Related Research Articles
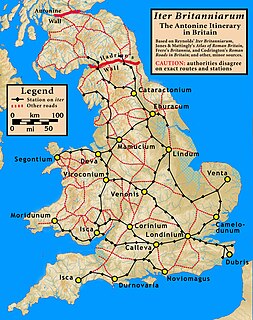
There are many Roman sites in Great Britain that are open to the public. There are also many sites that do not require special access, including Roman roads, and sites that have not been uncovered.

Camulodunum, the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important town in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. It is claimed to be the oldest town in Britain. Originally the site of the Brythonic-Celtic oppidum of Camulodunon, capital of the Trinovantes and later the Catuvellauni tribes, it was first mentioned by name on coinage minted by the chieftain Tasciovanus some time between 20 and 10 BC. The Roman town began life as a Roman legionary base constructed in the AD 40s on the site of the Brythonic-Celtic fortress following its conquest by the Emperor Claudius. After the early town was destroyed during the Iceni rebellion in AD 60/61, it was rebuilt, reaching its zenith in the 2nd and 3rd centuries. During this time it was known by its official name Colonia Claudia Victricensis, often shortened to Colonia Victricensis, and as Camulodunum, a Latinised version of its original Brythonic name. The town was home to a large classical temple, two theatres, several Romano-British temples, Britain's only known chariot circus, Britain's first town walls, several large cemeteries and over 50 known mosaics and tessellated pavements. It may have reached a population of 30,000 at its height. It was not until the late 18th century that historians realised that Colchester's physical Brythonic and Roman remains were the city mentioned in ancient literature as "Camulodunum".
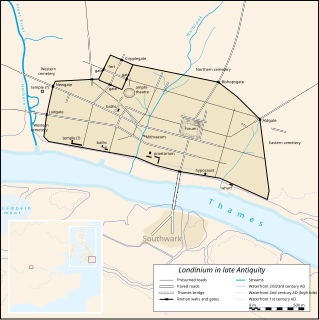
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. It was originally a settlement established on the current site of the City of London around AD 47–50. It sat at a key crossing point over the River Thames which turned the city into a road nexus and major port, serving as a major commercial centre in Roman Britain until its abandonment during the 5th century.

Colchester is a historic market town and the largest settlement within the borough of Colchester in the county of Essex. Colchester occupies the site of what was Camulodunum, the first major Roman city in, and sometime capital of, Roman Britain. Colchester lays claim to be Britain's oldest recorded town. Colchester has been a military garrison since the Roman era and is currently home to the 16th Air Assault Brigade.
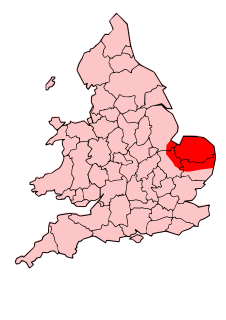
The Iceni or Eceni were a Brittonic tribe of eastern Britain during the Iron Age and early Roman era. Their territory included present-day Norfolk and parts of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, and bordered the area of the Corieltauvi to the west, and the Catuvellauni and Trinovantes to the south. In the Roman period, their capital was Venta Icenorum at modern-day Caistor St Edmund.

Roman roads in Britannia were initially designed for military use, created by the Roman Army during the nearly four centuries (AD 43–410) that Britannia was a province of the Roman Empire.
The title of oldest town in Britain is claimed by a number of settlements in Great Britain.

Fingringhoe is a village and civil parish in Essex, England located five miles south-east of Colchester. The centre of the village is classified as a conservation area featuring a traditional village pond and red telephone box. The Roman River flows nearby before entering the River Colne. It has frequently been noted on lists of unusual place names.

Caistor St Edmund is a village and former civil parish on the River Tas, now in the parish of Caistor St Edmund and Bixley, near Norwich, Norfolk, England. The parish covered an area of 6.55 square kilometres (2.53 sq mi) and had a population of 270 in 116 households at the 2001 census, the population increasing to 289 at the 2011 Census. On the 1st of April 2019 the parish was merged with Bixley to form Caistor St Edmund and Bixley.

The River Tas is a river which flows northwards through South Norfolk in England - towards Norwich. The area is named the Tas Valley after the river. The name of the river is back-formed from the name of village of Tasburgh.

Venta Icenorum was the civitas or capital of the Iceni tribe, located at modern-day Caistor St Edmund in the English county of Norfolk. The Iceni inhabited the flatlands and marshes of that county and are famous for having revolted against Roman rule under their queen Boudica in the winter of AD 61.
The A118 is a road in east London, England which links Bow Interchange with Gallows Corner in Romford via Stratford and Ilford. The section from Bow Interchange to Gallows Corner formed the original route of the A12 until the designation was transferred to the Eastern Avenue soon after the latter opened in 1925. Parts of the route have an even older pedigree, forming the Camulodunum (Colchester) to Londinium (London) extension of the Pye Road.

The A140 is an 'A-class' road in Norfolk and Suffolk, East Anglia, England partly following the route of the Roman Pye Road. It runs from the A14 near Needham Market to the A149 south of Cromer. It is of primary status for the entirety of its route. It is approximately 56 miles (90 km) in length.

Whitechapel Road is a major arterial road in Whitechapel, Tower Hamlets, in the East End of London. It is named after a small chapel of ease dedicated to St Mary and connects Aldgate to the west with Mile End Road to the east. The road is part of the historic Roman road from London to Colchester, now the A11.

The Battle of Camulodunum, also known as the Massacre of the Ninth Legion, was the major military victory of the Iceni and their allies over an organised Roman army during the revolt of Boudica against the Roman occupation of Britain. A large vexillation of the Legio IX Hispana were destroyed by the rebels. While attempting to relieve the besieged colonia of Camulodunum, legionaries of the Legio IX Hispana led by Quintus Petillius Cerialis, were attacked by a horde of British tribes, led by the Iceni. Possibly 80% of the Roman foot-soldiers were killed in the battle. The event is recorded by the historian Tacitus in his Annals.

Coddenham is a village and civil parish in the Mid Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located to the north of the A14 road, 8 miles north of Ipswich, the parish also includes the hamlet of Coddenham Green. In 2005 its population was 570, increasing to 620 at the 2011 Census. Village facilities include a community village shop & café, a country club offering themed evenings, darts, pool & snooker and the Coddenham Centre.

Gosfield is a village in the Braintree district of Essex, England. It is located around two miles west of the town of Halstead.
This is part of a series on the History of Norfolk

Caistor St Edmund Chalk Pit is a 23.6-hectare (58-acre) geological Site of Special Scientific Interest south of Norwich in Norfolk. It is a Geological Conservation Review site.
Sitomagus was a Roman Britain town in the province Flavia Caesariensis about 30 miles south of Venta Icenorum on the road to Londinium on route IX in the Antonine Itinerary, the location of which in Suffolk or Norfolk is uncertain.
References
- ↑ Hagger, Nicholas (2012). A View of Epping Forest. Alresford: CPI Group for O-Books. p. 24. ISBN 978-1-84694-587-8.
- ↑ "Ancient Landscape according to Tom Williamson". Archived from the original on 5 May 2005.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
- ↑ Chaffey, Gareth (2011). "Learning Legacy: Lessons Learned from the London 2012 Games construction project" (PDF). Olympic Delivery Authority. Retrieved 19 February 2015.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
Coordinates: 52°18′42″N1°06′13″E / 52.31173°N 1.10353°E