In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as applied ontology.
MEDLINE is a bibliographic database of life sciences and biomedical information. It includes bibliographic information for articles from academic journals covering medicine, nursing, pharmacy, dentistry, veterinary medicine, and health care. MEDLINE also covers much of the literature in biology and biochemistry, as well as fields such as molecular evolution.
Text mining, text data mining (TDM) or text analytics is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extracting information from different written resources." Written resources may include websites, books, emails, reviews, and articles. High-quality information is typically obtained by devising patterns and trends by means such as statistical pattern learning. According to Hotho et al. (2005) we can distinguish between three different perspectives of text mining: information extraction, data mining, and a knowledge discovery in databases (KDD) process. Text mining usually involves the process of structuring the input text, deriving patterns within the structured data, and finally evaluation and interpretation of the output. 'High quality' in text mining usually refers to some combination of relevance, novelty, and interest. Typical text mining tasks include text categorization, text clustering, concept/entity extraction, production of granular taxonomies, sentiment analysis, document summarization, and entity relation modeling.

Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization, clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures.
PubMed is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintain the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval.

The Entrez Global Query Cross-Database Search System is a federated search engine, or web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website. The NCBI is a part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), which is itself a department of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which in turn is a part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The name "Entrez" was chosen to reflect the spirit of welcoming the public to search the content available from the NLM.
BRENDA is an information system representing one of the most comprehensive enzyme repositories. It is an electronic resource that comprises molecular and biochemical information on enzymes that have been classified by the IUBMB. Every classified enzyme is characterized with respect to its catalyzed biochemical reaction. Kinetic properties of the corresponding reactants are described in detail. BRENDA contains enzyme-specific data manually extracted from primary scientific literature and additional data derived from automatic information retrieval methods such as text mining. It provides a web-based user interface that allows a convenient and sophisticated access to the data.
Unstructured data is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically text-heavy, but may contain data such as dates, numbers, and facts as well. This results in irregularities and ambiguities that make it difficult to understand using traditional programs as compared to data stored in fielded form in databases or annotated in documents.
PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives open access full-text scholarly articles that have been published in biomedical and life sciences journals. As one of the major research databases developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), PubMed Central is more than a document repository. Submissions to PMC are indexed and formatted for enhanced metadata, medical ontology, and unique identifiers which enrich the XML structured data for each article. Content within PMC can be linked to other NCBI databases and accessed via Entrez search and retrieval systems, further enhancing the public's ability to discover, read and build upon its biomedical knowledge.

Information Hyperlinked over Proteins is an online text mining service that provides a gene-guided network to access PubMed abstracts. The service was established by Robert Hoffmann and Alfonso Valencia in 2004.
Biomedical text mining refers to the methods and study of how text mining may be applied to texts and literature of the biomedical domain. As a field of research, biomedical text mining incorporates ideas from natural language processing, bioinformatics, medical informatics and computational linguistics. The strategies in this field have been applied to the biomedical literature available through services such as PubMed.
Europe PubMed Central is an open-access repository which contains millions of biomedical research works. It was known as UK PubMed Central until 1 November 2012.
Integrative bioinformatics is a discipline of bioinformatics that focuses on problems of data integration for the life sciences.
The National Centre for Text Mining (NaCTeM) is a publicly funded text mining (TM) centre. It was established to provide support, advice and information on TM technologies and to disseminate information from the larger TM community, while also providing services and tools in response to the requirements of the United Kingdom academic community.

Co-occurrence network, sometimes referred to as a semantic network, is a method to analyze text that includes a graphic visualization of potential relationships between people, organizations, concepts, biological organisms like bacteria or other entities represented within written material. The generation and visualization of co-occurrence networks has become practical with the advent of electronically stored text compliant to text mining.
Biovista Inc. is a private drug development services company based in Charlottesville, Virginia, US. Biovista's core business activities include drug repositioning and drug de-risking as well as disease cohort analysis, adverse event prediction and clinical hold analysis services. Biovista is also applying its technology platform to develop its own drug repositioning programs in the areas of central nervous system (CNS), diabetes/obesity, eye disorders, and oncology.
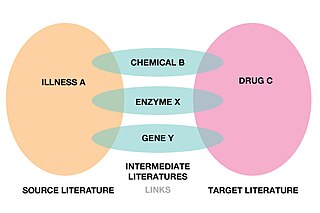
Literature-based discovery (LBD), also called literature-related discovery (LRD) is a form of knowledge extraction and automated hypothesis generation that uses papers and other academic publications to find new relationships between existing knowledge. Literature-based discovery aims to discover new knowledge by connecting information which have been explicitly stated in literature to deduce connections which have not been explicitly stated.
Anne O'Tate is a free, web-based application that analyses sets of records identified on PubMed, the bibliographic database of articles from over 5,500 biomedical journals worldwide. While PubMed has its own wide range of search options to identify sets of records relevant to a researchers query it lacks the ability to analyse these sets of records further, a process for which the terms text mining and drill down have been used. Anne O'Tate is able to perform such analysis and can process sets of up to 25,000 PubMed records.
Semantic Scholar is a research tool powered by artificial intelligence for scientific literature. It was developed at the Allen Institute for AI and publicly released in November 2015. It uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers. The Semantic Scholar team is actively researching the use of artificial intelligence in natural language processing, machine learning, human–computer interaction, and information retrieval.
Biocuration is the field of life sciences dedicated to organizing biomedical data, information and knowledge into structured formats, such as spreadsheets, tables and knowledge graphs. The biocuration of biomedical knowledge is made possible by the cooperative work of biocurators, software developers and bioinformaticians and is at the base of the work of biological databases.





