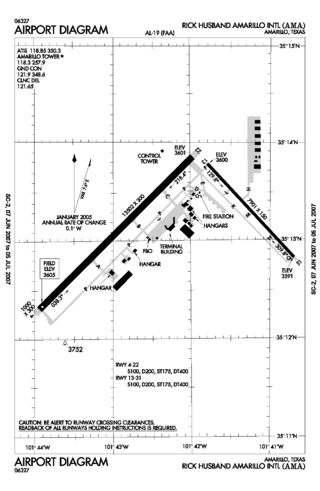
Historical airline service
Pueblo was initially a hub and crossroads for commercial airline traffic from the late 1920s through the 1970s. The first carrier to serve Pueblo was Colorado Airways which operated a north–south route from Cheyenne, WY to Pueblo with stops in Denver and Colorado Springs from 1926 through 1927. Western Air Express (WAE) acquired the route in 1927 and in 1929 the route was extended southward to El Paso, TX with stops in Trinidad, Las Vegas (NM), Santa Fe, and Albuquerque. This southward extension was initially operated by Mid-Continent Air Express but acquired by WAE in 1931. WAE also operated a route from Pueblo to Amarillo, TX from 1929 through 1934. [8] The first air carriers primarily focus was transporting mail and connecting with the transcontinental mainline routes of United Airlines at Cheyenne, with TWA at Albuquerque, and with American Airlines at El Paso. In 1934, the north–south route was divided between two new carriers, Wyoming Air Service, which operated the legs from Cheyenne to Pueblo, and Varney Speed Lines, which operated the legs from Pueblo to Albuquerque and El Paso. In 1937, Varney Speed Lines was changed to Continental Airlines and Continental then operated the route beginning in Denver and flying southward to El Paso. In 1939 Continental added an eastward extension from Pueblo to Wichita and later to Tulsa making stops in La Junta CO, Garden City, Dodge City, and Hutchinson, KS. Aircraft first used included the Lockheed Vega, Lockheed Model 12 Electra Junior, Lockheed Model 14 Super Electra, Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar, and the Douglas DC-3 by the mid-1940s. In the late 1940s Convair 240 aircraft were introduced followed by the Convair 340 and the Vickers Viscount in the 1950s. The eastbound route to Tulsa ended in 1961 and the north–south route ended in 1963 which ended all Continental service to Pueblo. [9]
Braniff Airways began service in 1943 on a route from Denver to Brownsville, TX with stops in Colorado Springs, Pueblo, Amarillo, Wichita Falls, Fort Worth, Dallas, Houston, and Corpus Christi. At times some flights operated from Pueblo to Amarillo, Oklahoma City, Tulsa, Little Rock, and Memphis. Douglas DC-3 aircraft were used and Braniff's service to Pueblo continued through 1952. [10]
Monarch Air Lines began service on November 27, 1946, with a route from Denver to Durango making stops in Colorado Springs, Pueblo, Canon City, and Monte Vista, CO using DC-3 aircraft. Monarch was merged with two other carriers to become Frontier Airlines on June 1, 1950. [11]
Frontier Airlines continued serving Pueblo with DC-3s and extended the route from Durango westward to Phoenix with several more stops in New Mexico and Arizona. A new route from Denver to Grand Junction was also started with stops in Pueblo, Gunnison, and Montrose, CO. Convair 340 aircraft were introduced in the late 1950s and upgraded to the Convair 580 by the mid-1960s. Frontier acquired the original north–south route from Denver to El Paso in 1963 previously operated by Continental Airlines. The direct flights to Phoenix ended in 1971 and the southward legs from Pueblo to Albuquerque and El Paso ended in 1974. A route from Pueblo to Amarillo, Oklahoma City, and Tulsa was also operated from 1967 through 1977. These flights would then continue onto Kansas City or to Memphis. Boeing 727-200 and 737-200 jets were flown from Pueblo to Colorado Springs and Denver from 1971 through 1981. These flights typically continued onto Kansas City and St. Louis. 737 jets were also flown to Durango, CO briefly in the late 1970s. All Frontier service at Pueblo ended on March 14, 1982. [12]
Central Airlines began serving Pueblo in 1961 with routes from Denver to Kansas City and Oklahoma City stopping in Pueblo and Amarillo as well as several more points in Colorado, Kansas, and Oklahoma. Douglas DC-3 aircraft were first used and upgraded to Convair 600s by the mid-1960s. Central Airlines was merged into Frontier Airlines in 1967 and Frontier continued operating these routes through the 1970s.
