The Kwacha is the currency of Zambia. It is subdivided into 100 Ngwee.

Sterling is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. In British English, its most common nickname is "quid."

Decimal Day in the United Kingdom and in Ireland was Monday 15 February 1971, the day on which each country decimalised its respective £sd currency of pounds, shillings, and pence.
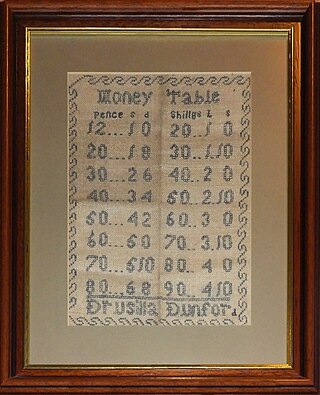
£sd is the popular name for the pre-decimal currencies once common throughout Europe, especially in the British Isles and hence in several countries of the British Empire and subsequently the Commonwealth. The abbreviation originates from the Latin currency denominations librae, solidi, and denarii. In the United Kingdom, these were referred to as pounds, shillings, and pence.
The British West Indies dollar (BWI$) was the currency of British Guiana and the Eastern Caribbean territories of the British West Indies from 1949 to 1965, when it was largely replaced by the East Caribbean dollar, and was one of the currencies used in Jamaica from 1954 to 1964. The monetary policy of the currency was overseen by the British Caribbean Currency Board (BCCB). It was the official currency used by the West Indies Federation The British West Indies dollar was never used in British Honduras, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, the Bahamas, or Bermuda.

The pound was the currency of Australia from 1910 until 14 February 1966, when it was replaced by the Australian dollar. Like other £sd currencies, it was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
The pound is the currency of Guernsey. Since 1921, Guernsey has been in currency union with the United Kingdom and the Guernsey pound is not a separate currency but is a local issue of sterling banknotes and coins, in a similar way to the banknotes issued in Scotland, England and Northern Ireland. It can be exchanged at par with other sterling coinage and notes.
George Edward Kruger Gray was an English artist, best remembered for his designs of coinage and stained glass windows.

The Jamaican dollar has been the currency of Jamaica since 1969. It is often abbreviated to J$, the J serving to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 cents, although cent denominations are no longer in use as of 2018. Goods and services may still be priced in cents, but cash transactions are now rounded to the nearest dollar.

The pound is the currency of Jersey. Jersey is in currency union with the United Kingdom, and the Jersey pound is not a separate currency but is an issue of banknotes and coins by the States of Jersey denominated in sterling, in a similar way to the banknotes issued in Scotland and Northern Ireland. It can be exchanged at par with other sterling coinage and notes.

The East African shilling was the sterling unit of account in British controlled areas of East Africa from 1921 until 1969. It was issued by the East African Currency Board. It is also the proposed name for a common currency that the East African Community plans to introduce.

The Rhodesian dollar was the currency of Rhodesia between 1970 and 1980. It was subdivided into 100 cents.
The pound was the currency of Malawi until 1971. From 1932, Malawi used the Southern Rhodesian pound. In 1955, a new currency was introduced, the Rhodesia and Nyasaland pound. This was replaced by the Malawian pound in 1964, following Malawi's independence. The pound was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence. The pound was replaced by the decimal kwacha in 1971, at a rate of 2 kwacha = 1 pound.

The pound was the currency of Southern Rhodesia from 1964 to 1965 and Rhodesia from 1965 until 1970. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
The coins of the Rhodesian dollar were part of the physical form of Rhodesia's historical currency, the Rhodesian dollar.

The pound was the currency of Zambia from independence in 1964 until decimalization on January 16, 1968. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.

The pound was the official currency of Jamaica between 1840 and 1969. It circulated as a mixture of sterling coinage and locally issued coins and banknotes and was always equal to the pound sterling. The Jamaican pound was also used in the Cayman and Turks and Caicos Islands.

The pound was the currency of Southern Rhodesia. It also circulated in Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland. The pound was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
The pound was the currency of the Australian Territory of New Guinea between 1915 and 1966, and replaced the New Guinean mark when Australia occupied the former German colony at the end of World War I. The New Guinean pound was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence, and was equal to the Australian pound.
The coins of the Rhodesian pound were part of the currency of Southern Rhodesia, which changed its name to Rhodesia, following the break-up of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, when the Rhodesian pound replaced the Rhodesia and Nyasaland pound, which had replaced the Southern Rhodesian pound.






















