
A railcar is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach, with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles "railmotors".
The Armagh rail disaster happened on 12 June 1889 near Armagh, County Armagh, in Ireland, when a crowded Sunday school excursion train had to negotiate a steep incline; the steam locomotive was unable to complete the climb and the train stalled. The train crew decided to divide the train and take forward the front portion, leaving the rear portion on the running line. The rear portion was inadequately braked and ran back down the gradient, colliding with a following train.
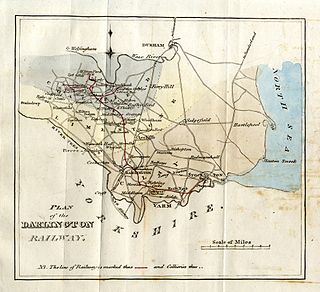
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.
The Locomotive Acts were a series of Acts of Parliament in the United Kingdom regulating the use of mechanically propelled vehicles on British public highways during the latter part of the 19th century.

A red flag could either be a literal red flag used for signaling or, as a metaphor, a sign of some particular problem requiring attention.

The Middleton Railway is the world's oldest continuously working railway, situated in the English city of Leeds. It was founded in 1758 and is now a heritage railway, run by volunteers from The Middleton Railway Trust Ltd. since 1960.

John Henry Knight, from Farnham, was a wealthy engineer, landowner and inventor. With the help of the engineer George Parfitt he built one of Britain's first petrol-powered motor vehicles, Frederick Bremer of Walthamstow having built the first in 1892. On 17 October 1895, with his assistant James Pullinger, they drove through Farnham, Surrey, whereupon he was prosecuted for using a locomotive with neither a licence nor a man walking in front with a red flag. This is sometimes misreported as the first person to be convicted of speeding in the UK, but that sobriquet subsequently fell to Walter Arnold of East Peckham, Kent, in January 1896.

The Highway Act 1835 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was one of the Highway Acts 1835 to 1885.

Nottingham and District Tramways Company Limited was a tramway operator from 1875 to 1897 based in Nottingham in the United Kingdom.

A horse-drawn vehicle is a piece of equipment pulled by one or more horses. These vehicles typically have two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have mostly been replaced by automobiles and other forms of self-propelled transport but are still in use today.

Taxicabs are regulated throughout the United Kingdom, but the regulation of taxicabs in London is especially rigorous with regard to mechanical integrity and driver knowledge. An official report observed that: "Little however is known about the regulation by anyone outside the trade. The Public Carriage Office (PCO), which regulates and licenses taxis and private hire was transferred from the Metropolitan Police to become part of Transport for London in 2000." In 2015, there were around 298,000 licensed drivers in England, of which 164,000 were private hire licences, 62,000 were taxi licences and 72,000 were dual licences.

Walter Hancock was an English inventor of the Victorian period. He is chiefly remembered for his steam-powered road vehicles, but also received a patent for preparing and cutting natural rubber into sheets. He was the younger brother of Thomas Hancock, the inventor of rubber mastication who is also claimed by some to be the inventor of rubber vulcanization.

A steam bus is a bus powered by a steam engine. Early steam-powered vehicles designed for carrying passengers were more usually known as steam carriages, although this term was sometimes used to describe other early experimental vehicles too.
Edward Butler (1862–1940) was an English inventor who produced an early three-wheeled petrol automobile called the Butler Petrol Cycle, which is accepted by many as the first British car.

The history of steam road vehicles comprises the development of vehicles powered by a steam engine for use on land and independent of rails, whether for conventional road use, such as the steam car and steam waggon, or for agricultural or heavy haulage work, such as the traction engine.

The Locomotives on Highways Act 1896 removed the strict rules and UK speed limits that were included in the earlier Locomotive Acts which had greatly restricted the adoption of motorised vehicles in the United Kingdom. It came into operation on 14 November 1896.
Causing bodily harm by wanton or furious driving is a statutory offence in England and Wales and Northern Ireland. It has been abolished in the Republic of Ireland.

Invalid carriages were usually single seater road vehicles, buggies, or self-propelled vehicles for disabled people. They pre-dated modern electric mobility scooters and, from the 1920s, were generally powered by small gasoline/petrol engines, although some were battery powered. They were usually designed without foot-operated controls.
The Railways Act, 1989 is an Act of the Parliament of India which regulates all aspects of rail transport. The Act came into force in 1989, replacing the Railways Act of 1890. The Act provides in detail the legislative provisions regarding railway zones, construction and maintenance of works, passenger and employee services.
Walter Charles Bersey was a British electrical engineer who developed electric-driven vehicles in the late 19th-century. He developed a new form of dry battery that enabled him to build, in 1888, an electric bus that he ran successfully for at least 3,000 miles (4,800 km). In March 1894 he built an electric parcel van that was used in central London and later developed electric private cars. Bersey also developed an electric cab design, 75 of which were built and used by the London Electrical Cab Company to run a service between 1897 and 1899. They were not financially successful owing to noise and vibration leading to excessive damage to tyres and batteries. In his later career Bersey developed designs for internal combustion engine cars and during the First World War served with the Royal Flying Corps and Royal Air Force.













