Related Research Articles
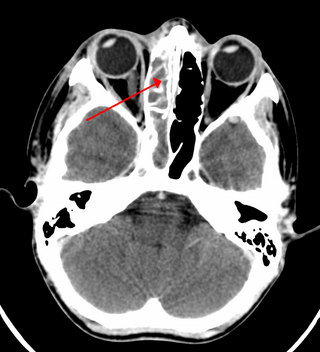
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain.

Mucus is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes, immunoglobulins, and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract.

An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold. Most infections are viral in nature, and in other instances, the cause is bacterial. URTIs can also be fungal or helminthic in origin, but these are less common.
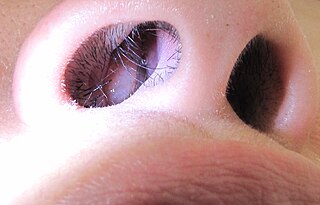
Nasal polyps (NP) are noncancerous growths within the nose or sinuses. Symptoms include trouble breathing through the nose, loss of smell, decreased taste, post nasal drip, and a runny nose. The growths are sac-like, movable, and nontender, though face pain may occasionally occur. They typically occur in both nostrils in those who are affected. Complications may include sinusitis and broadening of the nose.

Nasal irrigation is a personal hygiene practice in which the nasal cavity is washed to flush out mucus and debris from the nose and sinuses, in order to enhance nasal breathing. Nasal irrigation can also refer to the use of saline nasal spray or nebulizers to moisten the mucous membranes.
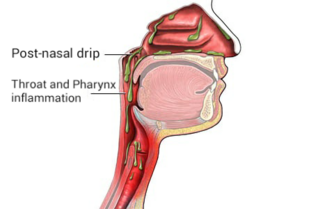
Post-nasal drip (PND), also known as upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), occurs when excessive mucus is produced by the nasal mucosa. The excess mucus accumulates in the back of the nose, and eventually in the throat once it drips down the back of the throat. It can be caused by rhinitis, sinusitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or by a disorder of swallowing. Other causes can be allergy, cold, flu, and side effects from medications.

Rhinorrhea, rhinorrhoea, or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is a common condition. It is a common symptom of allergies or certain viral infections, such as the common cold or COVID-19. It can be a side effect of crying, exposure to cold temperatures, cocaine abuse, or drug withdrawal, such as from methadone or other opioids. Treatment for rhinorrhea may be aimed at reducing symptoms or treating underlying causes. Rhinorrhea usually resolves without intervention, but may require treatment by a doctor if symptoms last more than 10 days or if symptoms are the result of foreign bodies in the nose.

Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of salivary glands, usually the major ones, the most common being the parotid gland, followed by submandibular and sublingual glands. It should not be confused with sialadenosis (sialosis) which is a non-inflammatory enlargement of the major salivary glands.
Chronic atrophic rhinitis, or simply atrophic rhinitis, is a chronic inflammation of the nose characterised by atrophy of nasal mucosa, including the glands, turbinate bones and the nerve elements supplying the nose. Chronic atrophic rhinitis may be primary and secondary. Special forms of chronic atrophic rhinitis are rhinitis sicca anterior and ozaena. It can also be described as the empty nose syndrome.

Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) is a procedure that is used to treat sinusitis and other conditions that affect the sinuses. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses that can cause symptoms such as congestion, headaches, and difficulty breathing through the nose.
A sinus is a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage. In common usage, "sinus" usually refers to the paranasal sinuses, which are air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose and connecting to it. Most individuals have four paired cavities located in the cranial bone or skull.

Adenoiditis is the inflammation of the adenoid tissue usually caused by an infection. Adenoiditis is treated using medication or surgical intervention.
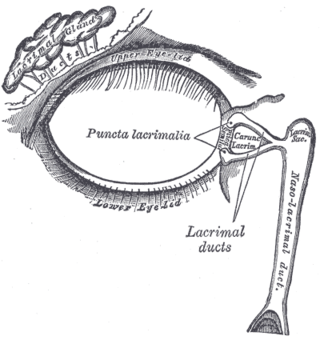
Dacryocystocele (Dacryocystitis) or timo cyst is a benign, bluish-gray mass in the inferomedial canthus that develops within a few days or weeks after birth. The uncommon condition forms as a result as a consequence of narrowing or obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, usually during prenatal development. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction disrupts the lacrimal drainage system, eventually creating a swelling cyst in the lacrimal sac area by the nasal cavity. The location of the cyst can cause respiratory dysfunction, compromising the airway. The obstruction ultimately leads to epiphora, an abundance of tear production.
ELOM-080 is the active ingredient of the herbal medicine named GeloMyrtol forte. The acronym ELOM stands for the oils from Eucalyptus, Lemon, (Sweet) Orange and Myrtle that it contains.

Dupilumab, sold under the brand name Dupixent, is a monoclonal antibody blocking interleukin 4 and interleukin 13, used for allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis (eczema), asthma and nasal polyps which result in chronic sinusitis. It is also used for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis and prurigo nodularis.
Antral lavage is a largely obsolete surgical procedure in which a cannula is inserted into the maxillary sinus via the inferior meatus to allow irrigation and drainage of the sinus. It is also called proof puncture, as the presence of an infection can be proven during the procedure. Upon presence of infection, it can be considered as therapeutic puncture. Often, multiple repeated lavages are subsequently required to allow for full washout of infection.
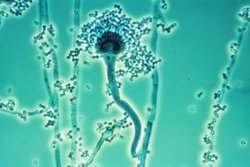
Fungal sinusitis or fungal rhinosinusitis is the inflammation of the lining mucosa of the paranasal sinuses due to a fungal infection. It occurs in people with reduced immunity. The maxillary sinus is the most commonly involved. Fungi responsible for fungal sinusitis are Aspergillus fumigatus (90%), Aspergillus flavus, and Aspergillus niger. Fungal sinusitis occurs most commonly in middle-aged populations. Diabetes mellitus is the most common risk factor involved.

Oroantral fistula (OAF) is an epithelialised oroantral communication (OAC). OAC refers to an abnormal connection between the oral cavity and antrum. The creation of an OAC is most commonly due to the extraction of a maxillary (upper) tooth closely related to the antral floor. A small OAC may heal spontaneously but a larger OAC would require surgical closure to prevent the development of persistent OAF and chronic sinusitis.

Odontogenic sinusitis is a type of sinusitis, specifically caused by dental infections or procedures. Comprising approximately 10-12% of all chronic sinusitis cases, this condition primarily affects the maxillary sinus, which is in close proximity to the upper teeth.
References
- ↑ Stuck, Boris A. "AWMF-Registernummer 053-012". www.awmf.org (in German). Retrieved 26 June 2021.
- ↑ Stuck, Boris A. "AWMF-Registernummer 017-049". www.awmf.org (in German). Retrieved 26 June 2021.
- ↑ "Kurzfassung der Leitlinie 017-049" (PDF). www.awmf.org (in German). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-05-28. Retrieved 26 June 2021.
- ↑ "Langfassung der Leitlinie 017-049" (PDF). www.awmf.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2021.