Related Research Articles

The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the second phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid.

Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases.

Zollinger–Ellison syndrome is a disease in which tumors cause the stomach to produce too much acid, resulting in peptic ulcers. Symptoms include abdominal pain and diarrhea.

The pylorus, or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the pyloric antrum and the pyloric canal. The pyloric canal ends as the pyloric orifice, which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the pyloric sphincter. The word pylorus comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word pylorus in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" and is thus linguistically related to the word "pylon".

Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid, is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the long chains of amino acids of proteins. Gastric acid is regulated in feedback systems to increase production when needed, such as after a meal. Other cells in the stomach produce bicarbonate, a base, to buffer the fluid, ensuring a regulated pH. These cells also produce mucus – a viscous barrier to prevent gastric acid from damaging the stomach. The pancreas further produces large amounts of bicarbonate and secretes bicarbonate through the pancreatic duct to the duodenum to neutralize gastric acid passing into the digestive tract.

A gastrectomy is a partial or total surgical removal of the stomach.

Rabeprazole, sold under the brand name Aciphex, among others, is a medication that decreases stomach acid. It is used to treat peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and excess stomach acid production such as in Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. It may also be used in combination with other medications to treat Helicobacter pylori. Effectiveness is similar to other proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It is taken by mouth.
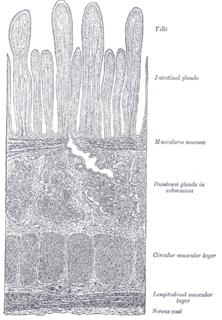
Brunner's glands are compound tubular submucosal glands found in that portion of the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter. It also contain submucosa which creates special glands. The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion i.e. mucous in order to:

Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals and in the tracts of carnivorous plants, where they aid in the digestion of food, as well as inside cells, especially in their lysosomes, where they function to maintain cellular survival. Digestive enzymes of diverse specificities are found in the saliva secreted by the salivary glands, in the secretions of cells lining the stomach, in the pancreatic juice secreted by pancreatic exocrine cells, and in the secretions of cells lining the small and large intestines.

Atrophic gastritis is a process of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa of the stomach, leading to a loss of gastric glandular cells and their eventual replacement by intestinal and fibrous tissues. As a result, the stomach's secretion of essential substances such as hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and intrinsic factor is impaired, leading to digestive problems. The most common are vitamin B12 deficiency which resulting from pernicious anemia and malabsorption of iron, leading to iron deficiency anaemia. It can be caused by persistent infection with Helicobacter pylori, or can be autoimmune in origin. Those with autoimmune atrophic gastritis (Type A gastritis) are statistically more likely to develop gastric carcinoma, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and achlorhydria.
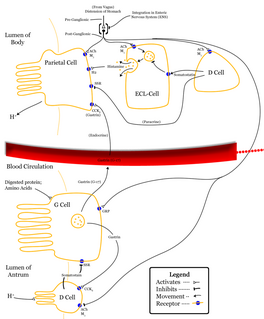
Enterochromaffin-like cells or ECL cells are a type of neuroendocrine cell found in the gastric glands of the gastric mucosa beneath the epithelium, in particular in the vicinity of parietal cells, that aid in the production of gastric acid via the release of histamine. They are also considered a type of enteroendocrine cell.

In anatomy, the G cell or gastrin cell, is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum, and occasionally in the pancreas and duodenum. The vagus nerve innervates the G cells. Gastrin-releasing peptide is released by the post-ganglionic fibers of the vagus nerve onto G cells during parasympathetic stimulation. The peptide hormone bombesin also stimulates gastrin from G cells. Gastrin-releasing peptide, as well as the presence of amino acids in the stomach, stimulates the release of gastrin from the G cells. Gastrin stimulates enterochromaffin-like cells to secrete histamine. Gastrin also targets parietal cells by increasing the amount of histamine and the direct stimulation by gastrin, causing the parietal cells to increase HCl secretion in the stomach.
Gastrinomas are neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), usually located in the duodenum or pancreas, that secrete gastrin and cause a clinical syndrome known as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES). A large number of gastrinomas develop in the pancreas or duodenum, with near-equal frequency, and approximately 10% arise as primary neoplasms in lymph nodes of the pancreaticoduodenal region.

Rapid urease test, also known as the CLO test, is a rapid diagnostic test for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori. The basis of the test is the ability of H. pylori to secrete the urease enzyme, which catalyzes the conversion of urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide.

The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands.

Gastric pits are indentations in the stomach which denote entrances to 3-5 tubular shaped gastric glands. They are deeper in the pylorus than they are in the other parts of the stomach. The human stomach has several million of these pits which dot the surface of the lining epithelium. Surface mucous cells line the pits themselves but give way to a series of other types of cells which then line the glands themselves.
Jejunoileal bypass (JIB) was a surgical weight-loss procedure performed for the relief of morbid obesity from the 1950s through the 1970s in which all but 30 cm (12 in) to 45 cm (18 in) of the small bowel were detached and set to the side.

Foveolar cells or surface mucous cells are mucus-producing cells which cover the inside of the stomach, protecting it from the corrosive nature of gastric acid. These cells line the gastric mucosa. The mucus-secreting cells of the stomach can be distinguished histologically from the intestinal goblet cells, another type of mucus-secreting cell.
The nervous system, and endocrine system collaborate in the digestive system to control gastric secretions, and motility associated with the movement of food throughout the gastrointestinal tract, including peristalsis, and segmentation contractions.