Related Research Articles

The Los Angeles Basin is a sedimentary basin located in Southern California, in a region known as the Peninsular Ranges. The basin is also connected to an anomalous group of east–west trending chains of mountains collectively known as the Transverse Ranges. The present basin is a coastal lowland area, whose floor is marked by elongate low ridges and groups of hills that is located on the edge of the Pacific plate. The Los Angeles Basin, along with the Santa Barbara Channel, the Ventura Basin, the San Fernando Valley, and the San Gabriel Basin, lies within the greater Southern California region. The majority of the jurisdictional land area of the city of Los Angeles physically lies within this basin.

Simi Valley is a synclinal valley in Southern California in the United States. It is an enclosed or hidden valley surrounded by mountains and hills. It is connected to the San Fernando Valley to the east by the Santa Susana Pass and the 118 freeway, and in the west the narrows of the Arroyo Simi and the Reagan Freeway connection to Moorpark. The relatively flat bottom of the valley contains soils formed from shales, sandstones, and conglomerates eroded from the surrounding hills of the Santa Susana Mountains to the north, which separate Simi Valley from the Santa Clara River Valley, and the Simi Hills.

The Beverly Hills Oil Field is a large and currently active oil field underneath part of the US cities of Beverly Hills, California, and portions of the adjacent city of Los Angeles. Discovered in 1900, and with a cumulative production of over 150 million barrels of oil, it ranks 39th by size among California's oil fields, and is unusual for being a large, continuously productive field in an entirely urban setting. All drilling, pumping, and processing operations for the 97 currently active wells are done from within four large "drilling islands", visible on Pico and Olympic boulevards as large windowless buildings, from which wells slant diagonally into different parts of the producing formations, directly underneath the multimillion-dollar residences and commercial structures of one of the wealthiest cities in the United States. Annual production from the field was 1.09 million barrels in 2006, 966,000 barrels in 2007, and 874,000 in 2008, and the field retains approximately 11 million barrels of oil in reserve, as estimated by the California Department of Conservation. The largest operators as of 2009 were independent oil companies Plains Exploration & Production and BreitBurn Energy.
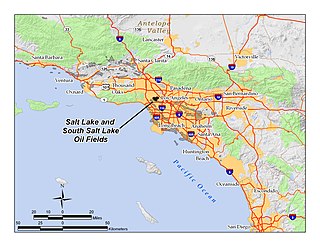
The Salt Lake Oil Field is an oil field underneath the city of Los Angeles, California. Discovered in 1902, and developed quickly in the following years, the Salt Lake field was once the most productive in California; over 50 million barrels of oil have been extracted from it, mostly in the first part of the twentieth century, although modest drilling and extraction from the field using an urban "drilling island" resumed in 1962. As of 2009, the only operator on the field was Plains Exploration & Production (PXP). The field is also notable as being the source, by long-term seepage of crude oil to the ground surface along the 6th Street Fault, of the famous La Brea Tar Pits.
The Fernando Formation is a Plio-Pleistocene marine mudstone, siltstone and sandstone formation in the greater Los Angeles Basin, Ventura Basin, and Santa Monica Mountains, in Los Angeles County of Southern California.
The Pico Formation is a Pliocene epoch stratigraphic unit and geologic formation in the greater Los Angeles Basin, the Santa Monica Mountains, and the Santa Susana Mountains, in Los Angeles County of Southern California.
The Merced Formation is a geologic formation in California, and also in Oregon and Washington state. It is named for Lake Merced, a natural lake on the western San Francisco coastline. The California portion is composed of a variety of sediments deposited on the coast of the San Francisco Bay Area in a small basin, which was split into two halves by the San Andreas Fault.

The Puente Formation is a geologic formation in California. It preserves fossils dating back to the middle to upper Miocene epoch of the Neogene period, most of which were deposited in a deepwater environment. Owing to its depositional environment, it is one of the very few geologic formations to preserve articulated specimens of fossilized deep-sea anglerfish.

The Punchbowl Formation is a sedimentary sandstone geologic formation in the northern San Gabriel Mountains, above the Antelope Valley in Los Angeles County, southern California.
The Hungry Valley Formation is a geologic formation in the San Emigdio Mountains — near Gorman in northeastern Los Angeles County, California.

The Etchegoin Formation is a Pliocene epoch geologic formation in the lower half of the San Joaquin Valley in central California.
The Crowder Formation is a geologic formation in the Central and Western Mojave Desert, in northern Los Angeles County and eastern San Bernardino County, in Southern California.
The Chanac Formation is a Cenozoic Era sandstone geologic formation in the southeastern San Joaquin Valley, within Kern County, California.
The Modelo Formation is a Miocene geologic formation in the Simi Hills and western Santa Susana Mountains of southern California, including under parts of Los Angeles.

The Mint Canyon Formation (Tm) is a Miocene geologic formation in the Sierra Pelona Mountains of Los Angeles County, southern California. The formation preserves fossils dating back to the Middle to Late Miocene.
The Tulare Formation is a Pliocene to Holocene epoch geologic formation in the central and southern San Joaquin Valley of central California.

The Santa Margarita Formation is a Neogene Period geologic formation in the San Joaquin Valley of central California.
The San Joaquin Formation is a Pliocene epoch geologic formation in the lower half of the San Joaquin Valley in central California.
The Tick Canyon Formation (Tt) or Tick Canyon strata, is an Early Miocene geologic formation in the Sierra Pelona Ridge of the San Gabriel Mountains in Los Angeles County, California.
The Juchipila Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Neogene period. Closely corresponding to the other Hemphillian faunal assemblages of North America, it is significant for understanding the palaeofauna of Miocene and Pliocene central Mexico.
References
- ↑ Repetto Formation, at Bureau of Economic Geology, University of Texas, Austin Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 Blake, Gregg H. 1991. "Review of the Neogene biostratigraphy and stratigraphy of the Los Angeles Basin and implications for basin evolution," In: Biddle, Kevin T. (ed), "Active Margin Basins", AAPG Memoir 52, 319pp.
- ↑ "Geolex — SycamoreCanyon publications". ngmdb.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2024-11-29.
- ↑ Sorlien, Christopher C.; Seeber, Leonardo; Broderick, Kris G.; Luyendyk, Bruce P.; Fisher, Michael A.; Sliter, Ray W.; Normark, William R. (June 2013). "The Palos Verdes anticlinorium along the Los Angeles, California coast: Implications for underlying thrust faulting". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 14 (6): 1866–1890. doi:10.1002/ggge.20112.