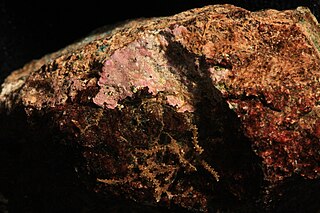Coralline algae are red algae in the order Corallinales. They are characterized by a thallus that is hard because of calcareous deposits contained within the cell walls. The colors of these algae are most typically pink, or some other shade of red, but some species can be purple, yellow, blue, white, or gray-green. Coralline algae play an important role in the ecology of coral reefs. Sea urchins, parrot fish, and limpets and chitons feed on coralline algae. In the temperate Mediterranean Sea, coralline algae are the main builders of a typical algal reef, the Coralligène ("coralligenous"). Many are typically encrusting and rock-like, found in marine waters all over the world. Only one species lives in freshwater. Unattached specimens may form relatively smooth compact balls to warty or fruticose thalli.

Conceptacles are specialized cavities of marine and freshwater algae that contain the reproductive organs. They are situated in the receptacle and open by a small ostiole. Conceptacles are present in Corallinaceae, and Hildenbrandiales, as well as the brown Fucales. In the Fucales there is no haploid phase in the reproductive cycle and therefore no alternation of generations. The thallus is a sporophyte. The diploid plants produce male (antheridia) and female (oogonia) gametangia by meiosis. The gametes are released into the surrounding water; after fusion, the zygote settles and begins growth.
Wataru Ishijima was a paleontologist and geologist. Ishijima was one of the most prolific researchers of fossil calcareous algae. After graduating from the Imperial Fisheries Institute in 1927, Ishijima joined the Institute of Geology and Paleontology, Faculty of Science, Tohoku Imperial University (Sendai) from 1927–1931. He then worked at the Institute of Geology, Taihoku Imperial University (Taipei) during 1942–1945 and then at the Rikkyo University (Tokyo) from 1945–1980. His doctoral dissertation was submitted to Tohoku University and was privately published by Yūhodō. He described a total of 139 taxa of fossil calcareous algae including at least 114 species of Corallinales, and he produced more than 45 publications on coralline algal taxonomy.

The Corallinaceae are one of the two extant Coralline families of red algae; they are differentiated from the morphologically similar Sporolithaceae by their formation of grouped sporangial chambers, clustered into sori. The Corallinoideae is monophyletic; the other subfamilies form another monophyletic group.

Peyssonnelia is a genus of thalloid red alga, named after naturalist Jean-André Peyssonnel (1694–1759) It includes the algae commonly known as rumoi-iwanokawa, mayoi-iwanokawa and akase-iwanokawa. Specimens can reach around 20 cm in size. Peyssonnelia produces tetraspores.
Trichocyte in algae are cells which grow on the outside of the thallus, from which hairs grow. In algae, trichocytes grow principally over the summer; their growth is mediated by water temperature and day length.

Calliarthron is a genus containing two species of thalloid intertidal alga. Specimens can reach around 30 cm in size. The thalli take a crustose form. The organisms lack secondary pit connections. Calliarthron reproduces by means of conceptacles; it produces tetraspores, dispores and carpospores. The genus has lignin and contains secondary cell walls, traits which are normally associated with the vascular plants. It is similar to the genus Bossiella.

Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.
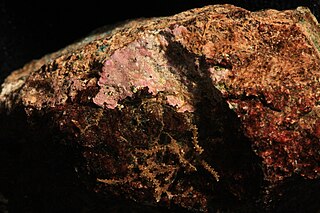
Hildenbrandia is a genus of thalloid red alga comprising about 26 species. The slow-growing, non-mineralized thalli take a crustose form. Hildenbrandia reproduces by means of conceptacles and produces tetraspores.
The Sporolithaceae is the only known family of algae in the Sporolithales order.
The Mastophoroideae are a subfamily of Corallinaceaen coralline algae with uniporate conceptacles.

The Lithophylloideae are a monophyletic subfamily of Corallinaceaen Coralline algae with uniporate conceptacles.
The Metagoniolithoideae are a monogeneric subfamily of genucilate Corallinaceaen coralline algae.

The Corallinoideae are a subfamily of coralline algae. All its genera are geniculate.
The Choreonematoideae are a monogeneric nongeniculate subfamily of Coralline algae.

The Corallinophycidae is a grouping of several calcifying red algal lineages recovered by molecular analysis.

Lithophyllum orbiculatum is a species of thalloid coralline algae, which are a red algae whose cell walls contain calcareous deposits.

The Gracilariaceae is a small family of red algae containing several genera of agarophytes. It has a world-wide distribution. 24 species are found in China, and 6 species are found in Great Britain and Ireland. It is found in Australia and Chile.

Liagoraceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales. The type genus is LiagoraJ.V.Lamouroux.

Halymeniales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae.