
The Furongian is the fourth and final epoch and series of the Cambrian. It lasted from 497 to 485.4 million years ago. It succeeds the Miaolingian series of the Cambrian and precedes the Lower Ordovician Tremadocian Stage. It is subdivided into three stages: the Paibian, Jiangshanian and the unnamed 10th stage of the Cambrian.
The Paibian is the lowest stage of the Furongian Series of the Cambrian System. The Paibian is also the first age of the Furongian Epoch of the Cambrian Period. It follows the Guzhangian and is succeeded by the Jiangshanian Stage. The base is defined as the first appearance of the trilobite Glyptagnostus reticulatus around 497 million years ago. The top, or the base of the Jiangshanian is defined as the first appearance of the trilobite Agnostotes orientalis around 494 million years ago.
Agnostus is a genus of agnostid trilobites, belonging to the family Agnostidae, that lived during the late Middle Cambrian – early Upper Cambrian. It is the type genus of the family Agnostidae and is subdivided into two subgenera, Agnostus and Homagnostus.
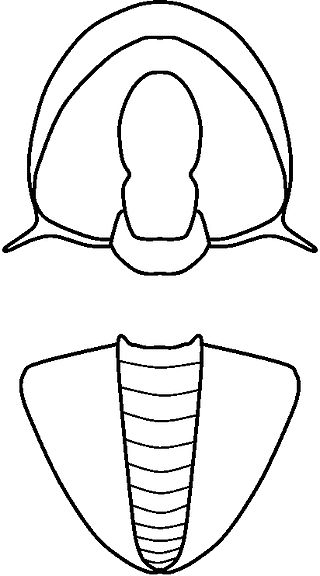
Acidiscus Rasetti, 1966, is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.
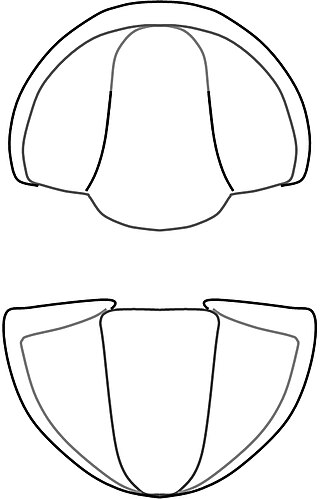
Cobboldites Kobayashi, 1943, is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.
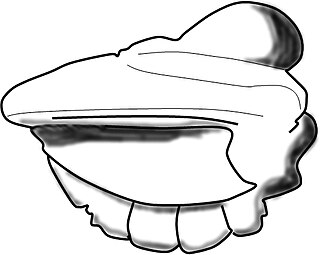
Chelediscus Rushton, 1966, is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). The Treatise assigns this genus to the Calodiscidae; Cotton and Fortey (2005) however move it to the Weymouthiidae. Chelediscus lived during the later part of the Botomian stage.
Peronopsis is a genus of trilobite restricted to the Middle Cambrian. Its remains have been found in Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.

Pagetia is a genus of small trilobite, assigned to the Eodiscinid family Pagetiidae and which had global distribution during the Middle Cambrian. The genus contains 55 currently recognized species, each with limited spatial and temporal ranges.
The Guzhangian is an uppermost stage of the Miaolingian Series of the Cambrian. It follows the Drumian Stage and precedes the Paibian Stage of the Furongian Series. The base is defined as the first appearance of the trilobite Lejopyge laevigata around 500.5 million years ago. The Guzhangian-Paibian boundary is marked by the first appearance of the trilobite Glyptagnostus reticulatus around 497 million years ago.

Ptychagnostus atavus is a species of agnostid trilobite. It was originally described by Swedish paleontologist Sven Axel Tullberg as Agnostus atavus in 1880. It is used in biostratigraphy as an index fossil. Its first appearance at the GSSP section in the Wheeler Shale of Utah is defined as the beginning of the Drumian Age of the Miaolingian.

Lejopyge laevigata is a species of agnostid trilobite belonging to the genus Lejopyge. It existed during the Guzhangian to the Paibian Age of the Cambrian. It has a cosmopolitan distribution and is an important index fossil in biostratigraphy.

The Miaolingian is the third Series of the Cambrian Period, and was formally named in 2018. It lasted from about 509 to 497 million years ago and is divided in ascending order into 3 stages: the Wuliuan, Drumian, and Guzhangian. The Miaolingian is preceded by the unnamed Cambrian Series 2 and succeeded by the Furongian series.

Glyptagnostus reticulatus is a species of agnostid trilobite belonging to the genus Glyptagnostus. It existed during the Paibian Age of the Cambrian. It has a cosmopolitan distribution and is an important index fossil in biostratigraphy. It was characterized by an unusual net-like pattern of furrows on both the cephalon and the pygidium.
Agnostotes orientalis is a species of agnostid trilobite belonging to the genus Agnostotes. It existed during the Jiangshanian Age of the Cambrian. It is an important index fossil in biostratigraphy.
Mallagnostus Howell, 1935, is a trilobite genus belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864) according to Whittington et al. 1997. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in USA, Canada (Newfoundland), Spain, England, Russia, Mongolia, and the early Middle Cambrian as reported from China and Russia (Yakutia).

The Peronopsidae comprise the earliest family of the Agnostina suborder. Species of this family occurred on all paleocontinents. The earliest representatives of this family first occur just before the start of the Middle Cambrian, and the last disappeared just after the start of the Upper Cambrian.

Pleuroctenium is an agnostid trilobite belonging to the family Condylopygidae Raymond (1913). The genus occurs in Middle Cambrian (Drumian) strata of Canada, the Czech Republic, England and Wales, France, and Sweden.

Condylopyge is a genus of agnostid trilobite that lived during the late Lower and early Middle Cambrian, in what are today Canada, the Czech Republic, England and Wales, France, Germany, Italy, Morocco, the Russian Federation, Spain, Turkey and Sweden. It can easily be distinguished from all other Agnostida because the frontal glabellar lobe is notably wider than the rear lobe. It belongs to the same family as Pleuroctenium but the frontal glabellar lobe does not fold around the rear lobe, as it does in that genus. Condylopyge is long ranging, possibly spanning the early Cambrian Terreneuvian Series in Nuneaton, central England into at least Drumian strata at various locations elsewhere.
The Calodiscidae Kobayashi, 1943 [nom. transl. Öpik, 1975 ex Calodiscinae Kobayashi, 1943] are a family of trilobites belonging to the order Agnostida that lived during the Lower Cambrian. They are small or very small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. The Calodiscidae includes five genera.

Genevievella is a genus of trilobites with a short inverted egg-shaped outline, a wide headshield, small eyes, and long genal spines. The backrim of the headshield is inflated and overhangs the first of the 9 thorax segments. The 8th thorax segment from the front bears a backward directed spine that reaches beyond the back end of the exoskeleton. It has an almost oval tailshield with 5 pairs of pleural furrows. It lived during the Upper Cambrian in what are today Canada and the United States.
















