
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an infection of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination may occur. Itching is uncommon. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms. Having BV approximately doubles the risk of infection by a number of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women.
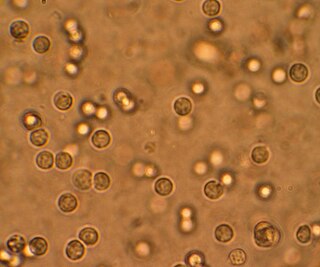
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age.

Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable.

Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy urine. Complications may include blood clots, infections, and high blood pressure.

Croup, also known as laryngotracheobronchitis, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "barking/brassy" cough, inspiratory stridor and a hoarse voice. Fever and runny nose may also be present. These symptoms may be mild, moderate, or severe. Often it starts or is worse at night and normally lasts one to two days.

Chancroid is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to spread from one individual to another solely through sexual contact. However, there have been reports of accidental infection through the hand.

Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess in the blood of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, which would be normally excreted in the urine. Uremic syndrome can be defined as the terminal clinical manifestation of kidney failure. It is the signs, symptoms and results from laboratory tests which result from inadequate excretory, regulatory, and endocrine function of the kidneys. Both uremia and uremic syndrome have been used interchangeably to denote a very high plasma urea concentration that is the result of renal failure. The former denotation will be used for the rest of the article.

Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea or simply as gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydration may also occur. This typically lasts less than two weeks. Although it is not related to influenza, in the U.S. and U.K., it is sometimes called the "stomach flu".

Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications may include pus around the kidney, sepsis, or kidney failure.
Ceratonova shasta is a myxosporean parasite that infects salmonid fish on the Pacific coast of North America. It was first observed at the Crystal Lake Hatchery, Shasta County, California, and has now been reported from Idaho, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia and Alaska.

Meningoencephalitis, also known as herpes meningoencephalitis, is a medical condition that simultaneously resembles both meningitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the meninges, and encephalitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the brain tissue.

Ventriculitis is the inflammation of the ventricles in the brain. The ventricles are responsible for containing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid throughout the brain. Ventriculitis is caused by infection of the ventricles, leading to swelling and inflammation. This is especially prevalent in patients with external ventricular drains and intraventricular stents. Ventriculitis can cause a wide variety of short-term symptoms and long-term side effects ranging from headaches and dizziness to unconsciousness and death if not treated early. It is treated with some appropriate combination of antibiotics in order to rid the patient of the underlying infection. Much of the current research involving ventriculitis focuses specifically around defining the disease and what causes it. This will allow for much more advancement in the subject. There is also a lot of attention being paid to possible treatments and prevention methods to help make this disease even less prevalent and dangerous.

Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is a disorder of the small blood vessels of the kidney. It is a common complication of bacterial infections, typically skin infection by Streptococcus bacteria types 12, 4 and 1 (impetigo) but also after streptococcal pharyngitis, for which it is also known as postinfectious glomerulonephritis (PIGN) or poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN). It can be a risk factor for future albuminuria. In adults, the signs and symptoms of infection may still be present at the time when the kidney problems develop, and the terms infection-related glomerulonephritis or bacterial infection-related glomerulonephritis are also used. Acute glomerulonephritis resulted in 19,000 deaths in 2013, down from 24,000 deaths in 1990 worldwide.
Enteric redmouth disease, or simply redmouth disease is a bacterial infection of freshwater and marine fish caused by the pathogen Yersinia ruckeri. It is primarily found in rainbow trout and other cultured salmonids. The disease is characterized by subcutaneous hemorrhaging of the mouth, fins, and eyes. It is most commonly seen in fish farms with poor water quality. Redmouth disease was first discovered in Idaho rainbow trout in the 1950s. The disease does not infect humans.

Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionally photophobia.
Bacterial kidney disease is a systemic infection caused by the bacterium Renibacterium salmoninarum. The disease affects populations of wild salmonid. BKD was originally discovered in the Scottish rivers of Dee and Spey in 1933.
Perianal cellulitis, also known as perianitis or perianal streptococcal dermatitis, is a bacterial infection affecting the lower layers of the skin (cellulitis) around the anus. It presents as bright redness in the skin and can be accompanied by pain, difficulty defecating, itching, and bleeding. This disease is considered a complicated skin and soft tissue infection (cSSTI) because of the involvement of the deeper soft tissues.
Bacterial cold water disease (BCWD) is a bacterial disease of freshwater fish, specifically salmonid fish. It is caused by the bacterium Flavobacterium psychrophilum, a psychrophilic, gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae. This bacterium is found in fresh waters with the optimal growth temperature below 13 °C, and it can be seen in any area with water temperatures consistently below 15 °C. Salmon are the most commonly affected species. This disease is not zoonotic.
Riemerella anatipestifer is a member of the Flavobacteriaceae family. It is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes septicaemia and death in young ducks and geese throughout the world. There are 21 known serotypes and infection is spread horizontally between birds. Infection may be referred to as duck septicaemia, goose flu, riemerellosis, new duck disease and polyserositis.
Piscirickettsia salmonis is the bacterial causative agent of piscirickettsiosis, an epizootic disease in salmonid fishes. It has a major impact on salmon populations, with a mortality rate of up to 90% in some species. The type strain, LF-89, is from Chile, but multiple strains exist, and some are more virulent than others. P. salmonis and piscrickettsiosis are present in various geographic regions from Europe to Oceania to South America, but the Chilean salmon farming industry has been particularly hard-hit. Different strategies of controlling the disease and farm-to-farm spread have been the subject of much research, but a significant amount is still unknown.












