Redroofs is an unincorporated settlement in British Columbia, located south of Halfmoon Bay [1] on the Sunshine Coast.
Redroofs is an unincorporated settlement in British Columbia, located south of Halfmoon Bay [1] on the Sunshine Coast.

The Greenbelt is a 203.5-square-kilometre (78.6 sq mi) protected green belt traversing Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It includes green space, forests, farms, and wetlands from Shirleys Bay in the west and to Green's Creek in the east. The National Capital Commission (NCC) owns and manages 149.5 square kilometres (57.7 sq mi), and the rest is held by other federal government departments and private interests. Real estate development within the Greenbelt is strictly controlled.
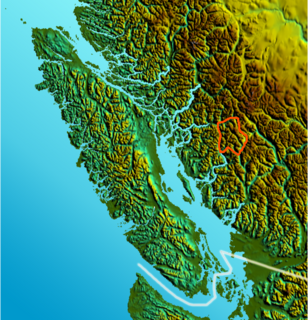
The Clendinning Range is a subrange of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia. About 1500 km2 in area and lies to the northwest of the better-known Tantalus Range near Squamish. Heavily glaciated and very rugged, with severe weather year-round, it is between the valleys of the Elaho River (east) and the Toba River (west).
Gold Muchalat Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located between the Gold and Muchalat Rivers.

Nuchatlitz Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located no the northwest side of Nootka Island, facing Nuchatlitz Inlet, on the west coast of Vancouver Island. Established in 1996, the park contains approximately 2105 ha.
Todagin South Slope Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located on the west side of Todagin Creek to the east of Kinaskan Lake in the Stikine Country, to the south of the community of Dease Lake. Created in 2001, it contains c. 3557 ha.
There are several lakes named Mud Lake within the Canadian province of Saskatchewan.
The Squamish Nation, Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw in Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Sníchim, is an Indian Act government originally imposed on the Squamish (Sḵwx̱wú7mesh) by the Federal Government of Canada in the late 19th century. The Squamish are Indigenous to British Columbia, Canada. Their band government comprises 16 elected councillors, serving four-year terms, with an elected band manager. Their main reserves are near the town of Squamish, British Columbia and around the mouths of the Capilano River, Mosquito Creek, and Seymour River on the north shore of Burrard Inlet in North Vancouver, British Columbia.

The Gwa'Sala-Nakwaxda'xw Nations are a union of two Kwakwaka'wakw peoples in a band government based on northern Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada, whose main reserve community is near the town of Port Hardy in the Queen Charlotte Strait region of the Central Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. The band government is a member of the Kwakiutl District Council and, for treaty negotiation purposes, the Winalagalis Treaty Group which includes three other members of the Kwakiutl District Council.
Woodlands is a part of the District of North Vancouver in British Columbia, Canada. It was first settled after the Second Boer War. The community is located at the foot of Mount Seymour on Indian Arm, itself a branch of Burrard Inlet, which forms Vancouver's harbour. It is about 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) from Downtown Vancouver.

Census Division No. 9 is part of the Central Plains Region of the Province of Manitoba, Canada. The major service centre of the area is the City of Portage la Prairie. The economic base of the area is agriculture, food processing and manufacturing. The population of the area as of the 2016 census was 24,391. Also included in the division are the Dakota Plains First Nation and the largest portion of the Long Plain First Nation.
The Pemberton Valley is a valley flanking the Lillooet River upstream from Lillooet Lake, including the communities of Mount Currie, Pemberton, British Columbia and the agricultural district surrounding them and flanking the river as far upstream as the Pemberton Meadows area. The term is normally used only to refer to inhabited parts of the valley, not the unsettled areas to the north of Pemberton Meadows although the official definition extends from the head of Lillooet Lake all the way up to the confluence of Meager Creek. Historically the region was part of the Lillooet Country but due to re-orientation of the area's economy and society since the opening and expansion of BC Highway 99 the area is now more considered to be part of the Sea-to-Sky Corridor.
Klootch Canyon, originally Klootchman Canyon, is a canyon on the Skeena River in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, south of the community of Cedarvale.

Fimbulheimen is a mountain range in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It stretches from Jutulstraumen by 1° west of Carsten Borchgrevink Ice at 18° east, about 200 km from the ice edge. Fimbulheimen is thus between Maudheim Plateau and Sør-Rondane.

The Rocky Mountain Foothills are an upland area flanking the eastern side of the Rocky Mountains, extending south from the Liard River into Alberta. Bordering the Interior Plains system, they are part of the Rocky Mountain System or Eastern System of the Western Cordillera of North America.
The Tlowitsis Nation, formerly the Klowitsis Tribe, the Turnour Island Band and the Tlowitsis-Mumtagila First Nation, is the Indian Act band government of the Ławit'sis (Tlowitsis) tribe of the Kwakwaka'wakw peoples, located in the Queen Charlotte Strait-Johnstone Strait area in the Discovery Islands between Vancouver Island and the British Columbia mainland in Canada. Ławit'sis territory covers parts of northern Vancouver Island, Johnstone Strait, and adjoining inlets of the mainland. Kalugwis, on Turnour Island, was their principal community in times past, but the band's offices are in the city of Campbell River to the southeast. Hanatsa IR No. 6 on Port Neville is the most populated of the band's Indian reserves.

The second HMS Fitzroy (K553) was a British Captain-class frigate of the Royal Navy in commission during World War II. Originally constructed as a United States Navy Buckley class destroyer escort, she served in the Royal Navy from 1943 to 1945.
HMS Cooke (K471) was a British Captain-class frigate of the Royal Navy in commission during World War II. Originally constructed as the United States Navy Evarts-class destroyer escort USS Dempsey (DE-267), she served in the Royal Navy from 1943 to 1946.
Chase River is a neighbourhood in the south end of the city of Nanaimo, British Columbia, Canada on the east coast of Vancouver Island. It is named for the Chase River which runs through the community.

The border between the countries of France and the United Kingdom in Europe is a maritime border that stretches along the Channel, the North Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, the Channel Tunnel links the two countries underground and is defined as a 'Land Frontier', and not widely recognised as a Land Border.

The Poindimié Islands are a group of seven tiny islets, with a collective area of about 3 ha, lying some 10–12 km off the north-eastern coast of Grande Terre, the principal island of the French Territory of New Caledonia in Melanesia in the south-west Pacific Ocean. They are formed of small banks of sand and dead coral, with little vegetation, and provide nesting sites for seabirds and sea turtles.
Coordinates: 49°30′00″N123°55′00″W / 49.50000°N 123.91667°W