 meeting of the NIAC. MagBeam is different from a traditional electrostatic ion thruster in several ways, the primary one being that instead of the fuel and propulsion system being part of the payload craft, they are instead located on a platform held in orbit. It has also been suggested that the technology could be used to reduce the amount of space debris in orbit around Earth.

An interstellar probe is a space probe that has left—or is expected to leave—the Solar System and enter interstellar space, which is typically defined as the region beyond the heliopause. It also refers to probes capable of reaching other star systems.

Jordin T. Kare was a physicist and aerospace engineer known for his research on laser propulsion. In particular, he was responsible for Mockingbird, a conceptual design for an extremely small reusable launch vehicle, and was involved in the Clementine lunar mapping mission. Kare was also known as developer of the Sailbeam interstellar propulsion concept and, in the science fiction fan community, as a composer, performer and recording artist of filk music.

Deep space exploration is the branch of astronomy, astronautics and space technology that is involved with exploring the distant regions of outer space. However, there is little consensus on the meaning of "distant" regions. In some contexts, it is used to refer to interstellar space. The International Telecommunication Union defines "deep space" to start at a distance of 2 million km from the Earth's surface. NASA's Deep Space Network has variously used criteria of 16,000 to 32,000 km from Earth. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights and by robotic spacecraft.
Project Icarus is a theoretical engineering design study aimed at designing a credible, mainly nuclear fusion-based, unmanned interstellar space probe. Project Icarus was an initiative of members of the British Interplanetary Society (BIS) and the Tau Zero Foundation (TZF) started in 2009. The project was under the stewardship of Icarus Interstellar until 2019. It remains a BIS project.
The Initiative for Interstellar Studies (i4is) is a UK-registered not-for-profit company, whose objectives are education and research into the challenges of Interstellar Travel. It pioneered small-scale laser sail interstellar probes and missions to interstellar objects. Several of its principals were involved in the 100 Year Starship winning team originated by NASA and DARPA.
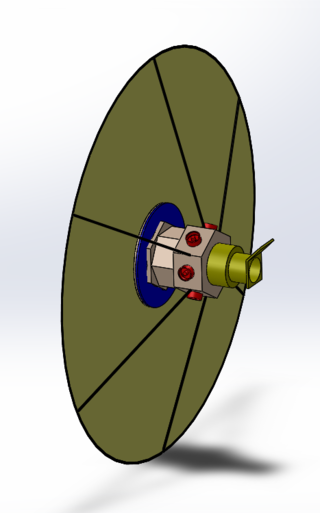
Project Dragonfly is the first conceptual design study that assesses the feasibility of a laser-propelled interstellar probe, conducted by the Initiative for Interstellar Studies. Contrary to past unmanned interstellar mission studies such as Project Daedalus and Project Icarus, the focus is particularly on a small spacecraft. The project was founded in 2013 by the Initiative for Interstellar Studies (i4is).
The Scientific Workgroup for Rocketry and Spaceflight (WARR) is a scientific workgroup situated at Technical University of Munich, composed mainly of its students. It was founded by students in 1962 with the goal to compensate for the lack of a chair for space technology at the university at the time. Since the establishment of such a chair in 1966, the group has conducted practical projects, starting with the first successful development and of a hybrid rocket in Germany. One rocket of this type was launched in 1972, another is on permanent display at Deutsches Museum. WARR has attained some public attention by for its projects in space elevator competitions, small satellites interstellar spaceflight concepts, and for winning all SpaceX Hyperloop pod competitions.

Breakthrough Starshot is a research and engineering project by the Breakthrough Initiatives to develop a proof-of-concept fleet of light sail interstellar probes named Starchip, to be capable of making the journey to the Alpha Centauri star system 4.37 light-years away. It was founded in 2016 by Yuri Milner, Stephen Hawking, and Mark Zuckerberg.

Project Hyperion, launched in December 2011 by Andreas M. Hein in the context of Icarus Interstellar. Project Hyperion was to perform a preliminary study that defines integrated concepts for a crewed interstellar starship or generation ship. This was a two-year study mainly based out of the WARR student group at the Technical University of Munich (TUM). The study aimed to provide an assessment of the feasibility of crewed interstellar flight using current and near-future technologies. It also aimed to guide future research and technology development plans as well as to inform the public about crewed interstellar travel.

Solar One is a proposed spacecraft that would combine beamed-powered propulsion, electromagnetic propulsion, and nuclear propulsion. The spacecraft would include a light sail, a laser system, a Bussard scoop, and a compact nuclear fusion reactor. Large mirrors would be assembled in orbit and sent close to the Sun to collect sufficient light to propel the light sail. The on board laser would help the Bussard scoop collect hydrogen to power the nuclear reactor which, in turn, would power both the laser and the electromagnetic scoop to decelerate the spacecraft. The main challenges are building large parabolic mirrors as well as reducing the weight of the on board laser system and compact nuclear reactor.
Adam Crowl is the former Director of Icarus Interstellar, an international non-profit organization that aims to achieve interstellar travel by 2100, as well as Team Leader for Project Icarus's Main Propulsion Module. Crowl is also a member on the Starship Congress Committee, a designer on the Project Forward Beamed Propulsion project, as well a designer on Project Tin Tin. In 2012, he proposed a mission for a spaceship that involves sending embryos into space to be raised by androids.