Air Midwest operated a late night mail route from Pueblo to Garden City and Dodge City, KS from 1967 through 1977 in which they occasionally transported passengers. A Beechcraft 99 aircraft was used.
Trans Central Airlines, a commuter airline, provided service along the north–south route from Denver to Albuquerque in 1968 through 1970. Stops were made at Pueblo, Trinidad, Raton, and Las Vegas (NM) and Cessna 402 aircraft were flown.
Pioneer Airlines took over service from Pueblo to Denver from 1982 through 1983 following the termination of service by Frontier. Swearingen Metroliner aircraft were used and service was also provided to Santa Fe, NM. [13]
Rocky Mountain Airways then provided service to Denver from 1983 through 1986 using de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter aircraft.
Mesa Airlines briefly served Pueblo in late 1987 with flights to Albuquerque using Beechcraft 99 and Beechcraft 1900C commuter aircraft.
America West Airlines operated Boeing 737-200 jet service from Pueblo to Phoenix and Las Vegas from 1985 through 1991. Many flights would stop in Colorado Springs.
Trans World Airlines (TWA) provided service to St. Louis with a stop in Colorado Springs from 1988 through 1992 using Boeing 727-200 and McDonnell Douglas MD-80 jets.
Continental Express, a feeder service for Continental Airlines reinstated Continental service to Pueblo in 1986 with flights to Denver. Rocky Mountain Airways first operated this service through 1991 then Britt Airways until 1994. In 1994 service was changed to Continental Connection operated by GP Express Airlines. GP Express also flew from Pueblo to Amarillo during this time. Most flights were flown with Beechcraft 1900C aircraft. All Continental service to Pueblo ended January 9, 1995. [14]
United Express, a feeder service for United Airlines began serving Pueblo in 1990 with flights to Denver. Mesa Airlines operated the service through 1998 then Great Lakes Airlines from 1998 until 2002. Both carriers used Beechcraft 1900D aircraft. [15]
Great Lakes Airlines then continued serving the Pueblo-Denver route under their own identity through 2004 then returned from 2006 through early 2014 using Beechcraft 1900D aircraft. Great Lakes returned once more from late 2015 through 2017 with flights to Denver using an Embraer EMB-120 Brasilia aircraft.
Mesa Airlines also returned to Pueblo and filled in the service to Denver from late 2004 through 2005 while Great Lakes stopped operating the route. Mesa also flew to Albuquerque during this time and continued to use Beechcraft 1900D aircraft.
Allegiant Air provided McDonnell Douglas MD-80 jet service to Las Vegas, Nevada from October, 2010 through April 8, 2012. Allegiant's flights operated twice per week.
United Express returned to service the Pueblo-Denver route in 2014. This service was operated by SkyWest Airlines using Embraer EMB-120 Brasilias and this service ended in mid-2015. United Express service returned in December 2017 and operated until January 2023 with CRJ-200 regional jets. [16]
Southern Airways Express currently operates the Pueblo-Denver route using Beechcraft Super King Air 200 turboprop aircraft.
Up until the mid-1990s, Pueblo was served by multiple airlines and for much of the year 1991, four airlines were operating at Pueblo simultaneously: America West, TWA, Continental Express, and United Express. Pueblo has also seen mainline jet service (727s, 737s, and MD-80s) by four airlines. Since 1995, however, service has only been provided by one airline with commuter or regional jet flights to Denver with the exception of the Allegiant Air service in 2010–2012. Pueblo falls under the Essential Air Service program in which the U. S. Government subsidizes an airline to provide air service to a city. This subsidy comes up for bid every two years; therefore, Pueblo has seen its air service provider frequently change. There have also been times where there has been no commercial air service to Pueblo, such as in the spring of 2014 and the summer and fall of 2015.