
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies. It is mainly used as an analgesic. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual; via inhalation; injection into a muscle, injection under the skin, or injection into the spinal cord area; transdermal; or via rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine are available as MS-Contin, Kadian, and other brand names as well as generically.

Opium is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy Papaver somniferum. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which is processed chemically to produce heroin and other synthetic opioids for medicinal use and for the illegal drug trade. The latex also contains the closely related opiates codeine and thebaine, and non-analgesic alkaloids such as papaverine and noscapine. The traditional, labor-intensive method of obtaining the latex is to scratch ("score") the immature seed pods (fruits) by hand; the latex leaks out and dries to a sticky yellowish residue that is later scraped off and dehydrated. The word meconium historically referred to related, weaker preparations made from other parts of the opium poppy or different species of poppies.

Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, Thēbai (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar to both morphine and codeine, but has stimulatory rather than depressant effects. At high doses, it causes convulsions similar to strychnine poisoning. The synthetic enantiomer (+)-thebaine does show analgesic effects apparently mediated through opioid receptors, unlike the inactive natural enantiomer (−)-thebaine. While thebaine is not used therapeutically, it is the main alkaloid extracted from Papaver bracteatum and can be converted industrially into a variety of compounds, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, nalbuphine, naloxone, naltrexone, buprenorphine, butorphanol and etorphine.

A poppy is a flowering plant in the subfamily Papaveroideae of the family Papaveraceae. Poppies are herbaceous plants, often grown for their colourful flowers. One species of poppy, Papaver somniferum, is the source of the narcotic drug mixture opium which contains powerful medicinal alkaloids such as morphine and has been used since ancient times as an analgesic and narcotic medicinal and recreational drug. It also produces edible seeds. Following the trench warfare in the poppy fields of Flanders, Belgium during World War I, poppies have become a symbol of remembrance of soldiers who have died during wartime, especially in the UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and other Commonwealth realms.

Secondary metabolites, also called specialised metabolites, toxins, secondary products, or natural products, are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of the organism. Instead, they generally mediate ecological interactions, which may produce a selective advantage for the organism by increasing its survivability or fecundity. Specific secondary metabolites are often restricted to a narrow set of species within a phylogenetic group. Secondary metabolites often play an important role in plant defense against herbivory and other interspecies defenses. Humans use secondary metabolites as medicines, flavourings, pigments, and recreational drugs.

Papaver rhoeas, with common names including common poppy, corn poppy, corn rose, field poppy, Flanders poppy, and red poppy, is an annual herbaceous species of flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It is a temperate native with a very wide distribution area, from Africa to temperate and tropical Asia and Europe.

Papaver is a genus of 70–100 species of frost-tolerant annuals, biennials, and perennials native to temperate and cold regions of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the type genus of the poppy family, Papaveraceae.

Papaver somniferum, commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable ornamental plant grown in gardens. Its native range was east of the Mediterranean Sea, but now is obscured by ancient introductions and cultivation, being naturalized across much of Europe and Asia.

Papaverine is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms, occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and acute mesenteric ischemia. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the analgesic morphine and its derivatives.

Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner was a German pharmacist and a pioneer of alkaloid chemistry. He is best known for his discovery of morphine in 1804.

Codeinone is an isoquinolone alkaloid found in the opium poppy. As an analgesic, it is one-third the potency of codeine. It is an important intermediate in the production of hydrocodone–a painkiller about three-quarters the potency of morphine–as well as of oxycodone, though the latter can also be synthesized from thebaine.

Poppy tea is an herbal tea infusion brewed from poppy straw or seeds of several species of poppy. The species most commonly used for this purpose is Papaver somniferum, which produces opium as a natural defense against predators. In the live flower, opium is released when the surface of the bulb, called the seed pod, is pierced or scraped. For the purpose of the tea, dried pods are more commonly used than the pods of the live flower. The walls of the dried pods contain opiate alkaloids, primarily consisting of morphine.
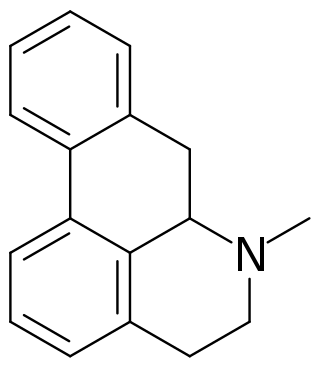
Aporphine is an alkaloid with the chemical formula C17H17N. It is the core chemical substructure of the aporphine alkaloids, a subclass of quinoline alkaloids. It can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, (R)-aporphine and (S)-aporphine.

Narcotoline is an opiate alkaloid chemically related to noscapine. It binds to the same receptors in the brain as noscapine to act as an antitussive, and has also been used in tissue culture media.

Poppy straw is derived from opium poppies that are harvested when fully mature and dried by mechanical means. Opium poppy straw is what remains after the seed pods have been harvested - that is, the dried stalks, stem and leaves of poppies grown for their seeds. The field-dried leaves, stalk, and seed pod are then used in commercial manufacture of morphine or other poppy-alkaloid derived drugs, by first processing the material, separating the seeds, and then making concentrate of poppy straw where no extraction using the traditional methods of latex extraction has been made. The straw was originally considered an agricultural by-product of the mechanised poppy seed harvest, which was primarily grown for its edible and oil-producing seed. This changed in 1927 when János Kabay developed a chemical process to extract morphine from the crushed capsule. Concentrated poppy straw, consisting mainly of the crushed capsule without the seeds, soon became a valuable source of morphine. Today, concentrate of poppy straw is a major source of many opiates and other alkaloids. It is the source of 90% of the world supply of legal morphine and in some countries it also is a source of illegal morphine, which could be processed into illegal heroin.

An opiate, is an alkaloid substance derived from opium It has a different meaning from the similar term opioid, used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Most opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America. Some, such as thebaine don't share the same effects and are not classified as controlled substances.

Papaver glaucum, the tulip poppy, Turkish tulip or Turkish red poppy, is a poppy found in the region of Anatolia.
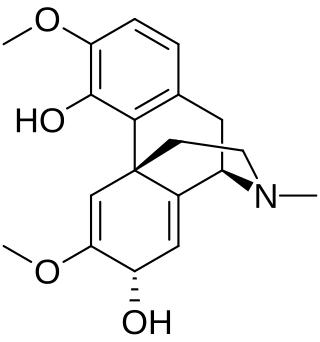
Salutaridinol is a modified benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid with the formula C19H23NO4. It is produced in the secondary metabolism of the opium poppy Papaver somniferum (Papaveraceae) as an intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway that generates morphine. As an isoquinoline alkaloid, it is fundamentally derived from tyrosine as part of the shikimate pathway of secondary metabolism. Salutaridinol is a product of the enzyme salutaridine: NADPH 7-oxidoreductase and the substrate for the enzyme salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase, which are two of the four enzymes in the morphine biosynthesis pathway that generates morphine from (R)-reticuline. Salutaridinol's unique position adjacent to two of the four enzymes in the morphine biosynthesis pathway gives it an important role in enzymatic, genetic, and synthetic biology studies of morphine biosynthesis. Salutaridinol levels are indicative of the flux through the morphine biosynthesis pathway and the efficacy of both salutaridine: NADPH 7-oxidoreductase and salutaridinol 7-O-acetyltransferase.
Papaver somniferum × Papaver bracteatum, also known as Sagan's poppy is a hybrid between the opium poppy and the Iranian poppy.

Isoquinoline alkaloids are natural products of the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from isoquinoline. They form the largest group among the alkaloids.



















