
The Strait of Magellan, also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. The strait is approximately 570 km long and 2 km wide at its narrowest point. In 1520, the Spanish expedition of the Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan, after whom the strait is named, became the first Europeans to discover it.
Southernmost settlements are cities, towns, weather stations or permanent military bases which are farther south than latitude 45°S. They are closely related to the Southern Ocean or either the Roaring Forties or Furious Fifties. Antarctic bases are excluded due to not having a permanent population.

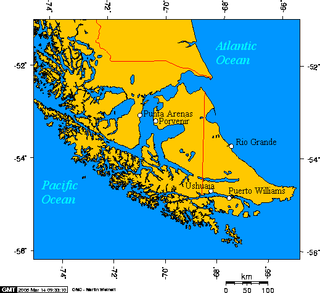
Porvenir is the capital of both the homonymous commune and the Chilean Province of Tierra del Fuego of the Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region. It is one of Chile's southernmost towns, and has 4,734 inhabitants, including several thousand soldiers. It is the largest settlement in the Chilean half of the island of Tierra del Fuego.

Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America, Cape Horn marks the northern boundary of the Drake Passage and marks where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans meet.

Cape Mendocino Light was a navigation light at Cape Mendocino, California. The former lighthouse was relocated to Shelter Cove near Point Delgada, California in 1998, and the historic Fresnel lens to Ferndale, California, in 1948. An automated beacon operated for a number of years but was removed in May 2013.

Punta Gorda Lighthouse is a lighthouse in the United States, 12 miles (19 km) south of Cape Mendocino, California, within Humboldt County. Access is via a short hike from the end of a 4WD road. It is managed by the Bureau of Land Management.

Chile has a large and intricate coastline of 4000 km with myriads of islands, islets, straits, bays, and fjords.

Punta Arenas is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. Although officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, the name was changed back to Punta Arenas in 1938. The city is the largest south of the 46th parallel south and the most populous southernmost city in Chile and the Americas. Due to its location, it is also the coldest coastal city with more than 100,000 inhabitants in Latin America. Punta Arenas is one of the world's most southerly ports and serves as an Antarctic gateway city.

Fuerte Bulnes is a Chilean fort located by the Strait of Magellan, 62 km south of Punta Arenas. It was founded in 1843 on a rocky hill at Punta Santa Ana, and named after President Manuel Bulnes Prieto.

Transbordadora Austral Broom S.A is a Chilean water transportation company.
Primera Angostura is a sound of the Strait of Magellan in the Chilean region of Magallanes. It is located near Punta Delgada.

Punta Dúngeness is a headland at the eastern entrance of the Strait of Magellan on its north shore, opposite Cabo del Espiritu Santo in Tierra del Fuego. West of the Punta Dungeness lies the Bahía Posesión. Punta Dungeness marks the border between Chile and Argentina, and according to the Treaty of Peace and Friendship the line between Punta Dungeness and Cabo del Espiritu Santo marks the limits of each country's territorial waters and the border between the Pacific and Atlantic Ocean. It is the southernmost point on the mainland of Argentina, and the easternmost point on the mainland of Chile. There is a lighthouse on the Chilean side. This is the only place where the Atlantic Ocean touches the shores on the mainland of Chile, at the entrance to the Strait of Magellan.

San Gregorio is a commune in the far south of Chile. It is part of Magallanes Region and Province, and is administered by the municipality of the same name located in Punta Delgada, the principal town in the commune.
Punta Delgada may refer to:

The Micalvi was an auxiliary vessel of the Chilean Navy.
Punta el Sombrerito, also known as Punta Sombrero, is a small hill overlooks the entrance to the Estero de Mulege and anchorage of the town of Mulege. It was described in 1851, as shaped as a hat or a pyramid on a round base like a fort. The hill now has a lighthouse at its apex, marking the entrance to the anchorage.

The Carranza Lighthouse, also known as Lighthouse Cabo Carranza, is an active 19th century Chilean lighthouse situated in the Maule Region. It is part of the network of lighthouses in Chile.

Punta Delgada or Alegranza Lighthouse is an active 19th century lighthouse on the Spanish island of Alegranza in the Canary islands. Alegranza lies to the north of the larger island of Lanzarote, it is part of the Chinijo Archipelago within the Teguise municipality.

















