
Aralia spinosa, commonly known as devil's walking stick, is a woody species of plant in the genus Aralia, family Araliaceae, native to eastern North America. The various names refer to the viciously sharp, spiny stems, petioles, and even leaf midribs. It has also been known as Angelica-tree.

Chamaerops is a genus of flowering plants in the family Arecaceae. The only currently fully accepted species is Chamaerops humilis, variously called European fan palm or the Mediterranean dwarf palm. It is one of the most cold-hardy palms and is used in landscaping in temperate climates.

Rubus saxatilis, or stone bramble, is a species of bramble widespread across Europe and Asia from Iceland and Spain east as far as China. It has also been found in Greenland.

Cotyledon is a genus of succulent plants in the family Crassulaceae. Mostly from Southern Africa, they also occur throughout the drier parts of Africa as far north as the Arabian peninsula.

Vachellia nilotica is a flowering plant tree in the family Fabaceae. It is native to Africa, the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent. It is also a Weed of National Significance in Australia as well as a Federal Noxious Weed in the United States.

Polylepis is a genus comprising 28 recognised shrub and tree species, that are endemic to the mid- and high-elevation regions of the tropical Andes. This group is unique in the rose family in that it is predominantly wind-pollinated. They are usually gnarled in shape, but in certain areas some trees are 15–20 m tall and have 2 m-thick trunks. The foliage is evergreen, with dense small leaves, and often having large amounts of dead twigs hanging down from the underside of the canopy. The name Polylepis is, in fact, derived from the Greek words poly (many) plus letis (layers), referring to the shredding, multi-layered bark that is common to all species of the genus. The bark is thick and rough and densely layered for protection against low temperatures. Some species of Polylepis form woodlands growing well above normal tree line within grass and scrub associations at elevations over 5000 m; which makes Polylepis appear to be the highest naturally occurring arboraceous angiosperm genus in the world.

Senegalia laeta, the gay acacia or daga, is a legume found in the family Fabaceae. It was formerly included in the genus Acacia.

Phoenix reclinata, the wild date palm or Senegal date palm, is a species of flowering plant in the palm family native to tropical Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Madagascar and the Comoro Islands. It is also reportedly naturalized in Florida, Puerto Rico, Bermuda and the Leeward Islands. The plants are found from sea level to 3000 m, in rain forest clearings, monsoonal forests and rocky mountainsides.

Phoenix sylvestris also known as silver date palm, Indian date, sugar date palm or wild date palm, is a species of flowering plant in the palm family native to southern Pakistan, most of India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar and Bangladesh. It is also reportedly naturalized in Mauritius, the Chagos Archipelago, Puerto Rico and the Leeward Islands. Growing in plains and scrubland up to 1300 m above sea level, the fruit from this palm species is used to make wine and jelly. The sap is tapped and drunk fresh or fermented into toddy. The fresh sap is boiled to make palm jaggery in West Bengal state of India and Bangladesh.
Laccosperma is a clustering genus of flowering plant in the family palm found in tropical Africa. Poorly studied and rarely cultivated, they are closely related to the genus Eremospatha and with it form a tribe in the Calameae characterized by dyads of hermaphrodite flowers. The genus name combines the Greek words for "reservoir" and "seed".

Myrialepis is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the palm family, the single species, Myrialepis paradoxa, native to Southeast Asia. The genus name is a combination of the Greek words meaning "innumerable" and "scale", a description of the fruit, and the epithet is Latin for "paradox".

Hydrophyllum occidentale is a species of flowering plant in the waterleaf family known by the common name western waterleaf.

The genus, Pterolobium, consists of 10 species of perennial flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpinioideae and tribe Caesalpinieae. They are sometimes called redwings and are native to the tropical to subtropical climes of Africa and Asia, including Indonesia and the Philippines. They are large scrambling or climbing shrubs that grow in riverside thickets, on rocky slopes or at forest margins. They bear colourful samara fruit, and have pairs of thorns below the rachis of their bipinnate leaves.

Thalictrum alpinum is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family known by the common names alpine meadow-rue and arctic meadow-rue. It is native to Arctic and alpine regions of North America and Eurasia, including Alaska, northern Canada, and Greenland, and it occurs in cold, wet, boggy habitats in high mountains farther south.

Senna italica, the Port Royal senna, Italian senna, or Senegal senna is a legume tree in the genus Senna. It is recognized by many other common names based on the regions it grows in. In India, it is used to produce a powder for treating hair-related diseases which is known as “neutral henna”. Whereas, in some parts of the world, this species is cultivated for the leaves which yield the drug senna, known commonly as Senna glycoside, which in turn is the base for a laxative. Senegal senna is easily distinguishable through its many distinctive features. There are 3 subspecies of this plant based on the size of the inflorescence and the length of the petiole. The subspecies are italica, micrantha, and arachoides. In many regions, this plant is cultivated commercially and medicinally.

Pterolobium hexapetalum, the Indian redwing, camp siege or bhoca, is a flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is found from Burma, Bhutan and Bangladesh to southern India, where it occurs up to 1200 m altitude. They are large scrambling or climbing shrubs that grow commonly in dry deciduous forest, or as pioneer plants in open land.

Pterolobium microphyllum is a flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. They are perennial climbing shrubs that occur from Burma eastwards to Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Malaysia and Indonesia.
Pterolobium membranulaceum is a flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. The woody vine is endemic to secondary forest of the Philippines. Its general appearance is comparable to others of its genus, with bipinate leaves and rufous samara fruit. The pubescent petiole and leaf rachis vary between 10 and 21 cm in length. The leaves carry 5 to 10 pairs of pinnae, with 6 to 8 pairs of oblong leaflets per pinna. The pubescent and loosely flowered inflorescences are borne on the side or tips of branches.

Erythrina zeyheri, commonly known as the ploughbreaker, is a deciduous, geoxylic subshrub and member of the Fabaceae, which is endemic to southern Africa. It grows no more than 60 cm tall and occurs naturally in the higher altitude grasslands of South Africa's central plateau, and that of adjacent Lesotho. They favour deep clay soil in the vicinity of creeks and marshes, and often form colonies. Its specific name commemorates the 19th century botanist, Karl Zeyher.
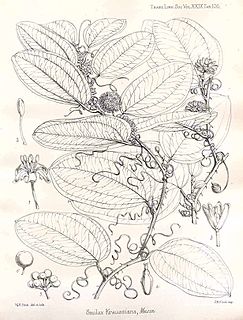
Smilax anceps is a vigorous scrambling vine or shrub, and is one of some 278 species in the genus Smilax in the family Smilacaceae. The species is widespread in Tropical Africa, Southern Africa, Réunion, Mauritius, Comoros, and Madagascar. The specific name 'anceps' is Latin for 'dangerous', a caution against the hooked prickles. Tarundia cinctipennis Stål, 1862, a hemipteran insect, is associated with this plant.





















