Guadeloupe is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the two inhabited Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat and north of the Commonwealth of Dominica. The region's capital city is Basse-Terre, located on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; however, the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both located on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 378,561 in 2024.

Martinique is an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the eastern Caribbean Sea. A part of the French West Indies (Antilles), Martinique is an overseas department and region and a single territorial collectivity of the French Republic. It is also part of the European Union as an outermost region within the special territories of members of the European Economic Area, but is not part of the Schengen Area or the European Union Customs Union. The currency in use is the euro.

Mayotte, officially the Department of Mayotte, is an overseas department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is located in the northern part of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean off the coast of Southeastern Africa, between Northwestern Madagascar and Northeastern Mozambique. Mayotte consists of a main island, Grande-Terre, a smaller island, Petite-Terre, as well as several islets around these two. Mayotte is the most prosperous territory in the Mozambique Channel, making it a major destination for immigration.

France is divided into eighteen administrative regions, of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France, while the other five are overseas regions.

The French West Indies or French Antilles are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
The overseas departments and regions of France are departments of the French Republic which are outside the continental Europe situated portion of France, known as "metropolitan France". The distant parts have exactly the same status as mainland France's regions and departments. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations apply to French overseas regions the same as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas regions cannot themselves pass new laws. On occasion referendums are undertaken to re-assess the sentiment in local status.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship and elect the President of France.
The French overseas collectivities are first-order administrative divisions of France, like the French regions, but have a semi-autonomous status. The COMs include some former French overseas colonies and other French overseas entities with a particular status, all of which became COMs by constitutional reform on 28 March 2003. The COMs differ from overseas regions and overseas departments, which have the same status as metropolitan France but are located outside Europe. As integral parts of France, overseas collectivities are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council. Though some are outside the European Union, all can vote to elect members of the European Parliament (MEPs). The Pacific COMs use the CFP franc, a currency pegged to the euro, whereas the Atlantic COMs use the euro itself. As of 31 March 2011, there were five COMs:

The Mayotte national football team represents the French overseas department and region of Mayotte in international football.

Prostitution in France was legal until April 2016, but several surrounding activities were illegal, like operating a brothel, living off the avails (pimping), and paying for sex with someone under the age of 18.

The legal status of prostitution in Africa varies widely. It is frequently common in practice, partially driven by the widespread poverty in many sub-Saharan African countries, and is one of the drivers for the prevalence of AIDS in Africa. Senegal and Côte d'Ivoire permit the operations of brothels. In other countries, prostitution may be legal, but brothels are not allowed to operate. In some countries where prostitution is illegal, the law is rarely enforced.

Overseas France consists of 13 French-administered territories outside Europe, mostly the remains of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonization. Some, but not all, are part of the European Union. "Overseas France" is a collective name; while used in everyday life in France, it is not an administrative designation in its own right. Instead, the five overseas regions have exactly the same administrative status as the metropolitan regions; the five overseas collectivities are semi-autonomous; and New Caledonia is an autonomous territory. Overseas France includes island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans, French Guiana on the South American continent, and several peri-Antarctic islands as well as a claim in Antarctica. Excluding the district of Adélie Land, where French sovereignty is effective de jure by French law, but where the French exclusive claim on this part of Antarctica is frozen by the Antarctic Treaty, overseas France covers a land area of 120,396 km2 (46,485 sq mi) and accounts for 18.0% of the French Republic's land territory. Its exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 9,825,538 km2 (3,793,661 sq mi) accounts for 96.7% of the EEZ of the French Republic.
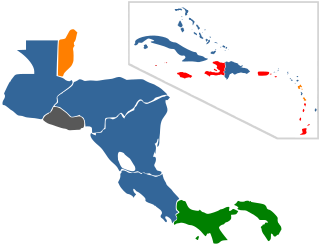
Legality of prostitution in the Americas varies by country. Most countries only legalized prostitution, with the act of exchanging money for sexual services legal. The level of enforcement varies by country. One country, the United States, is unique as legality of prostitution is not the responsibility of the federal government, but rather state, territorial, and federal district's responsibility.
The British Overseas Territories (BOT) or alternatively, United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are 14 territories under the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United Kingdom. They are the parts of the British Empire that have not been granted independence or have voted to remain British territories. These territories do not form part of the United Kingdom. Most of the inhabited territories are internally self-governing, with the UK retaining responsibility for defence and foreign relations. The rest are either uninhabited or have a transitory population of military or scientific personnel.

The Specialized Staff for Overseas and Foreign Affairs was historically dedicated to training the French Army in interculturality and was the maison mere (mother-parent) of the Troupes de marine. It is located at the Ecole militaire in Paris and at Fréjus.
The Coupe de France is a tournament in which all FFF affiliated teams can participate, including those from clubs from the overseas departments and territories. This is the list of overseas teams that played a match in the main competition.

Comorian nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of the Comoros, as amended; the Comorian Nationality Code, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of the Comoros. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Comorian nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in the Comoros, or jus sanguinis, born abroad to parents with Comorian nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalization. The country no longer allows for nationality to be acquired through investment.
The 2021–2022 French West Indies unrest is a social conflict that took place from November 17, 2021 until March 31, 2022 in the French West Indies, particularly in Guadeloupe and Martinique. Unrest has also been reported in other Overseas Territories like Saint Pierre and Miquelon.












